Python anonymous functions list
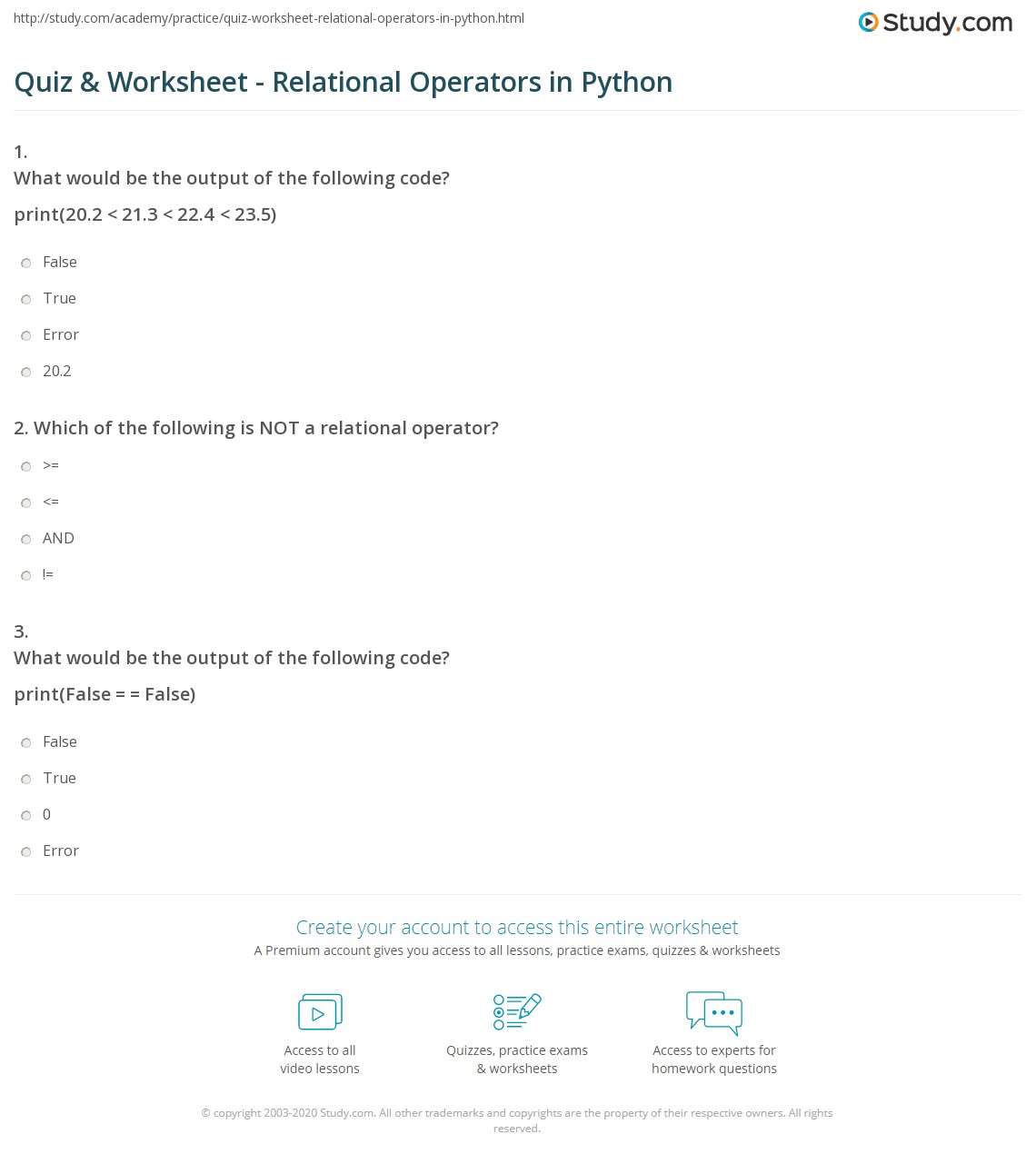
Python anonymous functions list
Here are the details of Python anonymous functions:
What is an Anonymous Function?
In Python, an anonymous function (also known as a lambda function) is a small, single-purpose function that does not have a name. It's a shorthand way to create a simple function without declaring it with the def keyword.
