Is list same as array in Python?
Is list same as array in Python?

I'd be happy to help!
In Python, the terms "list" and "array" are often used interchangeably, but technically speaking, they are not exactly the same thing.
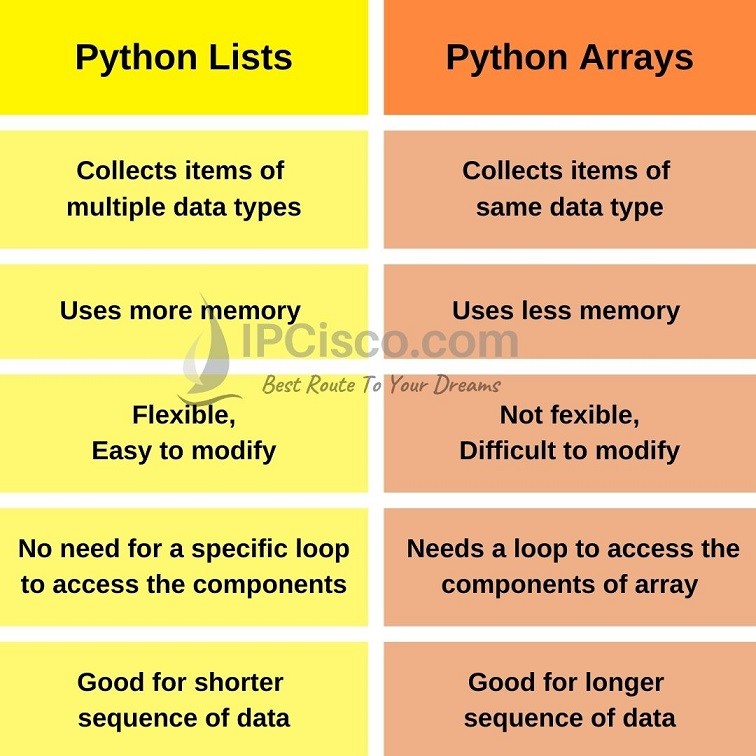
A list in Python is a data structure that stores a collection of items, which can be of any data type (integer, string, float, etc.). Lists are implemented as dynamic arrays, meaning their size can change during runtime. You can think of a list as a container that can hold multiple values, and you can access these values by their index (a zero-based integer). Lists are defined using square brackets [] and elements are separated by commas.
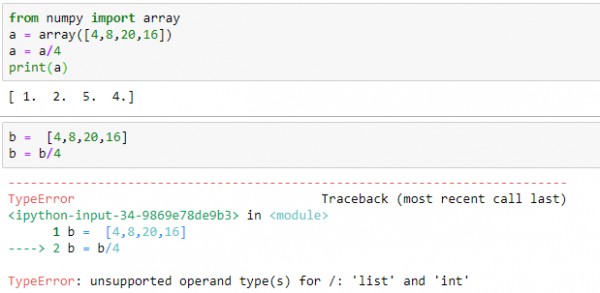
On the other hand, an array is a contiguous block of memory used to store a fixed-size, homogeneous collection of elements. In Python, arrays are not built-in data structures like lists, but you can use external libraries like NumPy to create arrays.
Now, here's where things get interesting: while Python doesn't have built-in arrays, the NumPy library does provide an array class that resembles a dynamic array. These arrays are similar to lists in that they can store different data types and their size can change during runtime. However, NumPy arrays are designed for numerical computations and offer additional features like vectorized operations and support for multi-dimensional arrays.
Here's a key difference between Python lists and NumPy arrays:
Homogeneity: Lists can contain elements of different data types (e.g., strings and integers), whereas NumPy arrays must have all elements of the same type (e.g., all integers or all floats). Performance: NumPy arrays are optimized for numerical computations and often provide better performance than lists when working with large datasets. Multidimensionality: NumPy arrays can be multi-dimensional, while Python lists are typically one-dimensional.So, to summarize:
In Python, "list" refers specifically to a dynamic array that can store elements of different data types.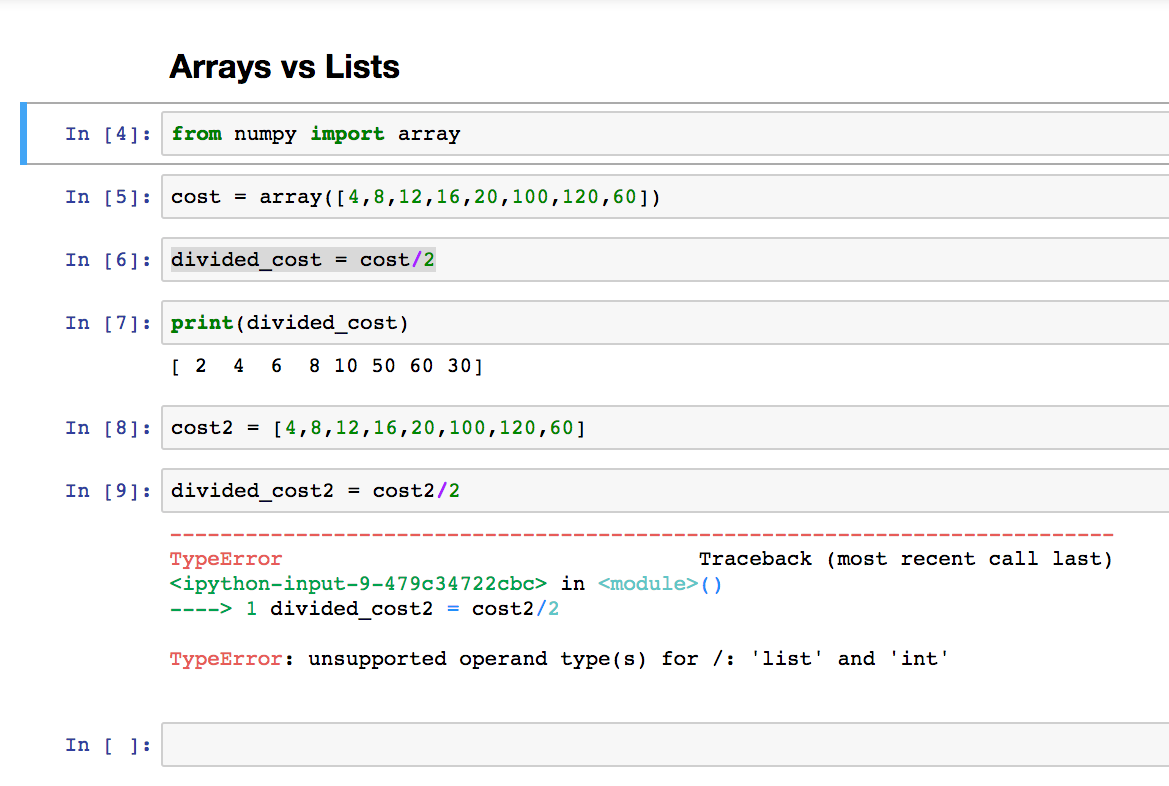
I hope this helps clarify the differences between Python lists and arrays (NumPy or otherwise)!
Python list vs array vs dictionary
Here's a detailed explanation of Python's data structures: lists, arrays, and dictionaries:
Lists
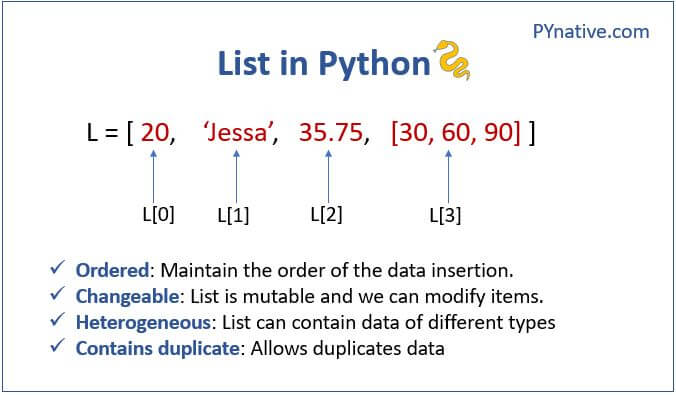
