What are the Python file handling modules?
What are the Python file handling modules?
I'll respond in English as requested!
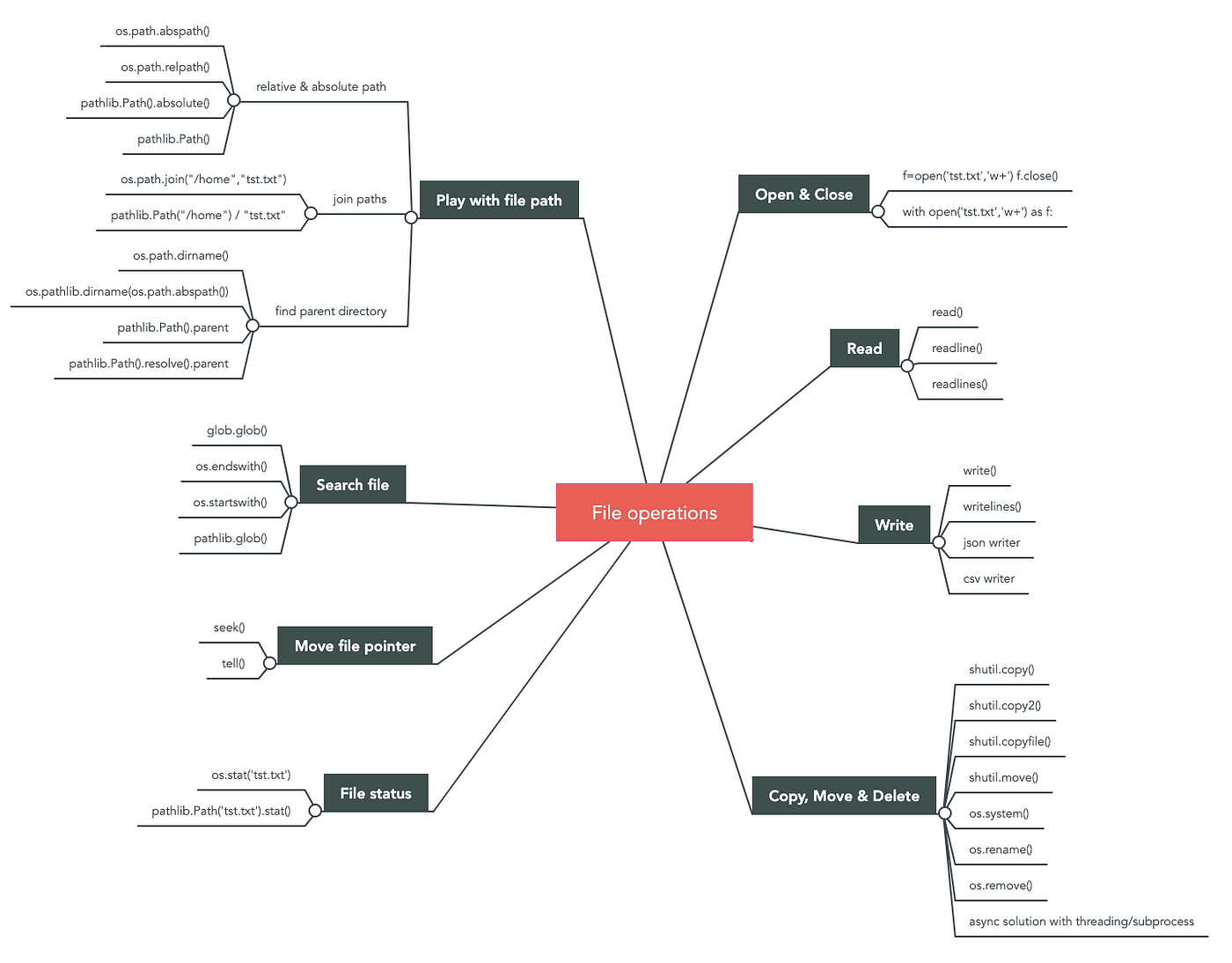
Python provides several built-in modules for handling files. These modules allow you to read and write data to and from a variety of file formats, including text files, images, audio files, and more. Here are some of the most commonly used Python file handling modules:
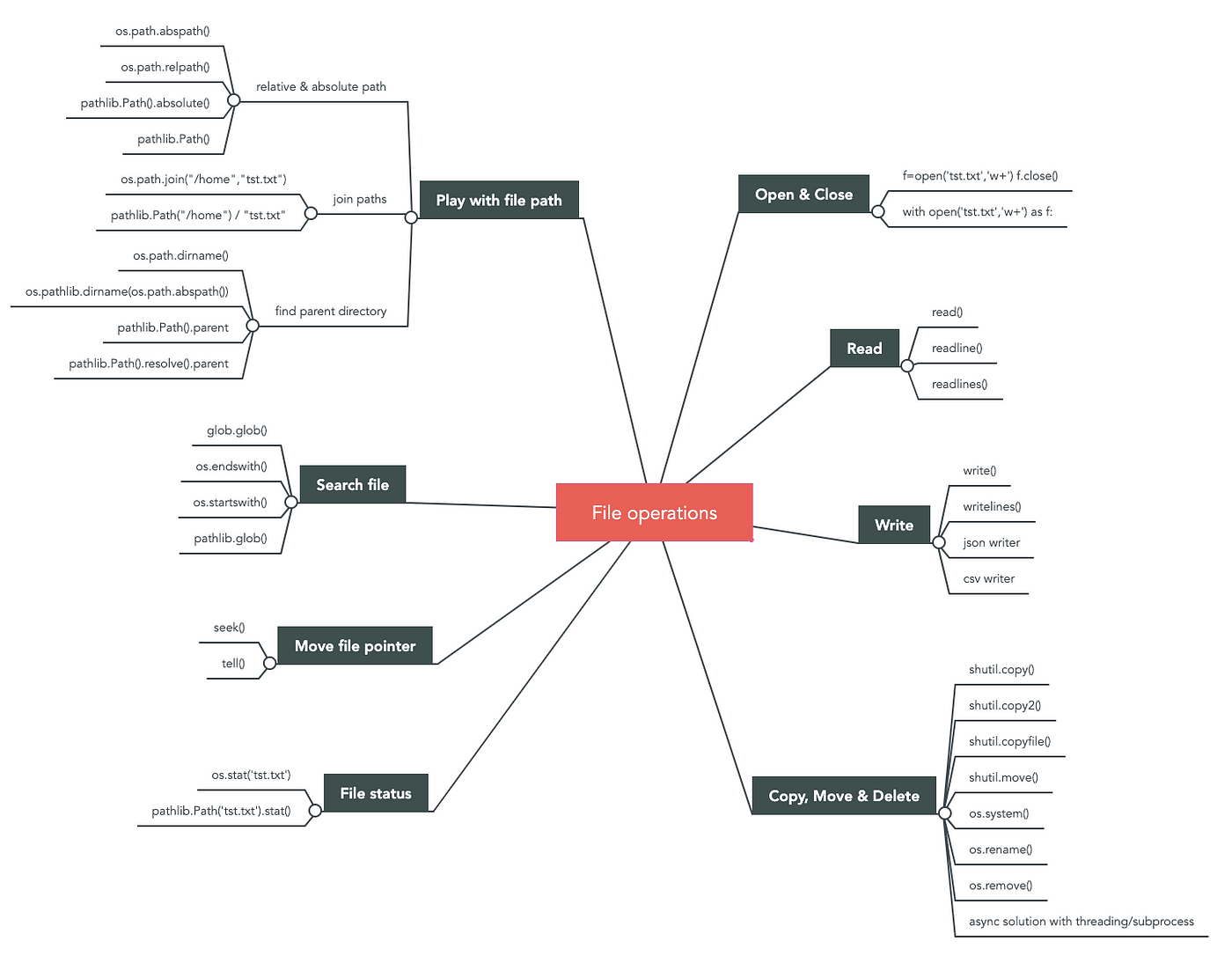
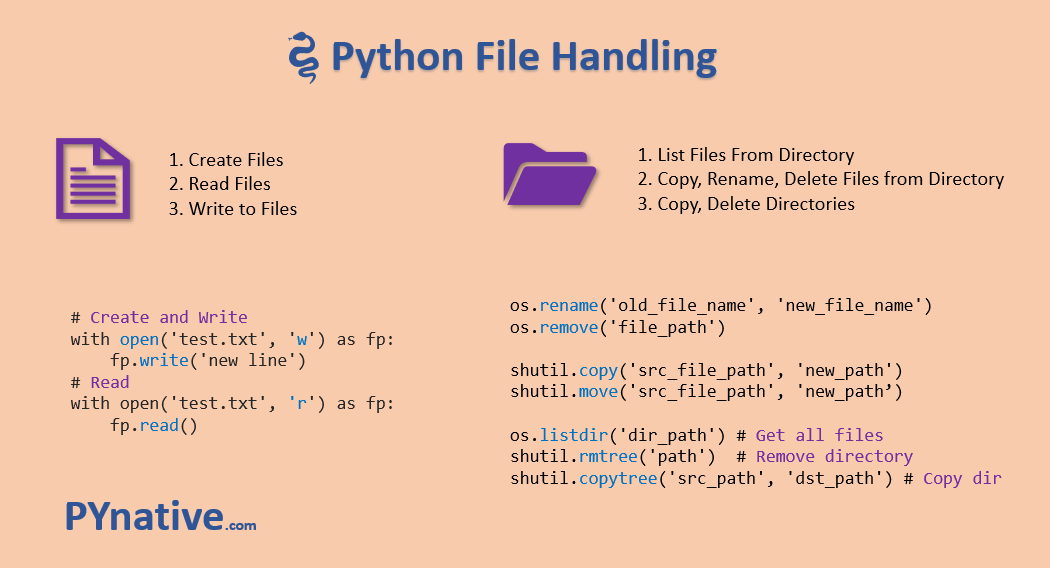
os module: The os module provides a way to interact with the operating system and perform tasks such as creating directories, changing the current working directory, and listing the contents of a directory. pathlib module: The pathlib module is a more modern alternative to the os.path module. It provides a more intuitive and Pythonic way to work with files and directories. It includes classes such as Path, PurePath, and WindowsPath. shutil module: The shutil module is used to perform high-level file operations, such as copying or moving files and directories.
fileinput module: The fileinput module is a powerful tool for modifying text files. It allows you to open a file and make changes to it in-place, without having to write the modified data to a new file. tempfile module: The tempfile module provides a way to create temporary files and directories that can be safely deleted when they are no longer needed.