How to Create an Anonymous Function
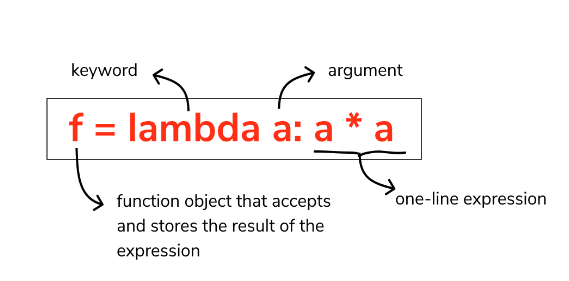
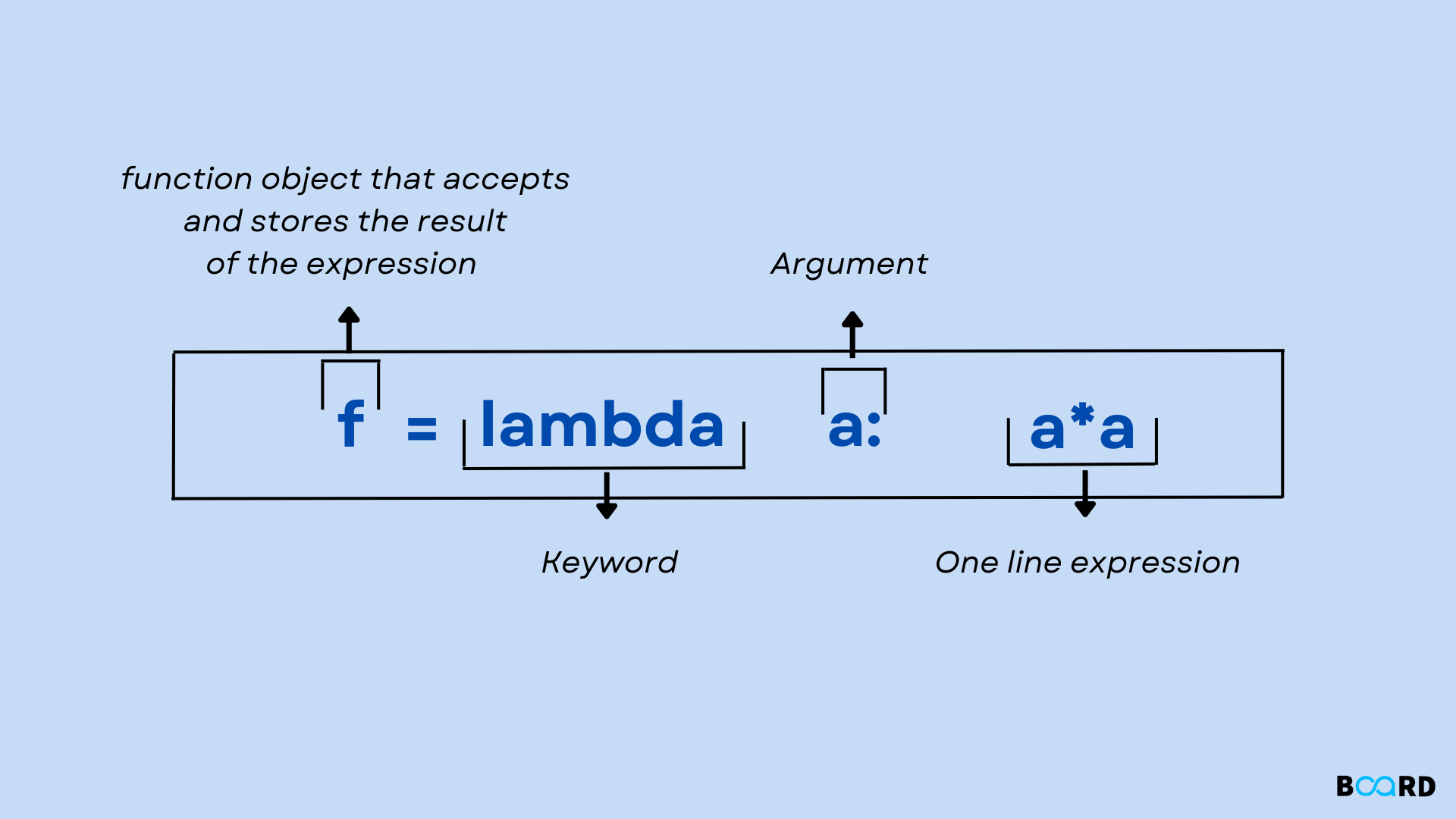
To create an anonymous function, you use the lambda keyword followed by the input parameters and the code block to be executed. The general syntax is:
anonymous_function = lambda arguments: expression
For example:
add_ten = lambda x: x + 10
print(add_ten(5)) # Output: 15
In this example, we created an anonymous function that takes a single argument x and returns the result of adding 10 to it.
