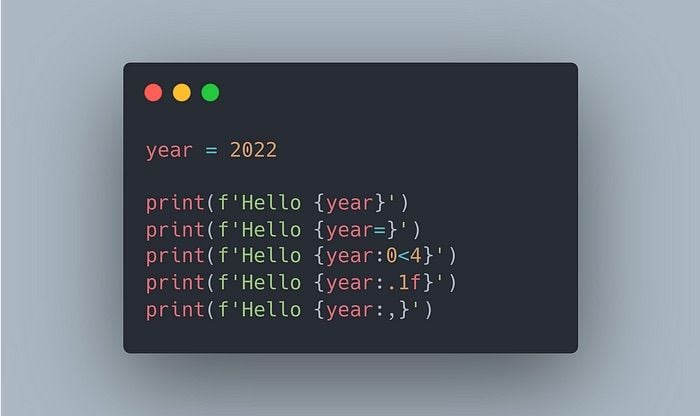
Python variables quiz
Python variables quiz

I'm happy to help! Here's a comprehensive guide to Python variable quizzes.
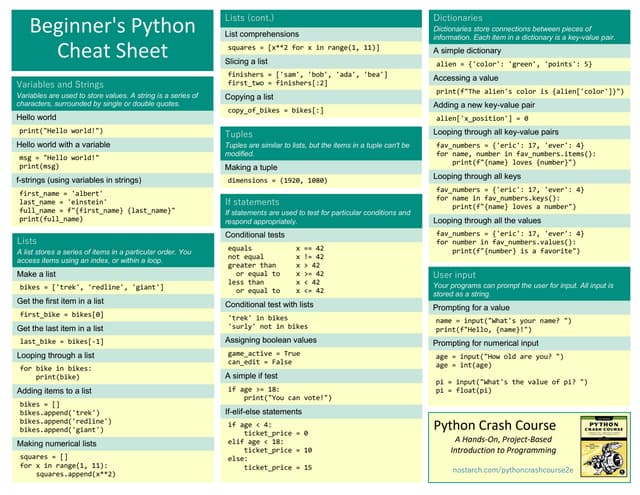
What is a Variable in Python?
A variable in Python is a name given to a value. You can think of it as a labeled box where you store a value. Variables are used to store and manipulate data in your program.
Types of Variables in Python
Python has the following types of variables:
Integer: Stores an integer value (e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc.).Example: x = 5
Example: y = 3.14
Example: name = "John" or greeting = 'Hello'
Example: is_admin = True
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
Example: colors = ('red', 'green', 'blue')
