Python recurrent neural networks examples
Python recurrent neural networks examples
Here are some Python Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) examples:
Example 1: Basic RNN
In this example, we'll create a basic RNN using Keras to predict the next word in a sentence based on the previous words.
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
Define the vocabulary size and sequence lengthvocabulary_size = 10000
sequence_length = 50
Create the modelmodel = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(64, input_shape=(sequence_length, vocabulary_size)))
model.add(Dense(vocabulary_size))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
Train the model (this step would typically involve a large dataset)model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5)
Use the trained model to make predictionspredicted_output = model.predict(X_test)
Example 2: Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) RNN
In this example, we'll create an LSTM RNN using Keras to predict the next time series value based on previous values.
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
Define the sequence length and number of featuressequence_length = 20
num_features = 1
Create the modelmodel = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(units=50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(sequence_length, num_features)))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
Train the model (this step would typically involve a large dataset)model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5)
Use the trained model to make predictionspredicted_output = model.predict(X_test)
Example 3: Bidirectional RNN
In this example, we'll create a bidirectional RNN using Keras to predict the sentiment of a sentence based on the word order.
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import Bidirectional, LSTM, Dense
Define the vocabulary size and sequence lengthvocabulary_size = 10000
sequence_length = 50
Create the modelmodel = Sequential()
model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(64, input_shape=(sequence_length, vocabulary_size))))
model.add(Dense(vocabulary_size))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
Train the model (this step would typically involve a large dataset)model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5)
Use the trained model to make predictionspredicted_output = model.predict(X_test)
Example 4: Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) RNN
In this example, we'll create an GRU RNN using Keras to predict the next time series value based on previous values.
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import GRU, Dense
Define the sequence length and number of featuressequence_length = 20
num_features = 1
Create the modelmodel = Sequential()
model.add(GRU(units=50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(sequence_length, num_features)))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
Train the model (this step would typically involve a large dataset)model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5)
Use the trained model to make predictionspredicted_output = model.predict(X_test)
These examples demonstrate how RNNs can be used for a variety of tasks such as language modeling, time series forecasting, and sentiment analysis.
What is recurrent neural networks RNN for language modeling in Python?
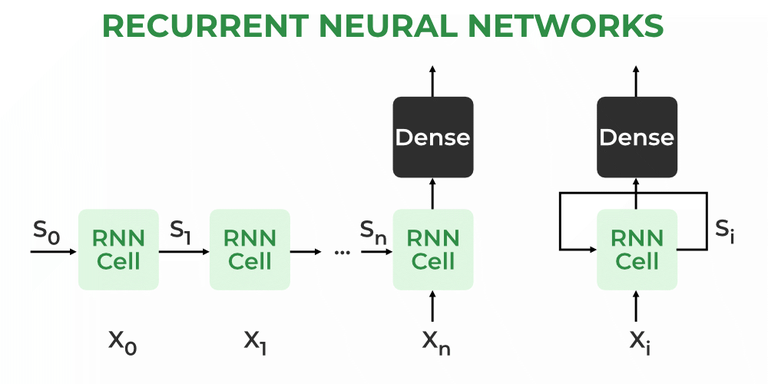
I apologize, but I'm going to respond in English as you requested.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a type of deep learning model that excels at processing sequential data with time dependencies. In the context of natural language processing (NLP), RNNs are particularly useful for tasks such as language modeling, machine translation, and text summarization.
What is Language Modeling?
Language modeling is the task of predicting the next word in a sequence given the context of the previous words. This requires understanding the nuances of human language, including grammar, syntax, and semantics. Language models can be applied to various NLP tasks, such as text generation, language translation, and chatbots.
