Why we are using slicing in Python?
Why we are using slicing in Python?

I'm glad you asked!
Slicing is a powerful feature in Python that allows us to access and manipulate specific parts of sequences, such as lists, tuples, strings, and bytes.
In general, when working with large datasets or complex data structures, it's often necessary to extract specific subsets of data for further processing, analysis, or manipulation. This is where slicing comes into play.
By using slicing, you can:
Extract a portion of a sequence: For example, if you have a list of numbers and want to isolate the first few elements, you can use slicing to get those specific elements. Modify a subset of a sequence: Imagine you have a long string with some unwanted characters at the beginning or end. You can use slicing to remove those unwanted characters by creating a new string that excludes them. Reorder or reformat data: Slicing enables you to create new sequences by rearranging or rearranging elements from an original sequence.Some common applications of slicing include:
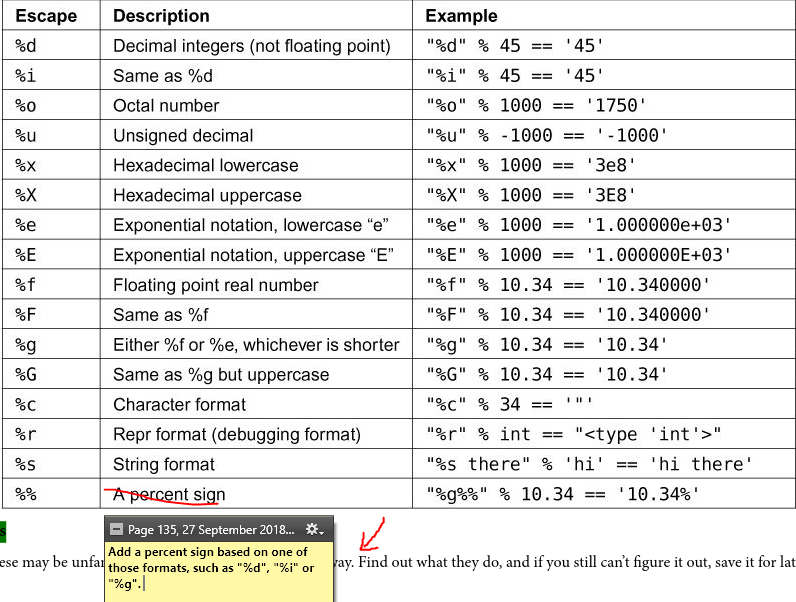
