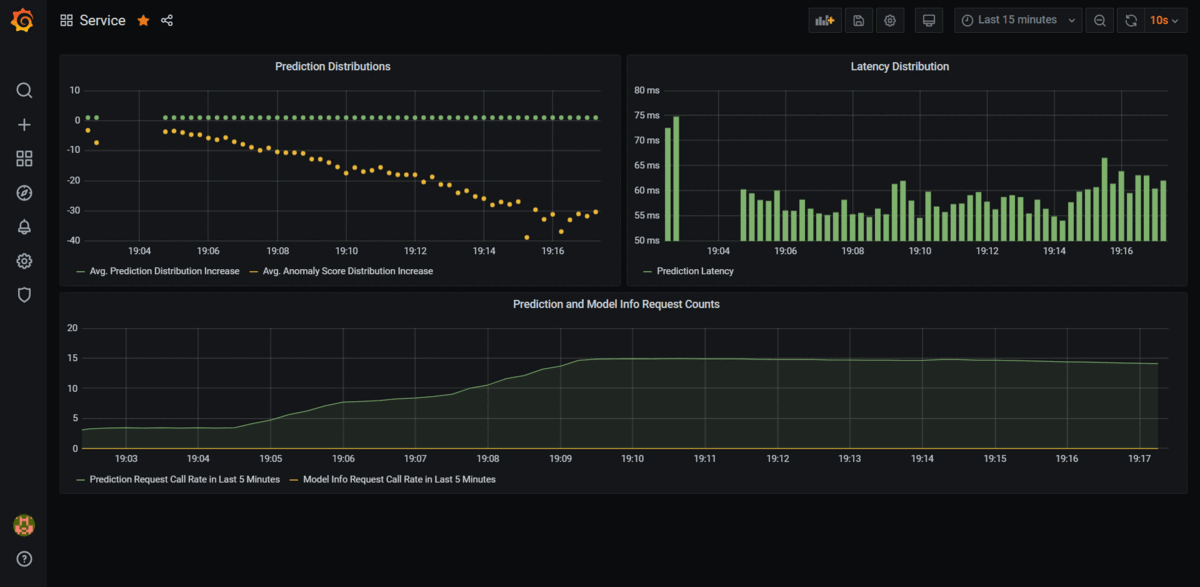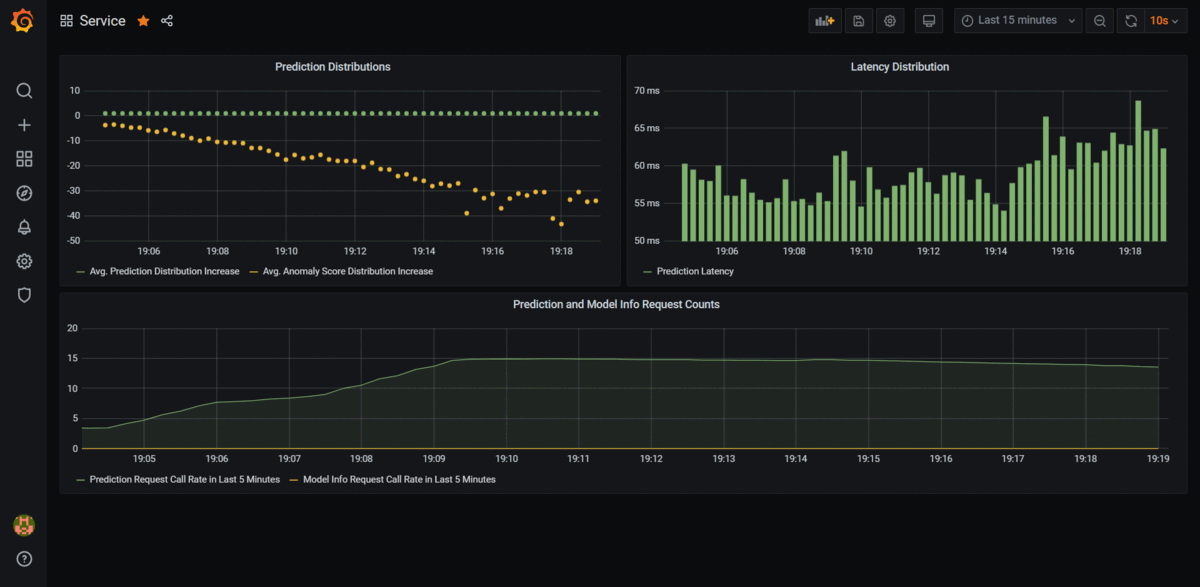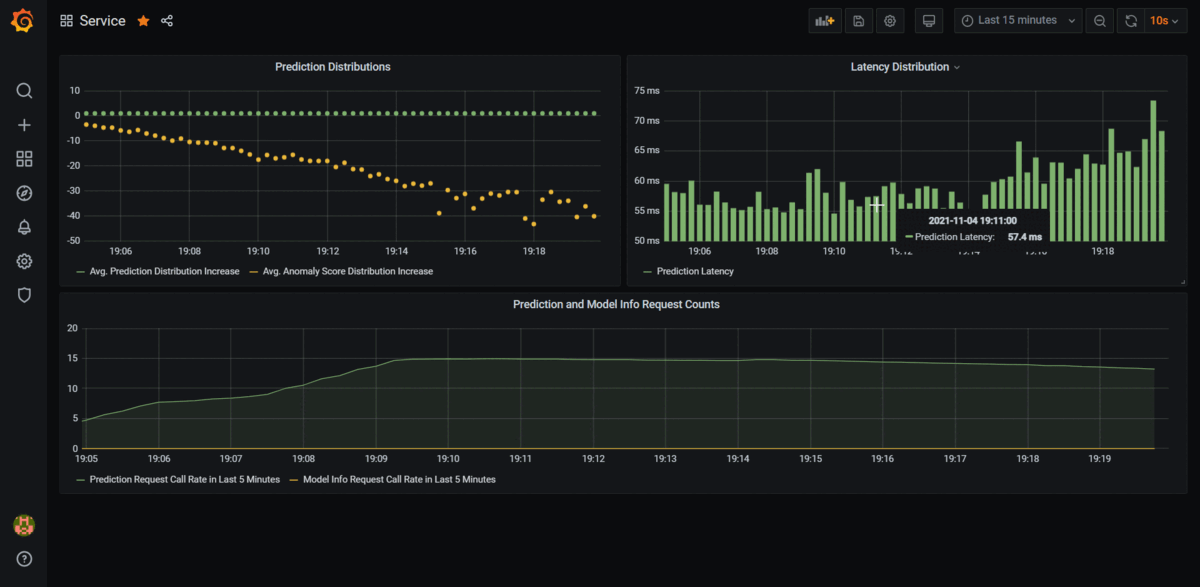