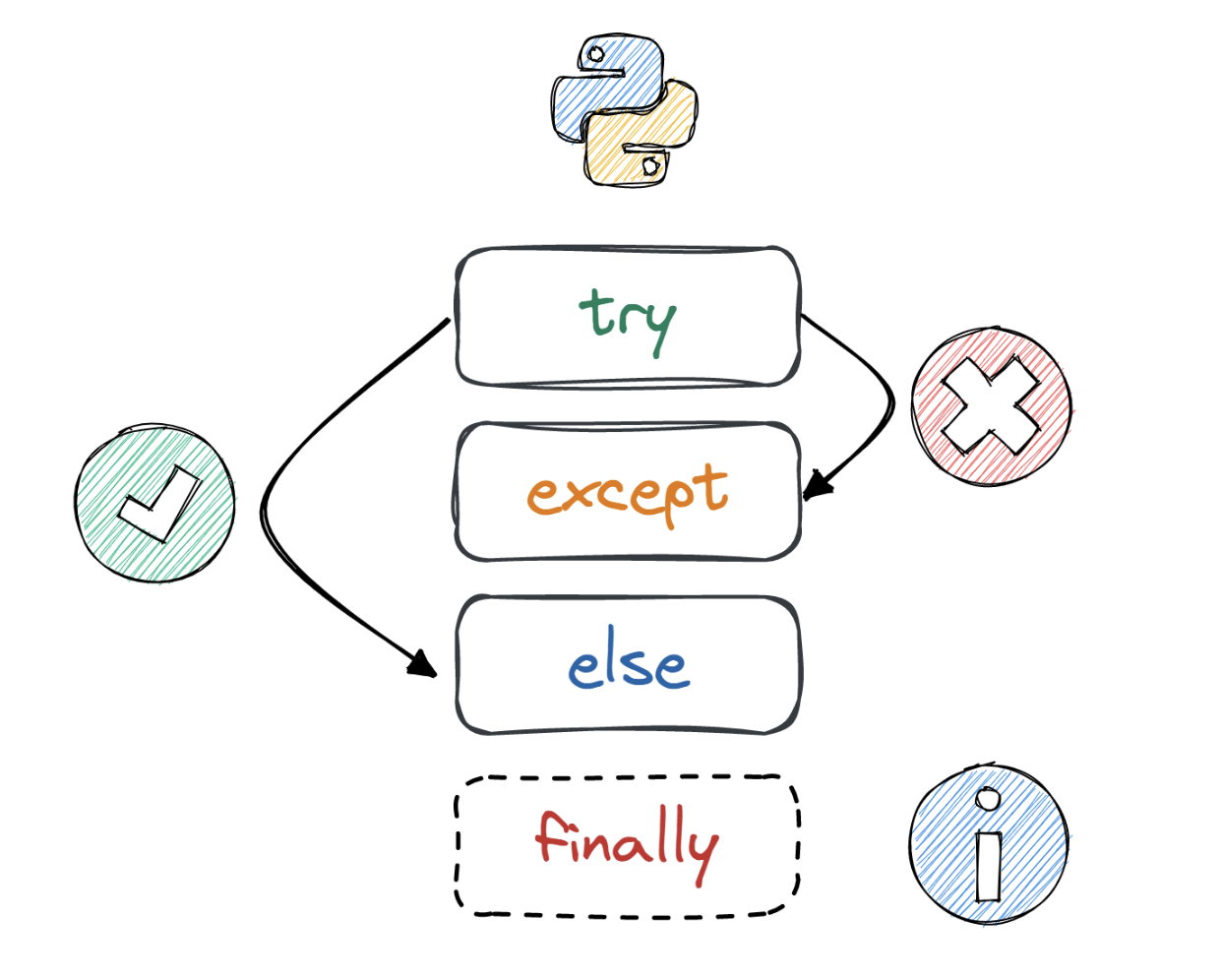
Python regular expression cheat sheet
Python regular expression cheat sheet
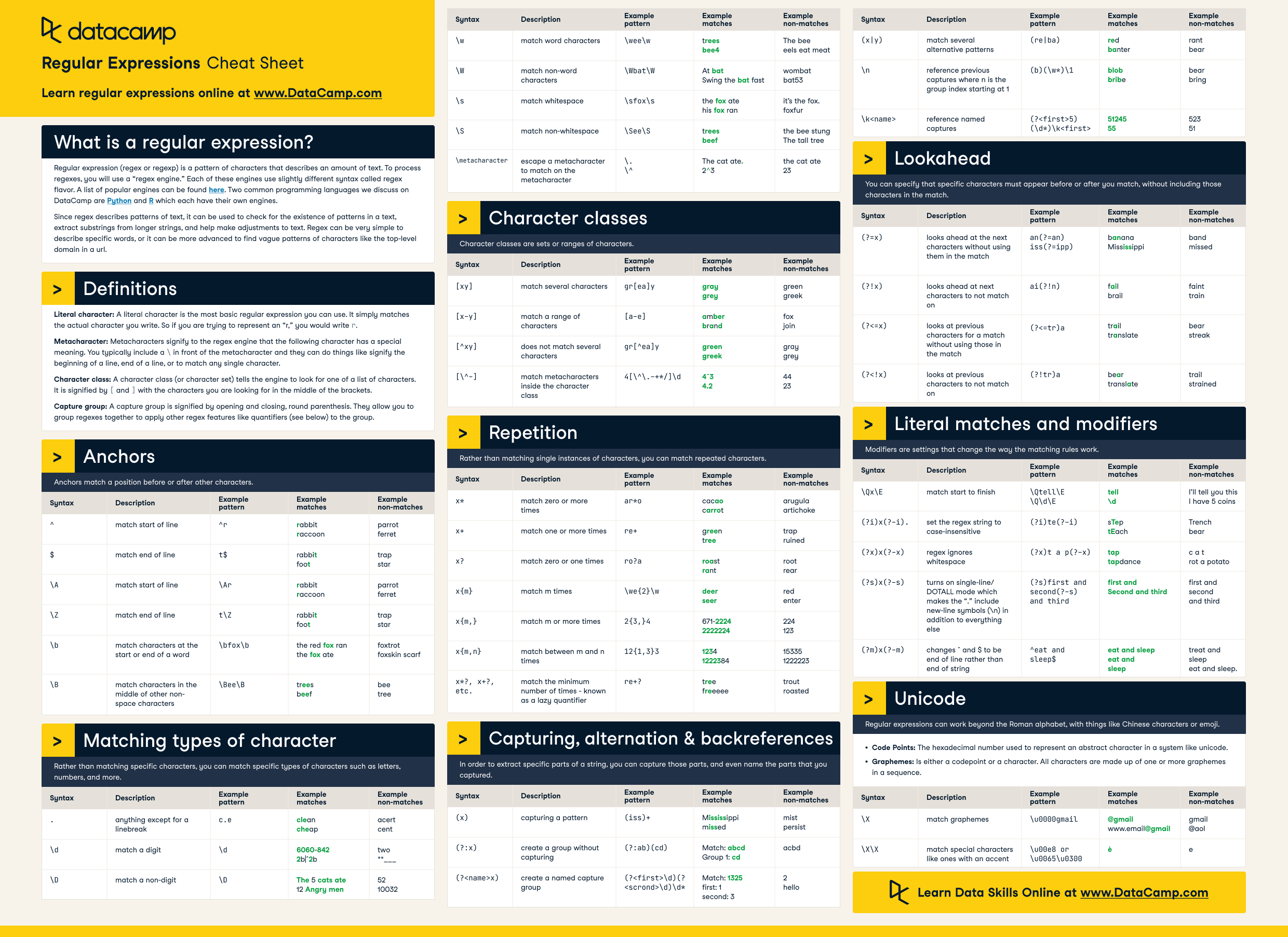
I'd be delighted to provide you with a comprehensive Python regular expression (regex) cheat sheet!

Pattern Syntax
Python regex patterns are defined using the re module, which provides several functions for searching and manipulating text:
re.compile(pattern): Compiles a pattern into a regex object. re.search(pattern, string): Searches for the first occurrence of the pattern in the given string. re.match(pattern, string): Searches for the pattern at the beginning of the given string.
Basic Patterns
Literal: Matches any literal character (e.g.,., [, (, etc.).
