Python comparison operators w3schools
Python comparison operators w3schools
I'll respond in English since you explicitly asked for it!
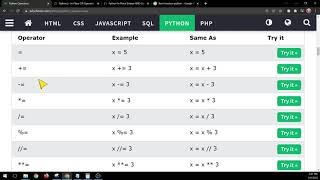
Python provides several comparison operators to compare the values of two expressions. These operators are used to determine if one expression is greater than, less than, equal to, or not equal to another.
Here's a list of Python comparison operators along with their meanings:
== (Equal To): This operator checks if the values of both expressions are equal.
a == b
Example: 5 == 5 returns True, while 5 == 6 returns False.
!= (Not Equal To): This operator checks if the values of both expressions are not equal.
a != b
Example: 5 != 5 returns False, while 5 != 6 returns True.
< (Less Than): This operator checks if the value of the first expression is less than the second.
a < b
Example: 4 < 6 returns True, while 6 < 4 returns False.
> (Greater Than): This operator checks if the value of the first expression is greater than the second.
a > b
Example: 6 > 4 returns True, while 4 > 6 returns False.
<= (Less Than or Equal To): This operator checks if the value of the first expression is less than or equal to the second.
a <= b
Example: 4 <= 6 returns True, while 6 <= 4 returns False.
>= (Greater Than or Equal To): This operator checks if the value of the first expression is greater than or equal to the second.
a >= b
Example: 6 >= 4 returns True, while 4 >= 6 returns False.
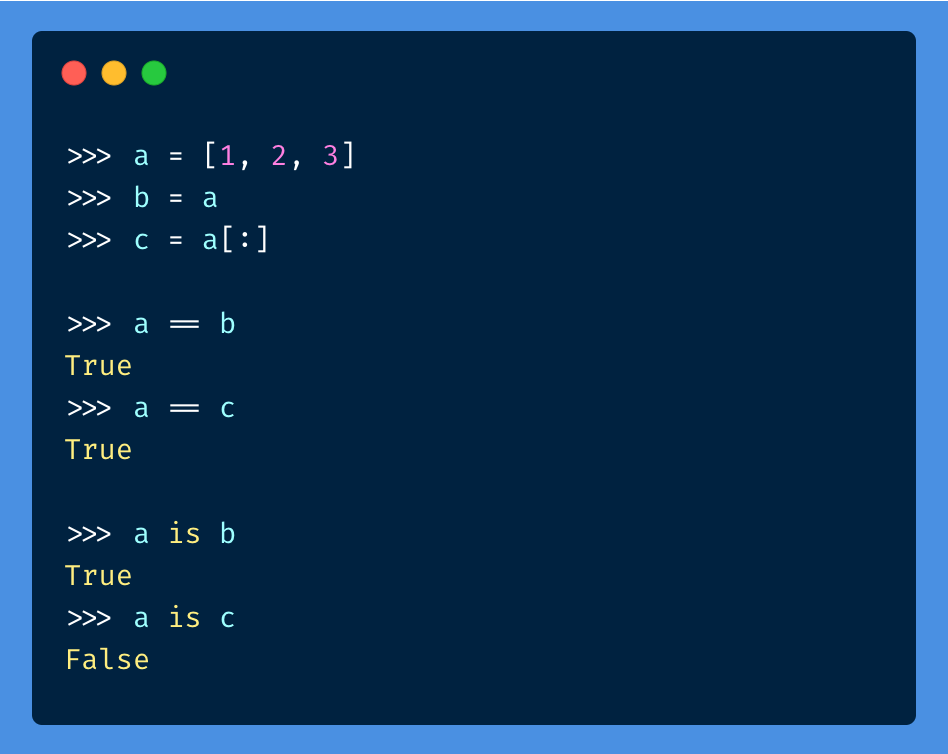
is (Object Identity): This operator checks if both expressions are identical, considering their memory addresses.
a is b
Example: x is x returns True for the same variable x, while 5 is '5' returns False because they have different data types.
is not (Object Non-Identity): This operator checks if both expressions are not identical.
a is not b
Example: x is not x returns False for the same variable x, while 5 is not '5' returns True because they have different data types.
For more information on these comparison operators, you can visit W3Schools' Python Comparison Operators page:
https://www.w3schools.com/python/default.asp#Comparison%20Operators
Happy coding!
What is |= in Python?

I'd be delighted to explain what = is in Python!
In the world of programming, = is an assignment operator, and it plays a crucial role in Python's syntax. This humble character is used to assign a value to a variable or to express a shorthand for more complex operations.
Assignment
When you use = to assign a value to a variable, it means you're giving a name to a specific value. For example:

x = 5
In this case, the value 5 is assigned to the variable x. From now on, whenever you refer to x, Python will recall that its value is 5.
Shorthand for Expressions
Another significant aspect of = is its ability to create a shorthand for more complex expressions. Consider this example:
result = 3 * (4 + 2)
By using =, you're assigning the result of the expression (4 + 2) multiplied by 3 to a variable named result. This can be a concise way to perform calculations and store the outcome in a variable.
Other Uses of =
Beyond assignments and shorthands, = has additional uses in Python. For instance:
= with augmented assignment operators (+=, -= , *= , /=, etc.) to perform operations on variables. For example:
x += 2 # equivalent to x = x + 2
This will increment the value of x by 2.
= operator is also used with the splat operator (*) for packing and unpacking arguments. For example:
def my_func(a, b):print(f"Arguments are {a} and {b}")
args = (1, 2)
my_func(*args) # equivalent to my_func(1, 2)
In this context, * is used to "splat" the elements of the tuple args into separate arguments for the function my_func.
Conclusion
In conclusion, = in Python is a multifaceted operator that enables assignments, shorthands, augmented assignments, and even helps with splatting. Its versatility has made it an essential part of the language's syntax. When working with Python, understanding how to effectively use the = operator will help you write more efficient, concise, and readable code.
I hope this explanation has provided a thorough introduction to what = means in Python! If you have any further questions or need clarification on specific aspects, please don't hesitate to ask.