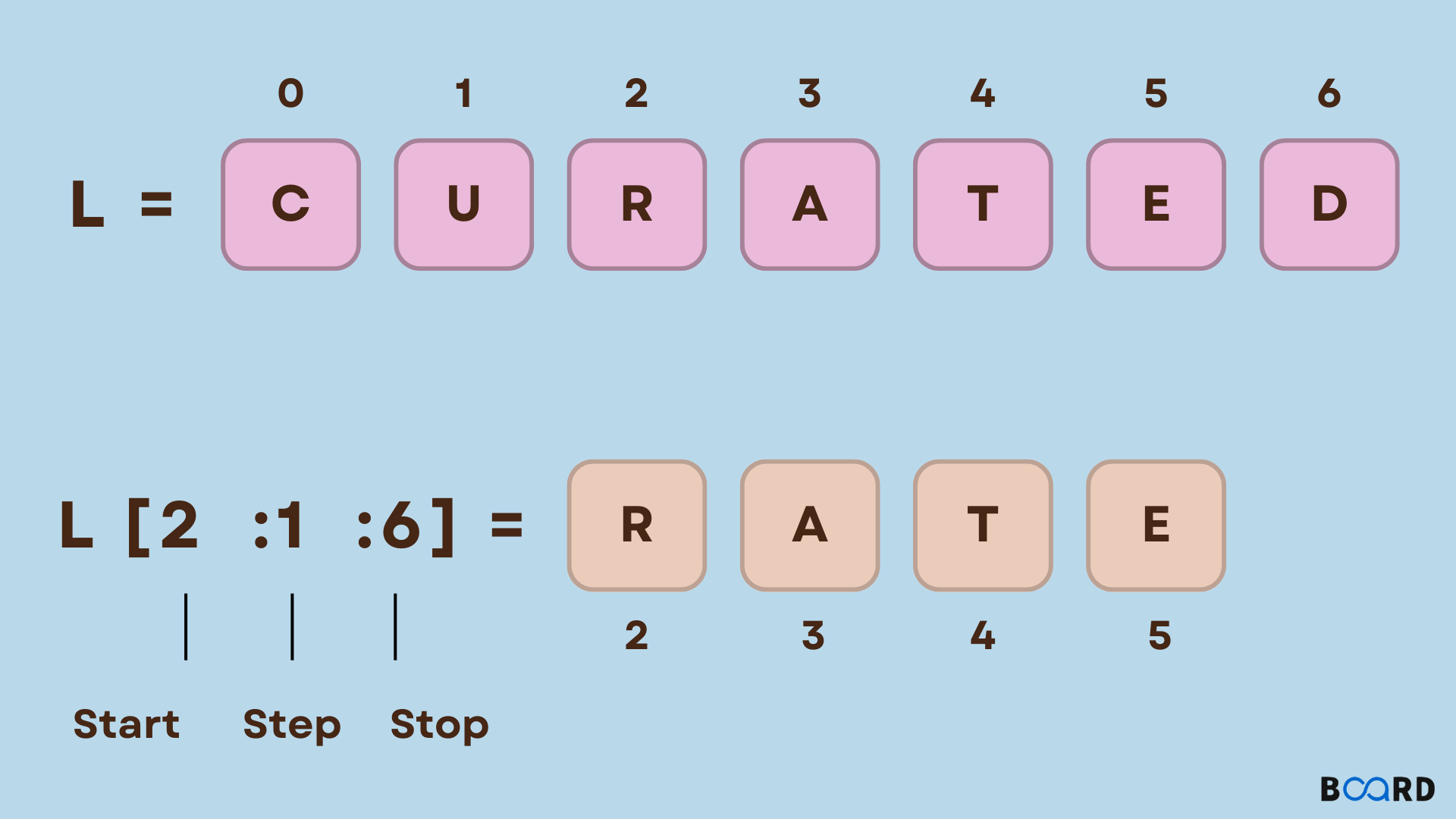
Data cleaning and preprocessing: Remove unnecessary characters, trim whitespace, or normalize data formats. Feature engineering: Extract relevant features from a dataset for machine learning model training. Text processing: Manipulate text strings to extract specific information, such as words, phrases, or sentences. Data visualization: Create subsets of data for plotting, charting, or other visualization purposes.Python's slicing syntax is simple and flexible. For example:
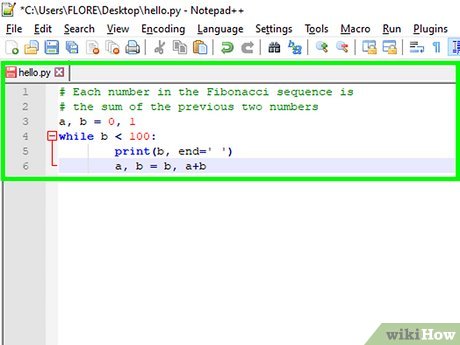
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Extract the first three elementsprint(my_list[:3]) # Output: [1, 2, 3]
Modify the last two elementsmy_list[3:] = [7, 8] # my_list becomes: [1, 2, 3, 7, 8]
Reorder elements in reverse orderprint(my_list[::-1]) # Output: [8, 7, 3, 2, 1]
As you can see, slicing is a fundamental concept in Python programming that enables efficient and flexible data manipulation. By mastering this technique, you'll be better equipped to tackle various tasks and challenges in your coding journey!
What is the [:] in Python?