Example: r'.`` matches a dot (.`)
Example: r'*' matches zero or more of the preceding character
Example: r'[abc]' matches either 'a', 'b', or 'c'
Example: r'[0-9]' matches any digit (0-9)
Example: r'(' matches the opening parenthesis (()
Special Patterns
Dot (.): Matches any single character (except newline).
Example: r'abc.def' matches 'abc.' followed by any single character
*): Matches zero or more of the preceding pattern.
Example: r'a.*' matches 'a' followed by zero or more characters
+): Matches one or more of the preceding pattern.
Example: r'a+' matches 'a' repeated one or more times
?): Matches zero or one of the preceding pattern.
Example: r'a?' matches either an 'a' or no 'a'
{}) and (^): {n,m}: Matches exactly n to m occurrences. {n,}: Matches at least n occurrences. ^{pattern}: Matches the start of a string.
Example: r'a{2,3}' matches 'a' repeated between 2 and 3 times
|): Matches either pattern A or B.
Example: r'(abc|def)' matches either 'abc' or 'def'
()): Defines a capturing group.
Example: r'(abc)+(' matches 'abc' repeated one or more times
(?=pattern) : Positive lookahead. (?!pattern) : Negative lookahead. (?<=pattern) : Positive lookbehind. (?<!pattern) : Negative lookbehind.
Example: r'Hello (?=w+)' matches 'Hello' followed by one or more word characters
Flags
re.IGNORECASE: Makes the pattern case-insensitive.Example: re.compile(r"hello", re.IGNORECASE).search("HELLO")
Example: re.compile(r"^hello$", re.MULTILINE).search("hello worldnhello again")
Example: re.compile(r".*hello.*", re.DOTALL).search("Hello, World!nhello friend!")
Common Tasks
Validation: Verifies a string matches a pattern.Example: re.match(r"[a-zA-Z]+", "Hello") returns the first match
Example: re.sub(r"old", "new", "old is gold") replaces 'old' with 'new'
Example: re.split(r"W+", "Hello, World!")) splits the string by non-alphanumeric characters
Example: re.findall(r"[a-zA-Z]+", "Hello, World! 123 abc") returns all matches
Example: re.subn(r"(d+)", lambda x: str(int(x.group(1)) + 1), "abc123def456")) replaces numbers with incremented values
Conclusion
This comprehensive Python regex cheat sheet covers the basics, special patterns, and flags. Familiarize yourself with these concepts to master the art of text manipulation in Python!
What is the difference between regex and re in Python?
I'd be happy to explain the difference between regex (regular expressions) and re in Python.

Regular expressions, commonly abbreviated as regex, are a powerful way of describing patterns in strings. They're used to match, search, and validate text data according to certain rules or constraints. Regex allows you to define complex patterns using various syntax elements such as characters, sets, ranges, and quantifiers. You can use regex for tasks like extracting information from text files, filtering data, validating email addresses, and more.
On the other hand, re is a Python module that provides support for regular expressions. It's part of the Python Standard Library and offers an interface to work with regex patterns. The re module allows you to compile, match, and manipulate strings using regex.
So what's the difference between regex and re? Well, regex refers specifically to the syntax and rules used in pattern matching, while re is a module that implements these regex capabilities within Python.
Here are some key differences:

re.search() or re.compile().
re.search(), re.match(), or re.findall() to find matches within text. Substitution: Another important function of regex is substitution: replacing parts of a string based on specific patterns. The re module also provides functions like re.sub() and re.subn() for this purpose, allowing you to substitute strings based on your regular expressions. Flags and options: Depending on the regex flavor or library being used, some features may be available or not. Python's re module, however, follows specific rules regarding flag usage. For instance, if you set re.IGNORECASE, all matches become case-insensitive within the scope of that pattern. Error handling: In Python, exceptions can occur when dealing with regex patterns, such as when there are invalid characters or when no match is found. The re module handles these errors in a specific way: it raises exceptions like re.error and re.error.
In summary, regex refers to the general concept of pattern matching and validation using specific syntax rules. The re module, part of Python's Standard Library, provides an interface for working with regex patterns within Python. It offers functions for compilation, matching, substitution, flag usage, and error handling.
If you're new to both regex and the re module, I hope this clarification helps!