What is >>= in Python?
What is >>= in Python?
I'd be happy to explain what >>>= (or augmented assignment) is in Python!
In Python, >>>= (also known as augmented assignment) is a shorthand way of writing an assignment statement that also performs a specific operation on the value being assigned.
Let's start with a simple example:
x = 5
x += 3
print(x) # Output: 8
In this case, we're assigning the result of x + 3 to x, which is equivalent to writing:
x = x + 3
print(x) # Output: 8
Now, let's use the >>>= syntax:
x = 5
x >>>= 3
print(x) # Output: 8
As you can see, both examples achieve the same result (assigning 3 to x and then printing x), but the >>>= syntax is more concise and easier to read.
This syntax applies to various operators in Python, such as:
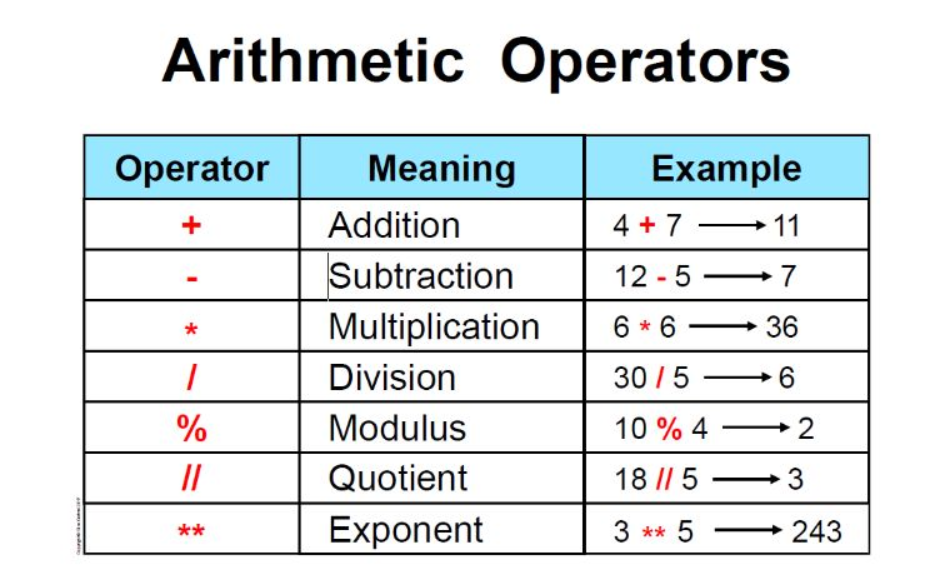
Arithmetic operations:+=, -= , *= , /= , %= , **= , etc. Comparison operations: <<=> , >>= , &= , ^= , |= , etc. Bitwise operations: ~= , &= , ^= , |= , <<= , >>= , etc.
Here are some examples using different operators:
x = 5
x += 3 # x becomes 8
y = 2
y <<= 1 # y becomes 4
x = 10
x -= 3 # x becomes 7
z = 1000
z >>= 2 # z becomes 250
a = "hello"
a += " world" # a becomes "hello world"
b = [1, 2, 3]
b += [4, 5] # b becomes [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
The >>>= syntax is useful when you need to update a variable with the result of an operation, and you want to do so in a concise and readable way.
In summary, >>>= (augmented assignment) is a Python feature that allows you to perform operations on a variable and assign the result back to the same variable. It's a shorthand way of writing complex assignments and can be used with various operators to make your code more efficient and easy to read!
What is the & symbol in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that!
In Python, the "&" symbol is used for various purposes depending on the context. Let's explore some of these uses:
1. Bitwise AND Operator
The "&" operator is used as a bitwise AND operation. It compares each corresponding bit in two numbers and returns an integer where all bits set to 1 are from both operands. In other words, it performs a logical AND operation on the binary representations of the input values.
Example:
a = 5 # Binary: 101
b = 3 # Binary: 011
result = a & b # Result: 001 (Binary)
print(result) # Output: 1
2. Reference Assignment
The "&" symbol is used to assign the value of one variable to another in Python. This is known as reference assignment or aliasing.
Example:
x = 5
y & x # Assigns the value of x (5) to y
print(y) # Output: 5
3. Compound Statement (else-elif-else)
The "&" symbol, often referred to as the "and" operator, is used in compound statements like if-else-elif. It's used to connect multiple conditions and perform a logical AND operation on each condition.
Example:
x = 5
if x > 10 & x < 20: # Condition 1 (AND)
print("x is within the range [10, 20)")
elif x == 5:
print("x equals 5")
else:
print("x is outside the range")
4. Operator Overloading
In Python, you can overload operators using special methods like and() or rand(). This allows you to perform custom operations when the "&" operator is used.
Example (simplified):
class Vector:
def init(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def and(self, other_vector):
return Vector(self.x and other_vector.x, self.y and other_vector.y)
v1 = Vector(2, 3)
v2 = Vector(4, 5)
result = v1 & v2 # Returns a new Vector instance with the AND operation performed on each component
print(result) # Output: (0, 1) - represents the AND operation result
In summary, the "&" symbol has different meanings in Python depending on the context:
As a bitwise AND operator to perform logical operations. For reference assignment or aliasing. In compound statements (else-elif-else) for conditional logic. For operator overloading and custom behavior.I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.