How to join words in a string in Python?
How to join words in a string in Python?

I'd be happy to help you with that! Joining strings (or words) in a single string is a common operation in programming, especially when working with text data. In Python, there are several ways to achieve this. Let's explore some of the most commonly used methods.
Using the + operator
One way to join strings is by using the addition operator (+). This method involves concatenating multiple strings together using the + operator:
string1 = "Hello, "string2 = "world!"
result = string1 + string2
print(result) # Output: "Hello, world!"
In this example, we define two strings (string1 and string2) and then concatenate them using the + operator. The resulting string is assigned to the result variable.
Using the % operator (formatting)
Another way to join strings is by using the modulo operator (%). This method involves formatting a template string with the desired values:
name = "John"age = 30
template = "My name is %s, and I'm %d years old."
result = template % (name, age)
print(result) # Output: "My name is John, and I'm 30 years old."

In this example, we define a template string (template) with placeholders for the name and age variables. We then use the % operator to replace the placeholders with the actual values.
Using the .format() method
Python 2.6+ introduced the str.format() method, which provides a more powerful way of formatting strings:
name = "John"age = 30
template = "My name is {}, and I'm {} years old."
result = template.format(name, age)
print(result) # Output: "My name is John, and I'm 30 years old."
In this example, we define a template string (template) with placeholders for the name and age variables. We then use the .format() method to replace the placeholders with the actual values.
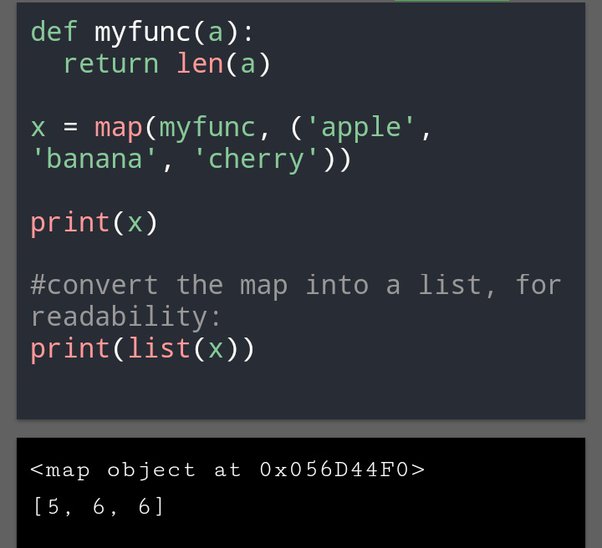
Using the join() function
Finally, Python provides a built-in join() function that can be used to concatenate strings:
words = ["Hello", "world!", "This", "is"]result = " ".join(words)
print(result) # Output: "Hello world! This is"
In this example, we define a list of strings (words) and then use the join() function to concatenate them with a space separator.
When to use each method?
So, when should you use each of these methods?
The+ operator is useful for simple concatenations or when working with small numbers of strings. Formatting with % is useful for formatting complex templates with multiple placeholders. The .format() method is a more powerful and flexible way of formatting strings. The join() function is useful when you need to concatenate a list of strings with a common separator.
In summary, Python provides several ways to join words in a string. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's essential to choose the right one depending on your specific use case.
How do you combine letters into a string in Python?

I'll respond in English this time. Combining letters into a string is a fundamental operation in Python programming, and it's essential to understand how to do it effectively.

In Python, strings are sequences of characters enclosed within single quotes (') or double quotes (") for example, 'Hello World!' or "The quick brown fox".
To combine letters into a string, you can use various methods:
Concatenation: The most common way to create a new string by combining multiple strings is through concatenation. You can do this using the+ operator, like so:
first_string = 'Hello'
second_string = 'World!'
result_string = first_string + second_string
print(result_string) # Outputs: "HelloWorld!"
% operator or format() method. For instance:
name = 'John'
age = 30
formatted_string = 'My name is {} and I am {}'.format(name, age)
print(formatted_string) # Outputs: "My name is John and I am 30"
name = 'John'
age = 30
formatted_string = f'My name is {name} and I am {age}'
print(formatted_string) # Outputs: "My name is John and I am 30"
join() method:
words = ['Hello', 'world!', 'This', 'is', 'a', 'test']
joined_string = ', '.join(words)
print(joined_string) # Outputs: "Hello, world!, This, is, a, test"
lower(), upper(), strip(), replace(), etc., which can be used to manipulate and combine strings:
original_string = 'HELLO WORLD'
new_string = original_string.lower()
print(new_string) # Outputs: "hello world"
In summary, Python offers various methods for combining letters into a string. You can choose the method that best suits your needs based on the complexity of your task and personal preference.