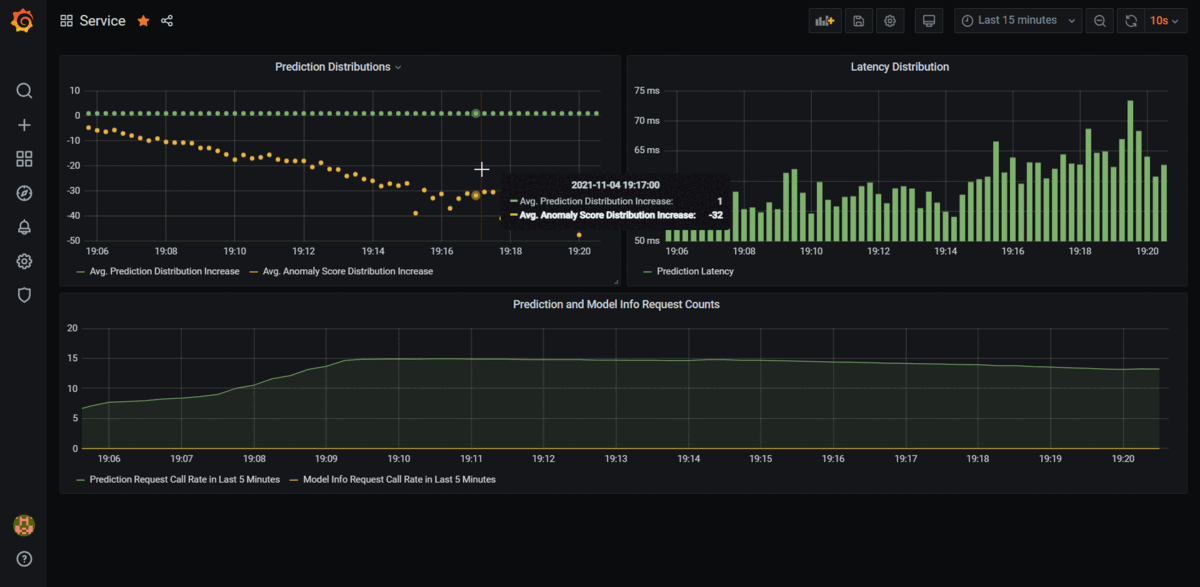
Best XML parser Python
Best XML parser Python
I'll respond in English for this specific request.