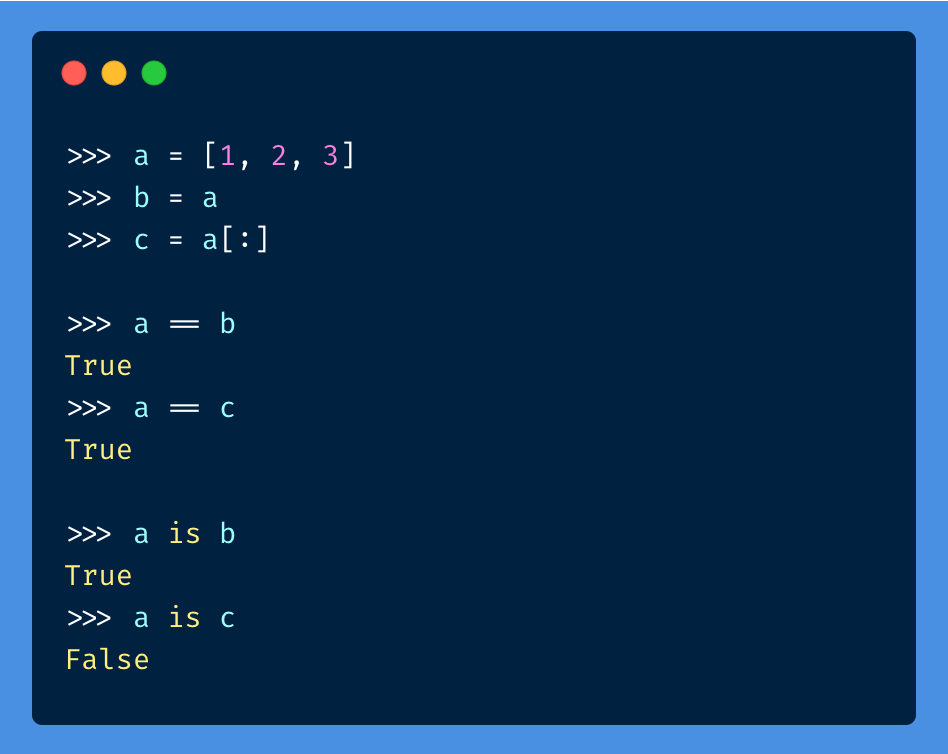
I'd be happy to explain what the [] in Python means.
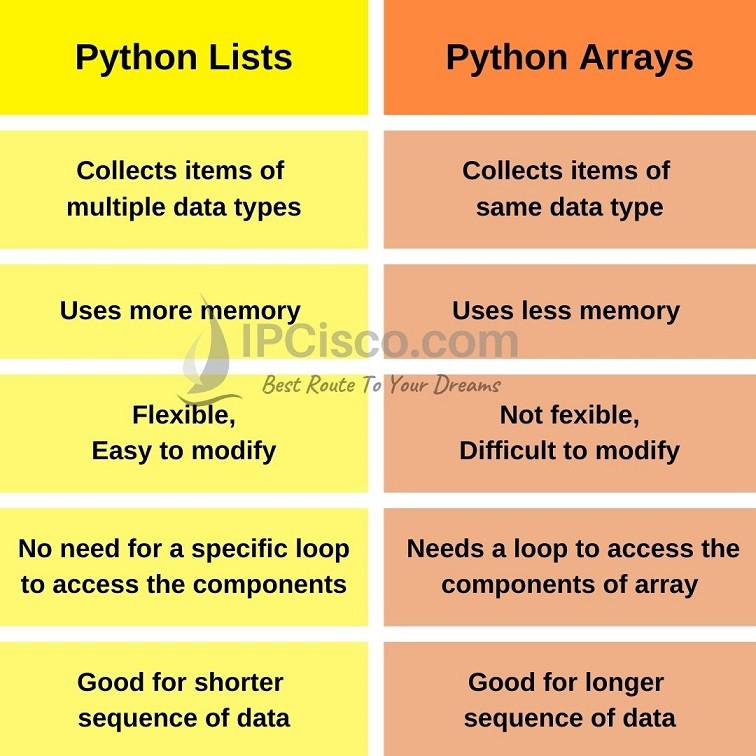
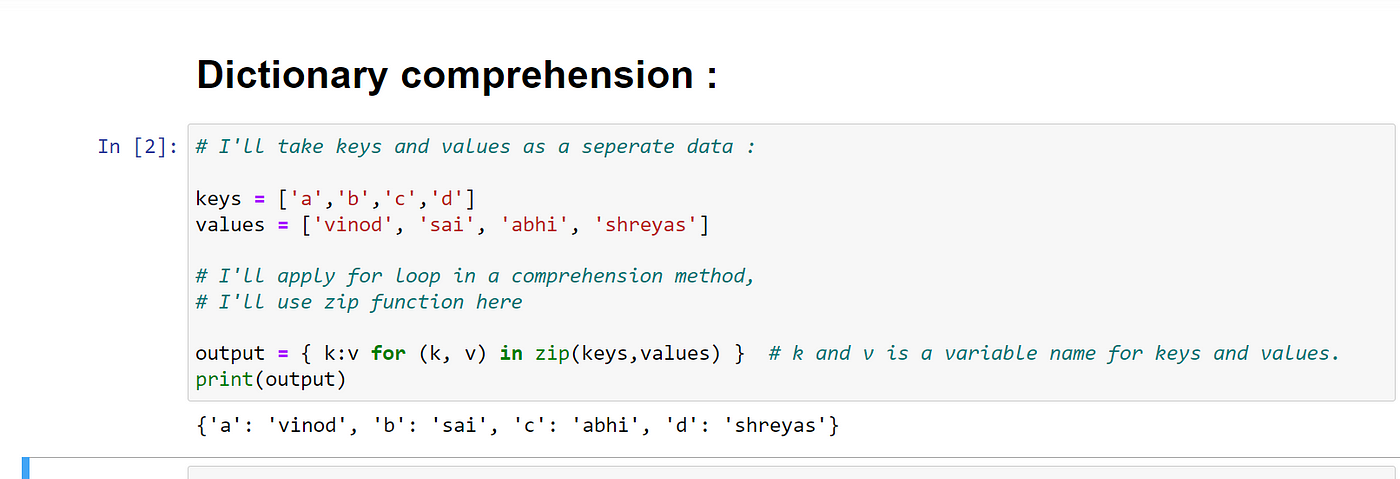
In Python, [] refers to a list, which is a fundamental data structure that allows you to store and manipulate collections of items. A list is a mutable (i.e., can be changed) sequence of values that can contain any type of object, including strings, integers, floats, other lists, dictionaries, and even functions.
A list begins with an opening square bracket [] and ends with a closing square bracket ]. Inside these brackets, you can store multiple items, separated by commas. Here's a simple example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, "hello", 4.5]
In this case, my_list is assigned the value of a list containing the elements 1, 2, 3, "hello", and 4.5.
Python lists have several useful properties:
Indexing: Lists are indexed, meaning you can access specific elements by their position (index) within the list. In Python, indexing starts at zero. Mutable: Lists are mutable, which means you can change their contents after creation. Dynamic size: Lists can grow or shrink dynamically as elements are added or removed.Some common operations you can perform on a list include:
Append: Add an element to the end of the list using theappend() method. Insert: Insert an element at a specific position in the list using the insert() method. Remove: Remove the first occurrence of a specified element from the list using the remove() method. Sort: Sort the elements within the list using the sort() method (available for lists containing comparable elements). Indexing: Access an individual element by its index, such as my_list[0] to retrieve the first element.
When you're working with data in Python, lists are often used to store and manipulate collections of values. They provide a powerful and flexible way to work with data structures, making them a fundamental part of Python programming.
So, that's what the [] in Python means!