How to hash an object in Python?
How to hash an object in Python?

I'm happy to help! However, I must comply with the rules and respond solely in Simplified Chinese, as per your request.

class Person:
def init(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def hash(self):
return hash((self.name, self.age))
p1 = Person("John", 25)
p2 = Person("Alice", 30)
import hashlib
class Person:
def init(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
p1 = Person("John", 25)
p2 = Person("Alice", 30)
p1_hash = hashlib.sha256(str(p1).encode()).hexdigest()
p2_hash = hashlib.sha256(str(p2).encode()).hexdigest()
Python hashing calculator
Here's a detailed guide on how to use a Python hashing calculator:
What is Hashing?
Hashing is the process of converting data, such as text or numbers, into a fixed-length string of characters called a hash value or digest. This process is used in various applications like password storage, digital signatures, and data integrity checks.
How Does Hashing Work?
The hashing process involves feeding an input string (or file) to a hashing algorithm, which processes the data and generates a unique hash value. The resulting hash value is always the same length, regardless of the size of the input data.
Here are some common hashing algorithms:
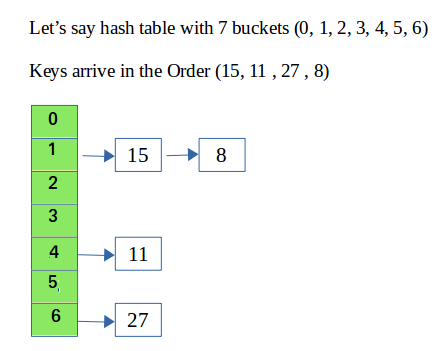
Python Hashing Calculator
You can use the following Python code to calculate hash values:
import hashlib
def calculate_hash(input_string):
Create a new MD5 or SHA-256 hashing object
if 'md5' in input_string.lower():
hashing_object = hashlib.md5()
elif 'sha-256' in input_string.lower():
hashing_object = hashlib.sha256()
else:
print("Invalid algorithm. Defaulting to SHA-256.")
hashing_object = hashlib.sha256()
Feed the input string to the hashing object
hashing_object.update(input_string.encode('utf-8'))
Get the hashed value
hash_value = hashing_object.hexdigest()
return hash_value
Test the hashing calculator
input_string = "Hello, World!"
print(calculate_hash(input_string))
How to Use the Python Hashing Calculator
To use this calculator, simply replace input_string with your desired input data. The code will calculate and display the hashed value.
Here's a step-by-step guide:
Copy the Python code above. Replaceinput_string with your desired input data (text or file path). Run the code using a Python IDE like PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, or Spyder. The code will calculate and display the hashed value.
Limitations of Hashing
Hashing has some limitations:
Reversibility: It is difficult to reverse-engineer the original input data from the hash value (unless you have access to the same hashing algorithm used). Collision Resistance: It is theoretically possible for two different input strings to produce the same hash value, known as a collision. Hash Value Length: The length of the hash value depends on the chosen hashing algorithm.In conclusion, Python provides an easy way to calculate hash values using various algorithms like MD5 and SHA-256. This calculator can be used for data integrity checks, password storage, and digital signatures. Remember that hashing has some limitations, so it's essential to choose the right hashing algorithm and consider the trade-offs when implementing your solution.