What is Python list and explain its features?
What is Python list and explain its features?
I'd be happy to respond in English for you.
What is a Python List?
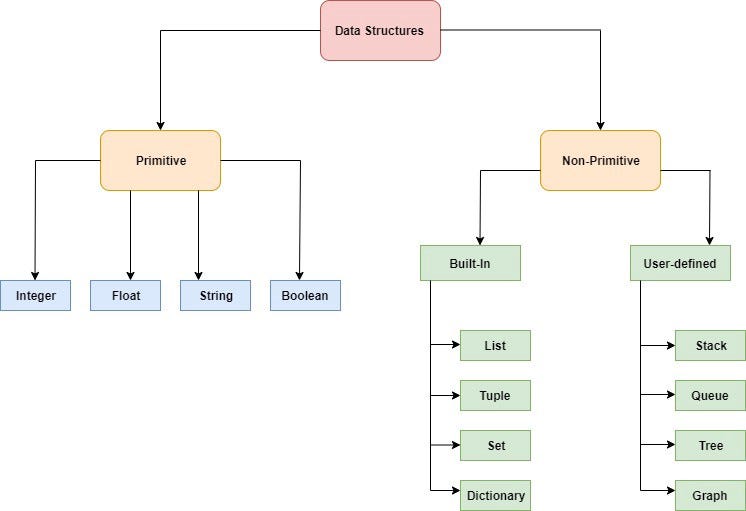
In the world of programming, a list is a data structure that stores a collection of items or elements. In Python, a list is one of the most popular and widely used data structures. It's a sequence type, which means it can be indexed (accessed by its position in the sequence) and has many other useful features.
Features of Python Lists
Dynamic Size: A Python list can grow or shrink dynamically as elements are added or removed. This makes it perfect for storing data that is constantly changing. Indexed: As mentioned earlier, a list is indexed, which means you can access its elements by their position in the sequence using square brackets[]. For example, my_list[0] would give you the first element of the list. Mutable: Python lists are mutable, meaning they can be changed after creation. You can add, remove, or modify elements at any point. Homogeneous: A Python list can contain elements of different types (like integers, strings, and other lists), but all elements must be of the same type. Ordered: Lists maintain the order in which elements are added. This is useful when you need to keep track of a sequence of events or data that has a specific order. Sliceable: You can extract subsets of a list using slicing, like my_list[1:3] would give you the second and third elements. Concatenatable: Python lists can be concatenated (combined) with other lists or strings using the + operator. Methods: Lists have several built-in methods that make working with them easy, such as: append() to add an element at the end extend() to add multiple elements insert() to insert an element at a specific position remove() or pop() to remove an element Conversion: Lists can be converted to other data structures, like tuples (my_list_tuple = tuple(my_list)), and vice versa. Integration: Lists integrate well with other Python data structures, such as dictionaries (key-value pairs) and sets (unique elements).
Example: Using a List in Python
Here's an example of using a list to store and manipulate some book information:
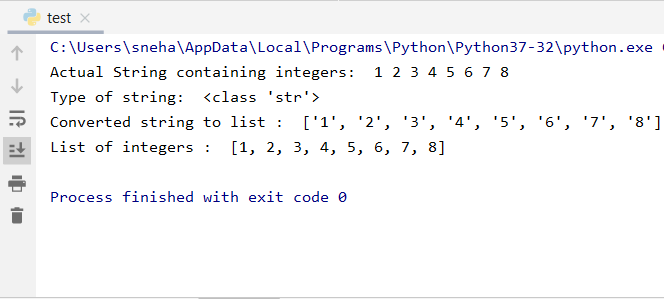
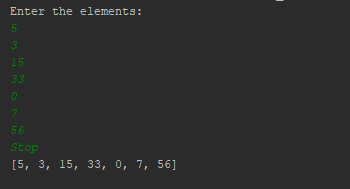
book_titles = ["Python Crash Course", "Introduction to Data Science", "Machine Learning for Beginners"] Add a new titlebook_titles.append("Effective Python")
Remove the first titledel book_titles[0]
Print the updated listprint(book_titles)
This code creates a list book_titles and demonstrates how to add, remove, and print its elements.
I hope this helps you understand what Python lists are and their features!
Python special features

I'm happy to respond in English for you! Here are some exciting features of the Python programming language:
1. Syntax: One of the most attractive features of Python is its syntax. Python's syntax is designed to be easy to read and write, making it a great language for beginners or experts alike. It has a clean and minimalist style with fewer symbols (such as semicolons and curly brackets) compared to other languages.