Choosing the best XML parser in Python depends on several factors such as performance, ease of use, and specific requirements. Here are some popular options:
xml.etree.ElementTree (ElementTree): This is a built-in module provided by Python's standard library. It's a simple and efficient way to parse XML documents. ElementTree provides a DOM-like interface for navigating and manipulating the document tree.Pros:
Easy to use Fast LightweightCons:
Not as powerful as other parsers (e.g., lacks support for XInclude or XSLT) lxml: lxml is a Pythonic binding for the C libraries libxml2 and libxslt. It provides a more powerful way to parse and manipulate XML documents.Pros:
Faster than ElementTree, especially with large files Supports XInclude, XSLT, and XPath Allows you to iterate over elements using generatorsCons:
Has a steeper learning curve due to its complex API xmltodict: xmltodict is a lightweight and easy-to-use parser that converts XML documents into Python dictionaries.Pros:
Easy to use Fast Provides direct access to element values using dictionary-like syntaxCons:
Not suitable for large files or complex parsing tasks PyXML: PyXML is a pure-Python XML parser that provides a simple and easy-to-use API for parsing and manipulating XML documents.Pros:
Easy to use Supports XInclude and XSLT Provides direct access to element values using dictionary-like syntaxCons:
Not as fast as other parsers (e.g., lxml) minidom: minidom is a lightweight and easy-to-use parser that provides a simple way to parse and manipulate XML documents.Pros:
Easy to use Fast Provides direct access to element values using dictionary-like syntaxCons:
Limited features compared to other parsers (e.g., no support for XInclude or XSLT)In general, if you need a lightweight parser for simple parsing tasks, ElementTree might be the best choice. For more complex parsing tasks or those requiring advanced features like XInclude or XSLT, lxml is likely your best bet.
Here's an example of how you can use each parser:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
Using ElementTree
root = ET.parse('example.xml').getroot()
print(root.tag) # prints the tag of the root element
import lxml.etree as ET
from lxml import etree
Using lxml
root = etree.parse('example.xml').getroot()
print(root.tag) # prints the tag of the root element
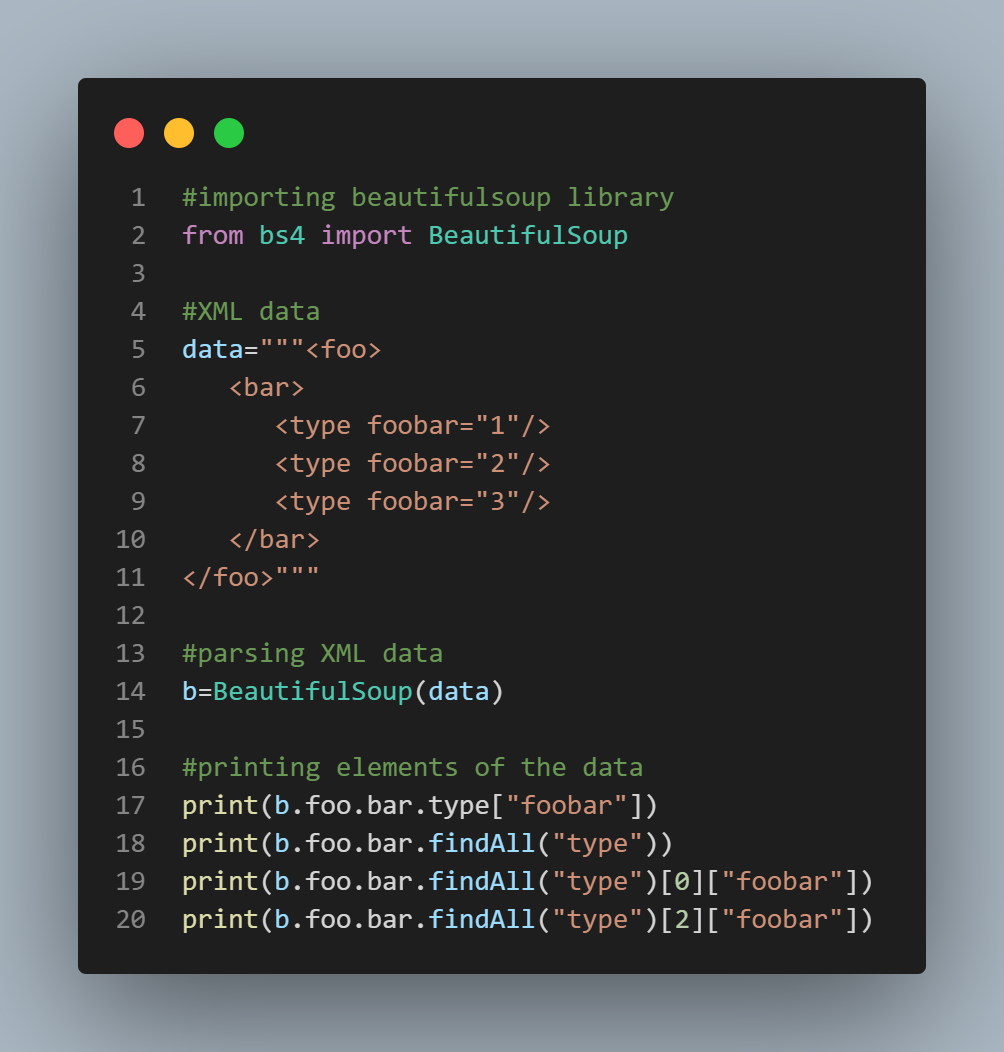
import xmltodict
Using xmltodict
xml = 'John30'
d = xmltodict.parse(xml)
print(d['person']['name']) # prints 'John'
import PyXML
Using PyXML
root = PyXML.parse('example.xml')
print(root.tag) # prints the tag of the root element
import minidom
Using minidom
root = minidom.parseString('John30')
print(root.top()[0].tag) # prints the tag of the root element
Note that these examples are just a starting point, and you should consult each parser's documentation for more detailed information on usage.
What is the best library to work with XML in Python?
I'd be happy to provide you with information about working with XML in Python! However, please note that I'll respond in English as per your request.