Example: person = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
How Do You Create Variables in Python?
You can create variables using the following syntax:
variable_name = value
For example:
x = 5y = 3.14
name = "John"
is_admin = True
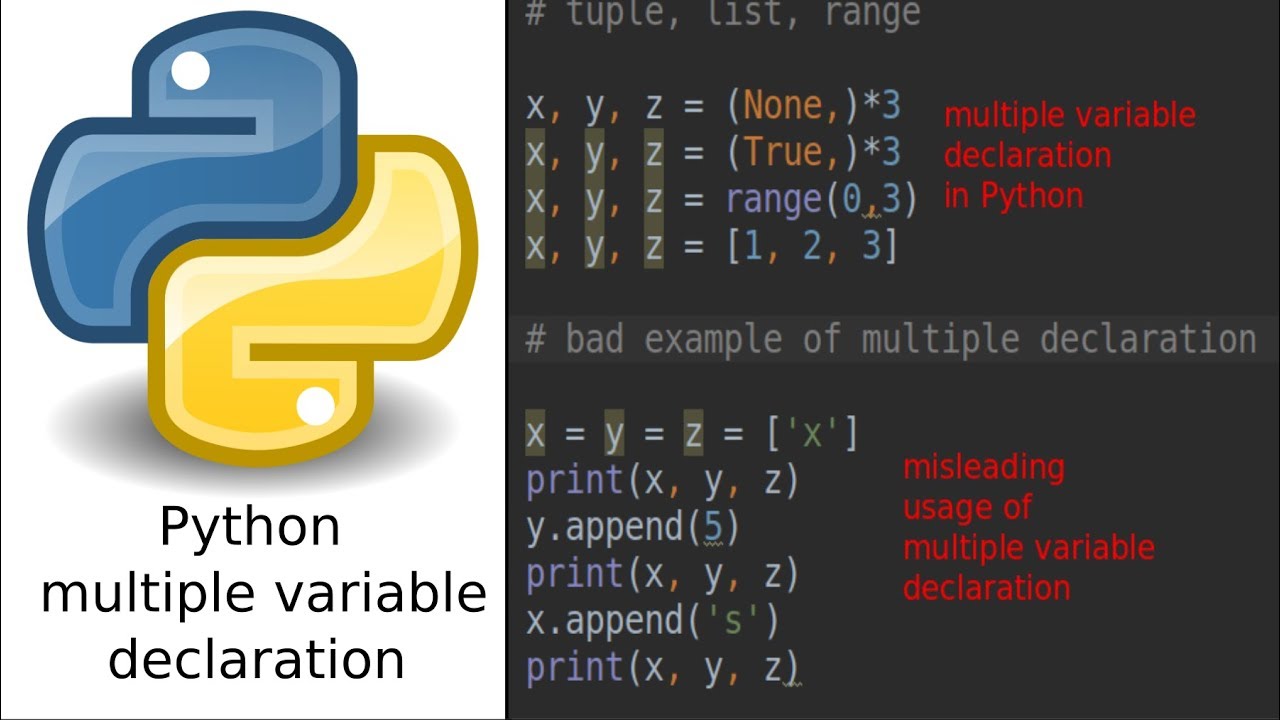
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
colors = ('red', 'green', 'blue')
person = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
How Do You Use Variables in Python?
You can use variables in various ways:
Assignment: Assign a value to a variable.Example: x = 5
Example: print(x)
Example: x = x + 1
Example: greeting = "Hello " + name + "!"
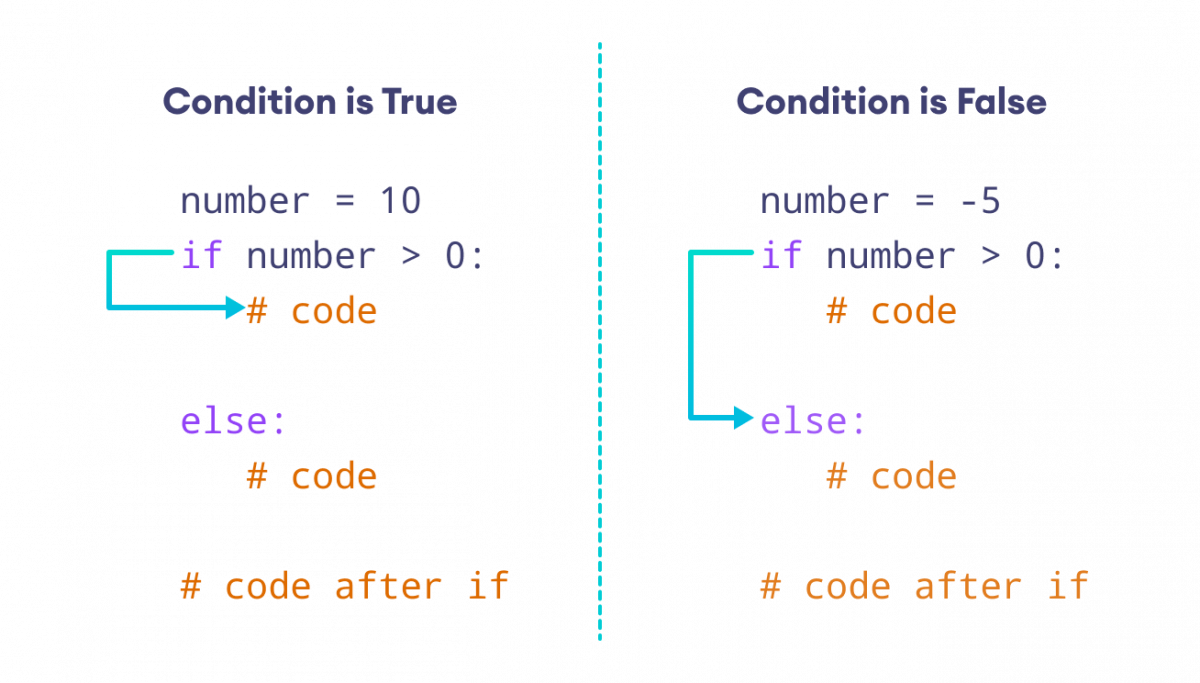
Example: if age >= 18: print("You are an adult.")