tarfile module: The tarfile module is used to read and write TAR archive files. TAR archives are a common format for compressing and storing multiple files in a single file.
zipfile module: The zipfile module is used to read and write ZIP archive files. ZIP archives are another common format for compressing and storing multiple files in a single file. csv module: The csv module is used to work with comma-separated value (CSV) files, which are commonly used for exchanging data between applications. json module: The json module is used to read and write JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) files. JSON is a lightweight format for exchanging data between applications. pickle module: The pickle module is used to serialize and deserialize Python objects, allowing you to store complex Python objects in a file or database.
These modules provide a range of ways to handle files in Python, from simple text processing to more advanced tasks such as compressing and archiving files.
Remember, it's always important to consider the specific requirements of your project when choosing which modules to use for file handling.
What are the Python modules for file handling?
I'd be happy to help you with that!
When it comes to file handling in Python, there are several built-in modules and libraries that can assist in reading, writing, and manipulating files. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
'r' for read-only or 'w' for write-only.
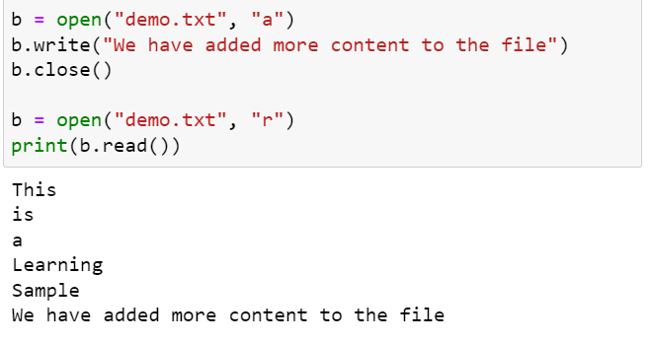
Example: file = open('example.txt', 'r')
Example: import os; os.listdir('path/to/directory') to list files in a directory.
os that provides utilities for working with file paths.
Example: import os.path; os.path.join('path', 'to', 'file.txt') to concatenate paths.
Example: shutil.copyfile('source_file.txt', 'destination_file.txt')
Example: import tempfile; temp = tempfile.TemporaryFile(); temp.write(b'Hello, world!'); temp.seek(0).
Example: from pathlib import Path; file_path = Path('path/to/file.txt')
Example: import json; data = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}; with open('data.json', 'w') as f: json.dump(data, f).
Example: import csv; with open('example.csv', 'r') as file: reader = csv.reader(file); for row in reader: print(row).
Example: import pandas as pd; df = pd.read_csv('data.csv'); print(df.head()) to view the first few rows of a CSV file.
Example: import sqlite3; conn = sqlite3.connect(':memory:') to create an in-memory database.
These are just a few of the many file-handling modules and libraries available for Python. Depending on your specific needs and requirements, you may find that one or more of these options suits your purposes perfectly!