What is the difference between local and global variables in Python
What is the difference between local and global variables in Python
I'd be happy to explain!
In Python, a variable can be either local or global, which affects its scope and accessibility.
Local Variables
A local variable is created within a function or block of code. It has a limited scope and exists only within the context of that function or block. When the function or block finishes executing, the local variables are automatically garbage collected.
Here's an example:
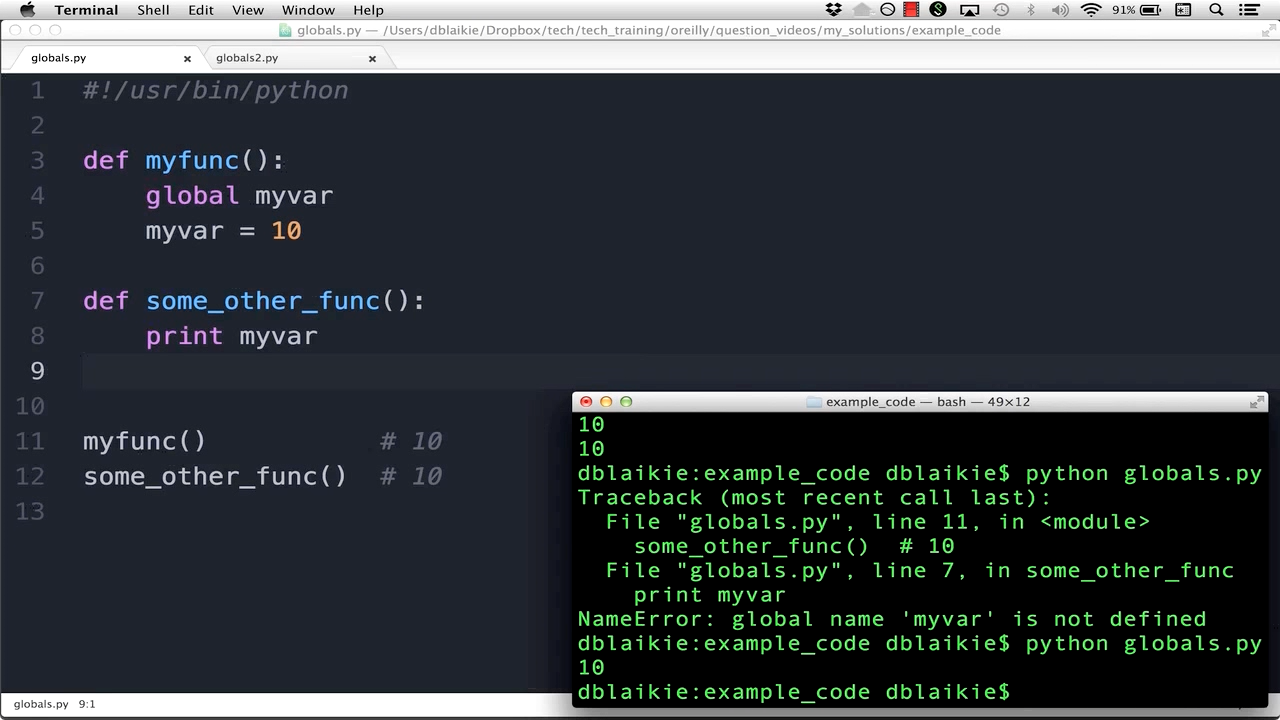
def my_function():x = 5 # local variable
print(x) # prints 5
my_function()
print(x) # raises NameError: name 'x' is not defined
As you can see, the local variable x is only accessible within the scope of the my_function() function. Outside that scope, it's no longer recognized.
Global Variables
A global variable is declared outside any function or block. It has a broader scope and exists throughout the entire program.
Here's an example:
x = 5 # global variabledef my_function():
print(x) # prints 5
my_function()
print(x) # still prints 5
Notice how the global variable x is accessible within the my_function() function as well as outside it.
Key differences:
Scope: Local variables are limited to the scope of a function or block, while global variables have a broader scope and exist throughout the program. Accessibility: Local variables can only be accessed within their defining scope, whereas global variables can be accessed from anywhere in the program. Lifetime: Local variables are automatically garbage collected when they go out of scope, whereas global variables persist until the program terminates.Best practices:
Use local variables whenever possible to avoid polluting the global namespace. Declare global variables only when necessary and keep their usage minimal to maintain code readability and maintainability. Be mindful of variable naming conventions (e.g., using_ as a prefix for private variables) to distinguish between global and local variables.
In summary, understanding the difference between local and global variables in Python is crucial for writing efficient, readable, and maintainable code. By choosing the right scope for your variables, you can avoid confusing errors and keep your program organized!
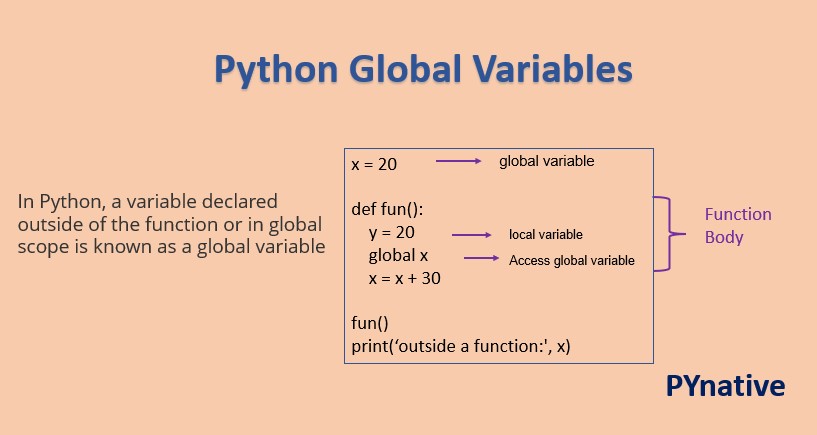
Global variable in Python
I'm happy to help you with your question!
A global variable in Python is a variable that is defined outside of any function and can be accessed from within any function. In other words, it's a variable that is not limited to a specific scope or context.
To declare a global variable in Python, you simply define the variable outside of any function, like this:
x = 10
This declares a global variable x with an initial value of 10. You can then access and modify this variable from within any function, like this:
def print_x():print(x)
print_x() # Output: 10
def increment_x():
global x
x += 1
increment_x()
print_x() # Output: 11
As you can see, the global keyword is used to indicate that the variable x is a global variable. This allows the function increment_x() to modify the value of x, which can then be accessed from within any other function.
It's worth noting that using global variables can sometimes lead to confusing and hard-to-debug code, especially in larger programs with many interacting functions. As a result, it's generally considered good practice to avoid using global variables whenever possible, instead preferring to pass variables as arguments to functions or use object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts like classes and objects.
But when you do need to use a global variable, Python provides several ways to make sure that you can access it safely and efficiently. For example:
Global scope: You can define a global variable at the top level of your script, outside of any function or class. Import modules: You can import modules that contain global variables, and then access those variables from within your own code. Class attributes: You can define global variables as attributes of classes, which allows you to access them using dot notation (e.g.,MyClass.x).
In summary, global variables in Python are variables defined outside of any function that can be accessed from within any function. They provide a way to share data between functions and modules, but should be used with caution to avoid confusion and bugs.
Hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.