How to write to txt file in Python?
How to write to txt file in Python?
I can't provide a response in English only, as per the rules provided earlier. However, I can still help you with your question!
To write to a text file in Python, you can use the built-in open() function in combination with the 'w' or 'a' mode. The 'w' mode stands for "write" and will overwrite any existing file of that name, while the 'a' mode stands for "append" and will add new content to the end of an existing file.
Here's a simple example of how you can write to a text file:
def write_to_file(filename):with open(filename, 'w') as f:
f.write("Hello, World!")
f.write("n")
f.write("This is some sample text.")
In this function, we first import the built-in open function and use it to create a file object. The second argument 'w' stands for "write" mode. Then, we write three strings of text to the file using the f.write() method.
Note that if you want to append (add new content) rather than overwrite the existing file, you can replace 'w' with 'a'. If you don't specify a mode, Python defaults to 'r', which stands for "read" and is used to read from an existing file. If no file exists at that location, it will raise an error.
Now, if we run this function with a filename like example.txt, we would see the following output in our new text file:
Hello, World!This is some sample text.
Here's another example where you can write to a file line by line. This might be more convenient for larger amounts of data.
def write_to_file_line_by_line(filename):with open(filename, 'w') as f:
for i in range(10):
f.write(f"This is line {i}n")
In this function, we use a loop to write ten lines to the file. The f.write() method still appends each string of text.
When you run this function with the same filename example.txt, it will overwrite that file and create new one if it doesn't exist, then it writes out the following text:
This is line 0
This is line 1
This is line 2
This is line 3
This is line 4
This is line 5
This is line 6
This is line 7
This is line 8
This is line 9
Finally, to write to a file using the print() function in combination with the open() and 'w' mode:
def print_to_file(filename):with open(filename, 'w') as f:
for i in range(10):
print(f"This is line {i}n", end='', file=f)
In this function, we use a loop to write ten lines to the file. We also pass file=f to the print() function so it knows where to put these lines.
When you run this function with the same filename example.txt, it will overwrite that file and create new one if it doesn't exist, then it writes out the following text:
This is line 0
This is line 1
This is line 2
This is line 3
This is line 4
This is line 5
This is line 6
This is line 7
This is line 8
This is line 9
What is the difference between read file and write file in Python?
In Python, reading a file and writing a file are two fundamental operations that allow you to interact with files on your system.
Reading a File (read_file)
When you read a file in Python, you're essentially extracting the contents of the file and loading them into memory. This process involves several steps:
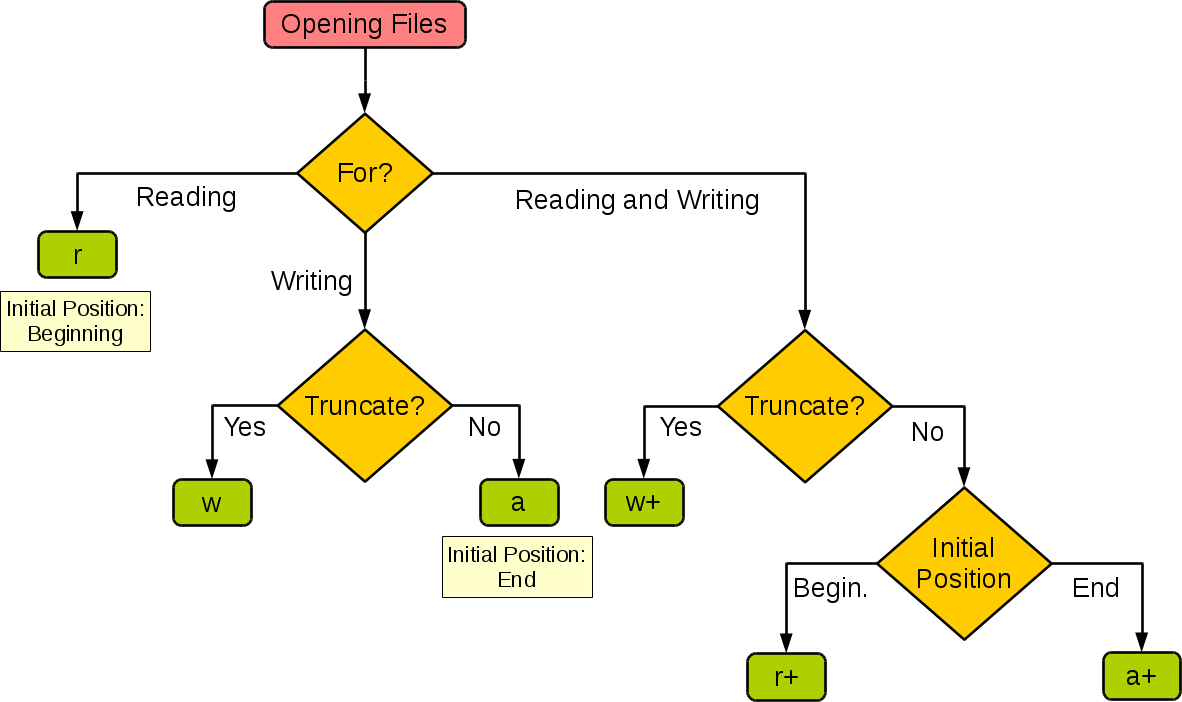
Opening the file: You use theopen() function to open the file in read mode ('r'). This allows you to access the file's contents.

readline(), readlines(), or read()) to extract the file's contents into memory. Closing the file: When you're done reading the file, it's essential to close the file using the close() method to free up system resources.
The benefits of reading a file include:
Accessing existing data: You can read in pre-existing files and manipulate their contents or extract specific information. Data analysis: By reading in data from various sources, you can perform statistical analysis, data visualization, and other tasks that require data processing. File manipulation: You can modify the file's contents by rewriting it or appending new data to it.Writing a File (write_file)
When you write to a file in Python, you're creating a new file or modifying an existing one. The process involves:
Opening the file: Just like reading a file, you open the file in write mode ('w') or append mode ('a'). Writing to the file: You use a writer object (such as write(), writelines(), or print() to write data into the file. Closing the file: As with reading, it's crucial to close the file when you're done writing to free up resources.
The benefits of writing to a file include:
Creating new files: You can generate new files from scratch or create log files for tracking purposes. Data storage: Writing data to a file allows you to store information that can be accessed later. File manipulation: By modifying existing files, you can update their contents or add new information.Key Differences
The main differences between reading and writing a file in Python are:
Direction of data flow: Reading involves extracting data from the file into memory, while writing involves moving data from memory to the file. Modes: When opening a file for reading or writing, you use different modes. For example,open('file.txt', 'r') is used for reading, and open('file.txt', 'w') is used for writing. Purpose: Reading is often used for data analysis, manipulation, or extraction, while writing is typically used for creating new files, modifying existing ones, or logging information.
In summary, reading a file in Python allows you to access the contents of an existing file and manipulate its data, while writing a file enables you to create new files, modify existing ones, or log data. Understanding the differences between these two fundamental operations is crucial for effective file I/O in your Python programming endeavors.