In Python, a list is a collection of items that can be of any data type, including strings, integers, floats, and other lists. Lists are denoted by square brackets [] and are defined using the comma-separated values inside the brackets.
For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, "hello", True]
Lists support various operations such as:
Indexing: Access individual elements using their index (0-based) Slicing: Extract a subset of elements from the list Appending: Add new elements to the end of the list Insertion: Insert new elements at specific positions in the list Removing: Remove elements from the listOne notable feature of lists is that they can store any type of data, including other lists. This allows for complex nested structures.
Arrays
Python does not have a built-in array data structure like some other programming languages (e.g., Java or C). Instead, Python's lists serve as an alternative to arrays. The key differences between lists and arrays are:
Dynamic size: Lists can grow or shrink dynamically based on the number of elements added or removed. Heterogeneous type: Lists can store different data types (like strings, integers, and floats) in a single collection.If you need a fixed-size array with homogeneous elements (e.g., all integers), you can use NumPy arrays. These are part of the NumPy library and provide additional features like vectorized operations.
Dictionaries
In Python, a dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs, denoted by curly braces {}. Each pair is separated by commas, and keys must be unique. Dictionaries support various operations such as:
Dictionaries can store any type of data, including strings, integers, floats, and other dictionaries.
Key differences
To summarize:
Lists are dynamic, heterogeneous collections with square bracket notation ([]). Python does not have arrays in the classical sense; lists serve as an alternative. Dictionaries are unordered, key-value pair collections with curly brace notation ({}). They support fast lookups and insertion/deletion operations.
When to use each:
Use lists when you need a dynamic collection of elements that can be of any data type. Use dictionaries when you need to store key-value pairs for fast lookup or updating operations. If the keys are strings, use dictionaries; if the keys are integers (e.g., indices), use lists.Remember, Python's built-in data structures are designed for flexibility and ease of use, so you can often achieve your goals with these fundamental building blocks!