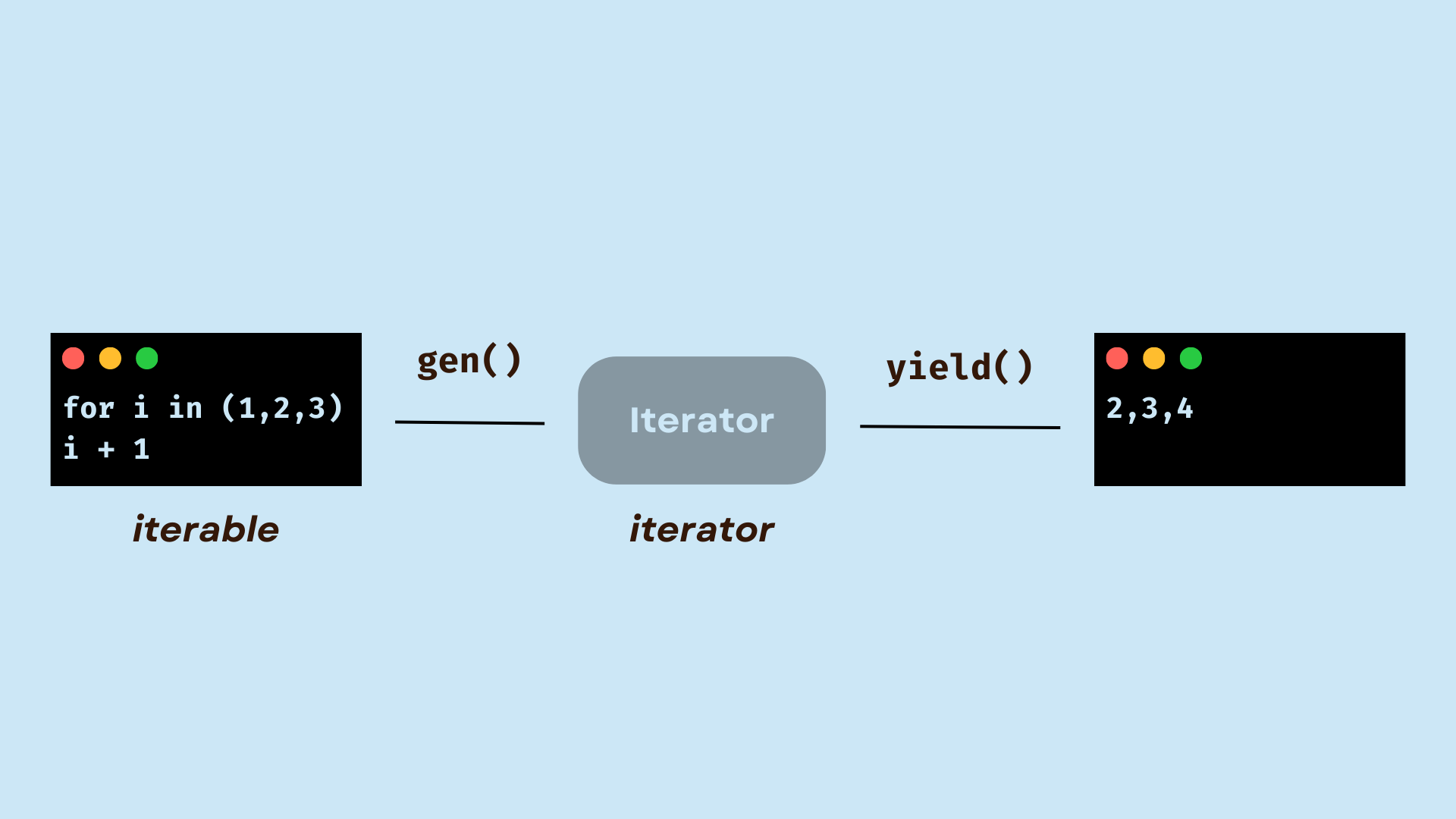
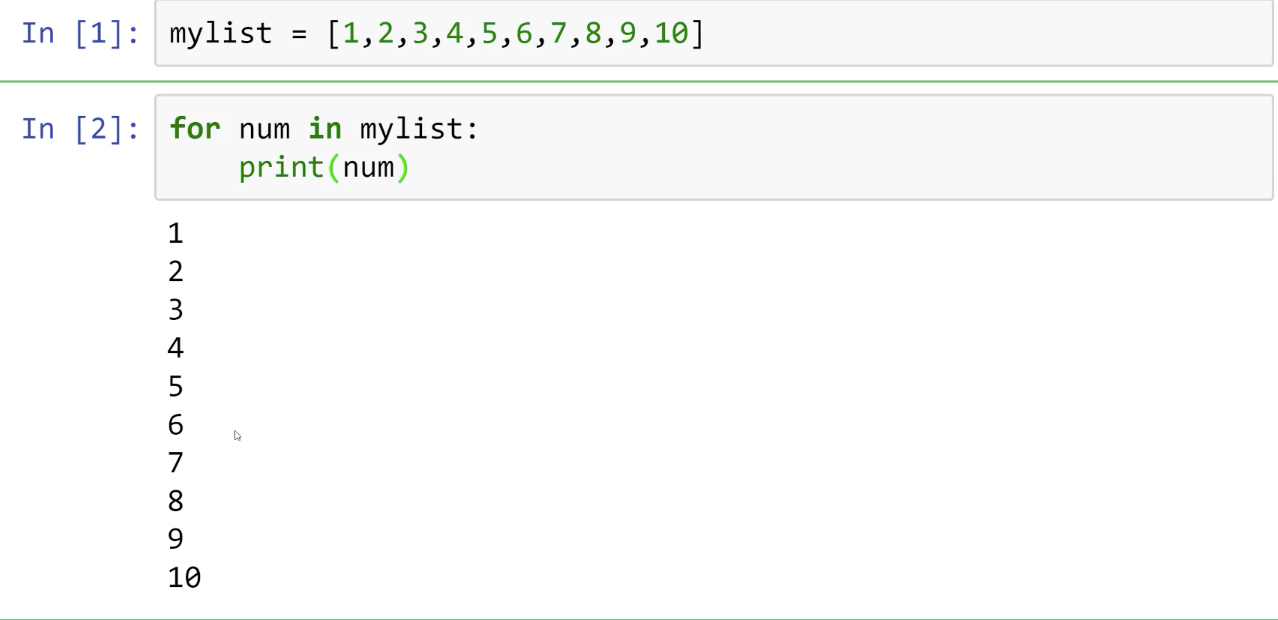
Example: for fruit in fruits: print(fruit)
Example: def greet(name): print("Hello " + name + "!")
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Naming conventions: Use consistent naming conventions (e.g., underscore notation for multi-word variable names). Data type conversion: Be careful when converting between data types, as some conversions can be lossy. Scope: Understand the scope of variables and avoid using global variables unnecessarily. Initialization: Initialize variables before using them to prevent unexpected behavior. Redundancy: Avoid redundant variable declarations or assignments.Conclusion
Variables are an essential part of programming in Python, allowing you to store and manipulate data in your program. Understanding the different types of variables, how to create and use them, and common mistakes to avoid will help you write effective Python code. Practice creating and using variables in your own programs to reinforce your understanding!
What is variable in Python with example
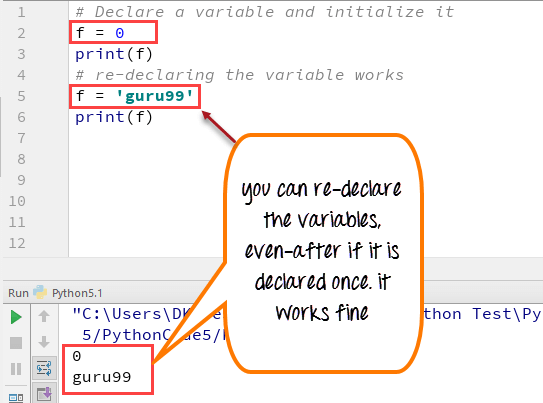
I'm glad to see you're interested in learning about variables in Python!