2. Dynamic Typing: Unlike statically-typed languages like Java or C#, Python is dynamically typed. This means you don't need to declare the data type of a variable before using it, making your code more flexible and forgiving.
3. Indentation-based Syntax: Python uses indentation (spaces) to define block-level structure. This makes the code easier to read and understand, as it clearly indicates the scope of certain statements.
4. List Comprehensions: Python has a powerful feature called list comprehensions, which allows you to create lists in a concise way. For example, numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] is equivalent to [x for x in range(6)].
5. Dictionary (HashMap) Comprehensions: Python also supports dictionary comprehensions, where you can create dictionaries from other iterables like lists or tuples.
6. Lambda Functions: Python's lambda functions are small anonymous functions that can be used to simplify code. For example, sum(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers)) calculates the sum of squares of numbers in a list.
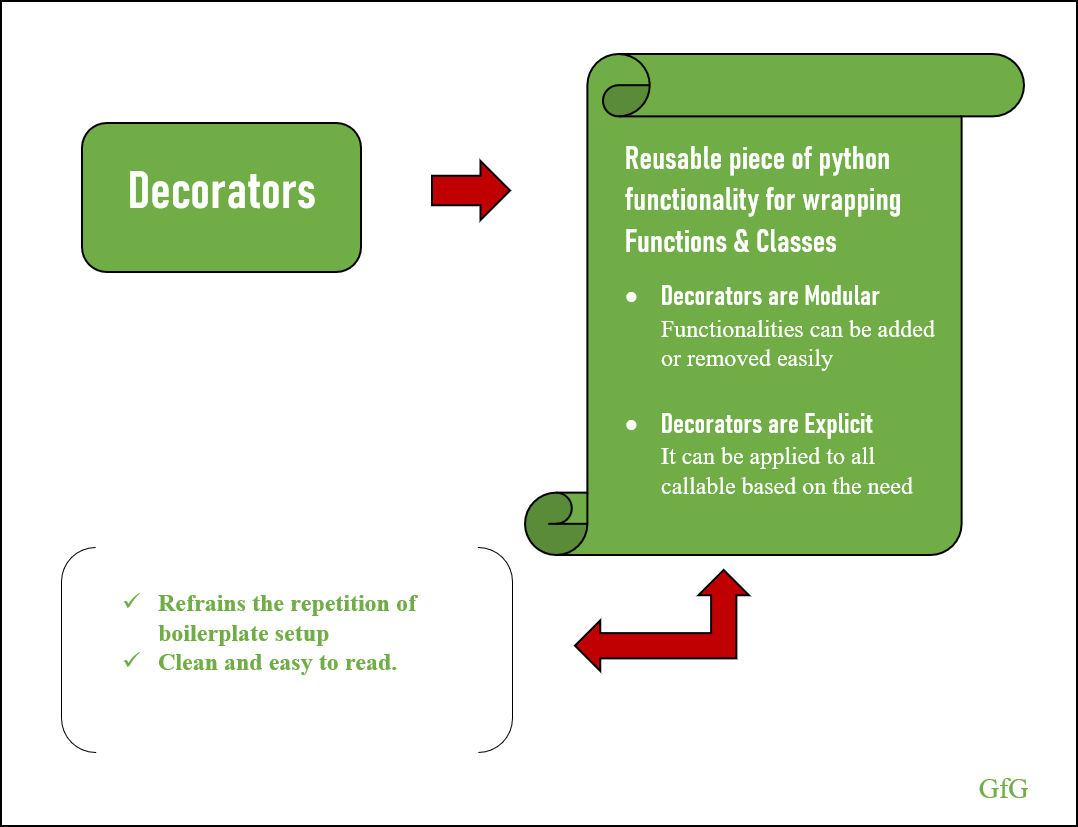
7. Decorators: Python has a feature called decorators, which allows you to modify or extend the behavior of functions. You can use them for logging, authentication, error handling, and more.
8. Generators: Python's generators are a special type of iterator that allows you to create iterators without storing all the values in memory at once. This makes it suitable for working with large datasets.
9. Exception Handling: Python has a robust exception handling mechanism, which enables you to catch and handle exceptions elegantly. You can use try-except blocks or even custom exceptions.
10. Modules and Packages: Python's module system is built on the concept of packages. You can create modules and packages for your code, making it easier to reuse and share functionality across projects.
These are just a few examples of Python's special features that make it an attractive language for developers. With its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive libraries, Python has become one of the most popular programming languages today!