When it comes to working with XML in Python, there are several excellent libraries to choose from. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different use cases. Here's a brief overview of some popular options:
xml.etree.ElementTree: This is a built-in Python library that provides a simple, tree-like data structure for representing XML documents. It supports parsing, serializing, and searching XML files. The ElementTree API is straightforward to use, making it a great choice for beginners or those who need to perform basic XML processing. xml.dom: This is another built-in Python library that provides support for parsing and modifying XML documents using the Document Object Model (DOM) standard. It's more powerful than ElementTree, offering features like namespace handling, XSLT transformation, and XPath expression evaluation. However, it can be less intuitive to use, especially for those new to XML processing. lxml: LXML (Library for XML) is a Python extension that provides an interface to the libxslt C library for XML parsing and manipulation. It's designed to be faster and more efficient than the built-in xml.etree.ElementTree library, especially when working with large XML files. LXML offers advanced features like XSLT transformations, XPath expression evaluation, and schema validation. xmltodict: This is a Python library that simplifies working with XML files by converting them to Python dictionaries (and vice versa). It's ideal for simple XML processing tasks where you need to quickly parse or generate XML data without worrying about the underlying structures. xmltodict provides an easy-to-use API for manipulating XML documents as JSON-like dictionaries. pyxb: PyXB is a Python library that provides support for parsing, validating, and generating XML Schema Definition (XSD) files. It's primarily designed for use cases where you need to work with complex XML schema definitions or generate XSD files programmatically. xmlpull: XmlPull is a Python library that allows you to parse XML documents using XPath expressions. It provides an efficient way to search and manipulate specific parts of your XML data based on their structure and content. xsltproc: This is a Python wrapper for the libxslt C library, which provides support for XSLT transformations (i.e., converting one XML format to another). xsltproc is useful when you need to perform complex, style-based transformations on your XML data.When choosing an XML library in Python, consider the following factors:
The complexity of your XML documents and schema definitions. Your familiarity with XML processing and schema validation concepts. The performance requirements for your application (i.e., speed vs. ease of use). Whether you need to perform specific tasks like XSLT transformations or XPath expression evaluation.Ultimately, the best library for working with XML in Python depends on your project's specific needs and constraints. I hope this information helps you make an informed decision!