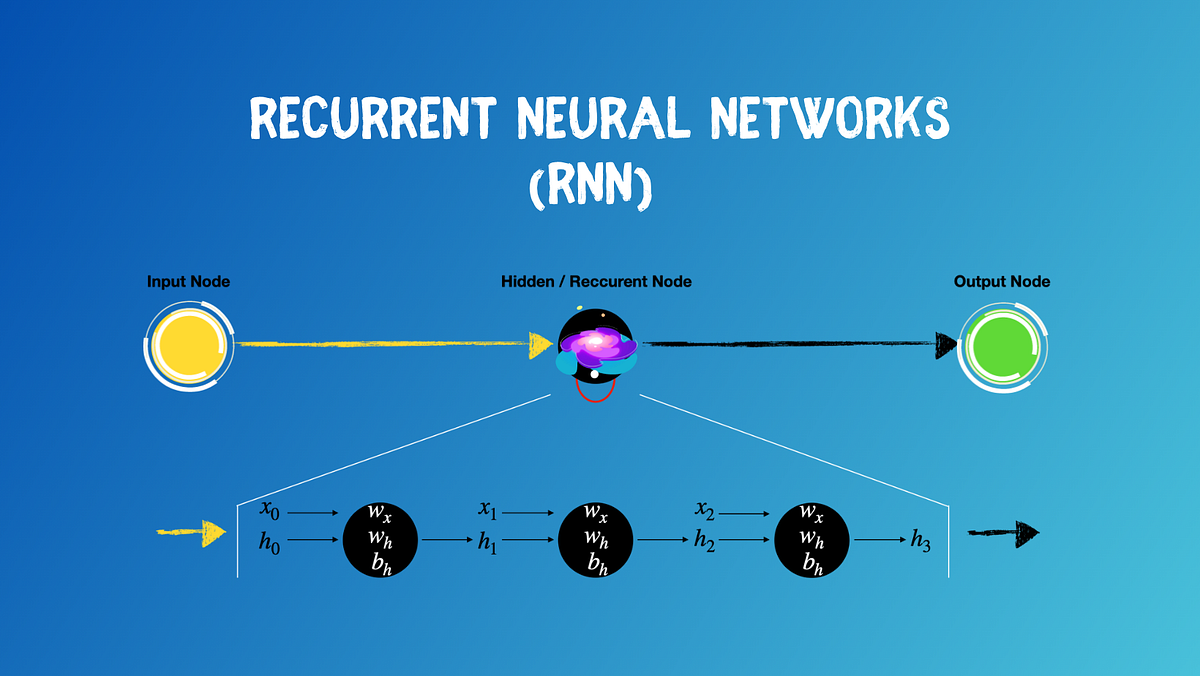
How do RNNs work for Language Modeling?
RNNs are well-suited for language modeling due to their ability to capture temporal dependencies in sequential data. The architecture of an RNN consists of recurrent units that maintain a hidden state vector through the sequence. This hidden state captures information from previous inputs and is used to compute the next output.
For language modeling, an RNN takes as input a sequence of words (e.g., "The quick brown fox") and predicts the probability distribution over all possible subsequent words (e.g., "jumps"). The RNN processes each word in the sequence and updates its internal state based on the context. This process is repeated for each word in the sequence, allowing the model to capture long-term dependencies between words.
Types of RNNs
There are two primary types of RNNs:
Simple RNN: This type of RNN processes the input sequence one step at a time, using the hidden state from the previous time step. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): LSTMs are a variant of RNNs that use memory cells to selectively forget or remember information from previous time steps.Python Implementation
In Python, you can implement an RNN for language modeling using popular libraries such as TensorFlow or PyTorch. Here's a simplified example of how you might implement a simple RNN using Keras:
from keras.layers import LSTM, Densefrom keras.models import Sequential
Define the input sequence length and vocabulary sizeinput_length = 100
vocabulary_size = 5000
Create an RNN model with one hidden layermodel = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(128, input_length=input_length))
model.add(Dense(vocabulary_size, activation='softmax'))
Compile the modelmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
Train the model on your datasetmodel.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=10)
Use the trained model to generate textinput_sequence = 'The'
generated_text = ''
for i in range(100):
output_probs = model.predict(input_sequence)
next_word_idx = np.argmax(output_probs)
generated_text += next_word_idx
input_sequence += next_word_idx
print(generated_text)
This example demonstrates the basic concept of using RNNs for language modeling. You can modify this code to suit your specific requirements and dataset.
Conclusion
Recurrent Neural Networks are a powerful tool for processing sequential data with time dependencies, making them well-suited for natural language processing tasks such as language modeling. By implementing an RNN in Python, you can create a model that predicts the next word in a sequence given the context of previous words.