Common Use Cases
Anonymous functions are useful when you need to:
Define a simple, one-time-use function: When you only need to use a function once or twice in your code, an anonymous function can be a quick and easy solution. Pass a function as an argument: Anonymous functions are often used as arguments to other functions, such asmap(), filter(), or reduce(). Create a small, ad-hoc transformation: For example, you might use an anonymous function to convert a list of strings to uppercase.
Examples
Here are some examples of using anonymous functions in Python:
# Example 1: Filtering out odd numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
even_numbers = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers)
print(list(even_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4]
Example 2: Mapping a transformation to a list
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
uppercase_fruits = map(lambda fruit: fruit.upper(), fruits)
print(list(uppercase_fruits)) # Output: ['APPLE', 'BANANA', 'CHERRY']
Example 3: Using an anonymous function as a reducer
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
sum_of_numbers = reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, numbers)
print(sum_of_numbers) # Output: 15
Example 4: Creating a simple filter function
def is_even(x):
return lambda x: x % 2 == 0
even_numbers = filter(is_even(3), [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(list(even_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4]
In this example, we used anonymous functions to:
Filter out odd numbers from a list Map a transformation (converting strings to uppercase) to a list Use an anonymous function as a reducer (calculating the sum of numbers) Create a simple filter functionI hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions.
Python anonymous functions examples
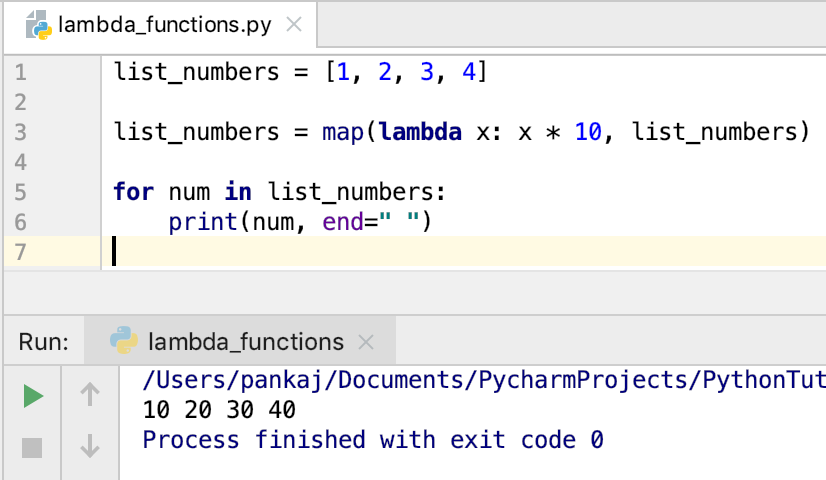
Python Anonymous Functions Examples!
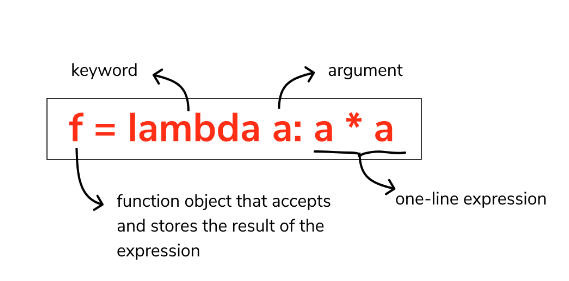
Anonymous functions are lambda functions without a name. They can simplify your code by avoiding the need to declare a separate function and assigning it to a variable.
Here's an example of using anonymous functions:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
In this example, the anonymous function lambda x: x ** 2 is used as a mapping function to square each number in the list. The map() function applies this anonymous function to each element in the list and returns a new list with the results.
Here's another example:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
even_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
print(even_numbers) # Output: [2, 4]
In this example, the anonymous function lambda x: x % 2 == 0 is used as a filtering function to find all even numbers in the list. The filter() function applies this anonymous function to each element in the list and returns an iterator over the elements that satisfy the condition.
Anonymous functions can also be used with the reduce() function from the functools module:
from functools import reduce
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
product = reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, numbers)
print(product) # Output: 120
In this example, the anonymous function lambda x, y: x * y is used to calculate the product of all elements in the list.
Anonymous functions can be used as event handlers:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
frame = tk.Frame(root)
frame.pack()
def handler():
print("Button clicked!")
button = tk.Button(frame, text="Click me!", command=lambda: handler())
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
In this example, the anonymous function lambda: handler() is used to define an event handler for a button. When the button is clicked, the handler() function is called.
These are just a few examples of how you can use anonymous functions in Python. They can be very useful in simplifying your code and making it more concise!