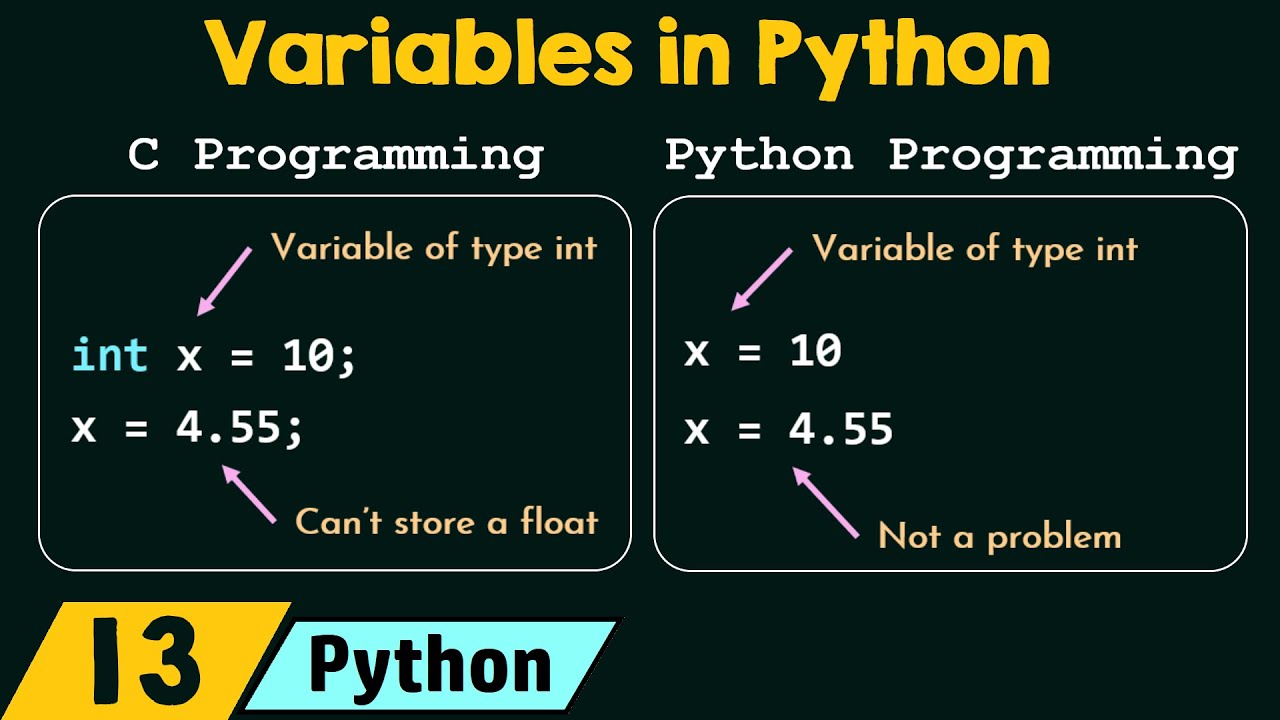
A variable in Python is a name given to a value. It's a way to store and reference values in your code. You can think of it as a labeled box where you can put a value inside, and then use the label (the variable name) to access that value later.
Let's explore some examples:
Declaring VariablesYou declare a variable by assigning a value to it using the assignment operator (=). Here's an example:
x = 5
y = "hello"
z = True
In this example, we're declaring three variables: x, y, and z. We're giving each one a value: an integer (5), a string ("hello"), and a boolean (True).
Once you've declared a variable, you can use it in your code. Here's an example:
print(x) # Output: 5
print(y) # Output: "hello"
print(z) # Output: True
In this example, we're using the variables x, y, and z to print their respective values.
You can modify a variable's value by assigning a new value to it. Here's an example:
x = 10 # Change the value of x
print(x) # Output: 10
y = "goodbye" # Change the value of y
print(y) # Output: "goodbye"
z = False # Change the value of z
print(z) # Output: False
In this example, we're modifying the values of x, y, and z. We're giving them new values: an integer (10), a string ("goodbye"), and a boolean (False).
Python has several built-in data types that can be used to store different types of values. Here are some common ones:
Integers (int): Whole numbers, like 1, 2, or 3. Floats (float): Decimal numbers, like 3.14 or -0.5. Strings (str): Sequences of characters, like "hello" or "goodbye". Booleans (bool): True or False values. Lists (list): Ordered collections of values. Dictionaries (dict): Unordered collections of key-value pairs. Best Practices
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when working with variables:
Use descriptive variable names that indicate what the variable is used for. Avoid naming variables with the same name as built-in Python functions or data types. Use variables consistently throughout your code. Avoid using global variables unless you really need to.Conclusion
In this example, we've covered the basics of variables in Python. We've seen how to declare and use variables, modify their values, and work with different data types. Remember to follow best practices when working with variables to make your code clear, concise, and maintainable.
Would you like me to elaborate on any specific topic or provide more examples?