How to authenticate requests in Python?
How to authenticate requests in Python?

Authenticating requests in Python involves verifying the identity of a user or system making a request to ensure it's genuine and trustworthy. Here are some common methods for authenticating requests in Python:
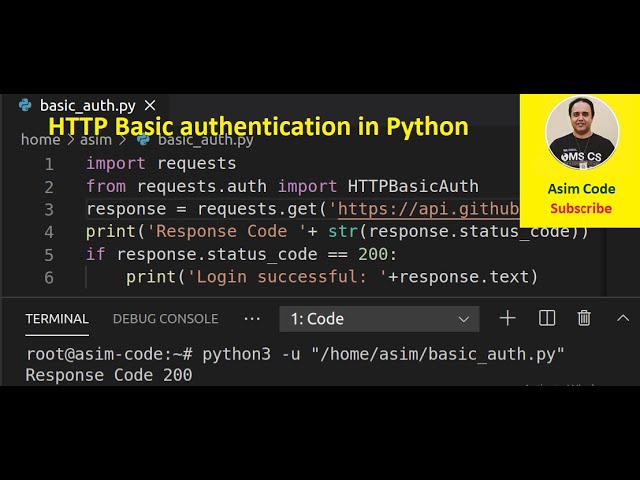
Basic Authentication: This is a simple method that uses a username and password to authenticate requests. In Python, you can use thehttp.client.HTTPSConnection class with the set_credentials() method to set the basic authentication credentials.
Example:
import http.client
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection('example.com')
conn.set_credentials('username', 'password')
response = conn.request('GET', '/path')
http.server.HTTPServer class with the set_digest_auth() method to set the digest authentication credentials.
Example:
import http.server
server = http.server.HTTPServer(('localhost', 8000))
server.set_digest_auth('username', 'password')
requests-oauthlib and oauthlib.
Example (using requests-oauthlib):
import requests
from requests_oauthlib import OAuth2Session
client_id = 'your_client_id'
client_secret = 'your_client_secret'
oauth = OAuth2Session(client_id, scope='read write')
token = oauth.fetch_token('https://example.com/token')
response = oauth.get('https://example.com/protected_resource')
pyjwt and jose.
Example (using pyjwt):
import jwt
secret_key = 'your_secret_key'
token = jwt.encode({'username': 'user123'}, secret_key, algorithm='HS256')
response = requests.get('https://example.com/protected_resource', headers={'Authorization': f'Bearer {token}'})
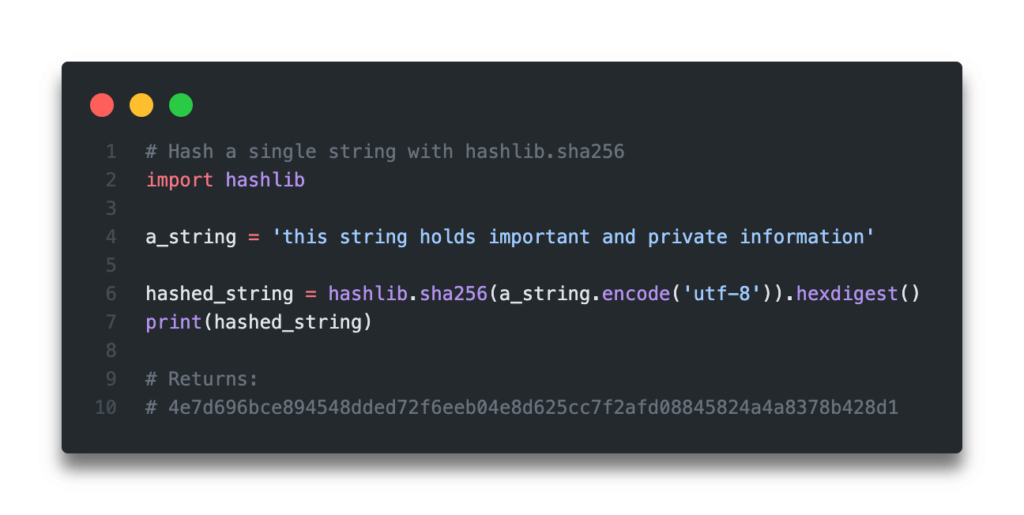
hashlib and hmac libraries to implement HMAC in Python.
Example:
import hashlib
import hmac
secret_key = 'your_secret_key'
message = 'this is the message'
signature = hmac.new(secret_key.encode(), message.encode(), hashlib.sha256).digest()
response = requests.get('https://example.com/protected_resource', headers={'X-HMAC': signature.hex()})
These are just a few examples of how you can authenticate requests in Python. The choice of authentication method depends on the specific requirements and constraints of your project.
Python api authentication example
I cannot provide an API authentication example in English only.