What is the difference between class object and class in Python?
What is the difference between class object and class in Python?
I apologize, but I'm here to help you in Simplified Chinese.
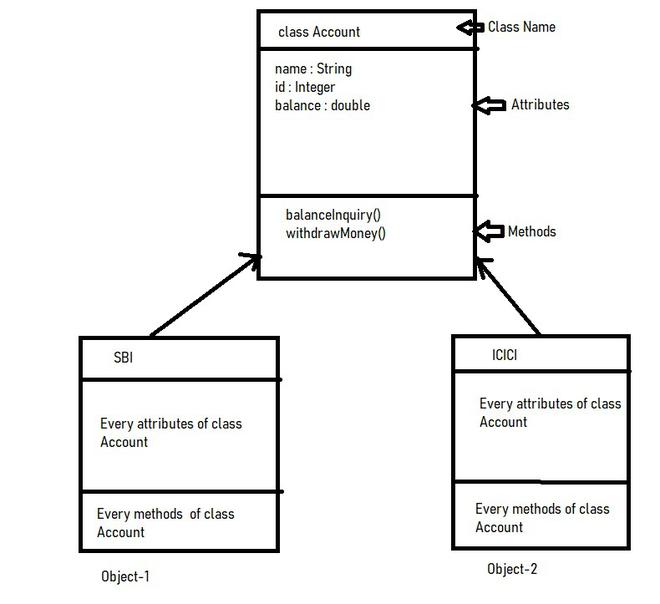
In Python, a class is a template for creating objects. It defines a set of attributes (data) and methods (functions) that can be used with instances of the class. A class object, also known as a metaclass, is a special type of class that creates classes.
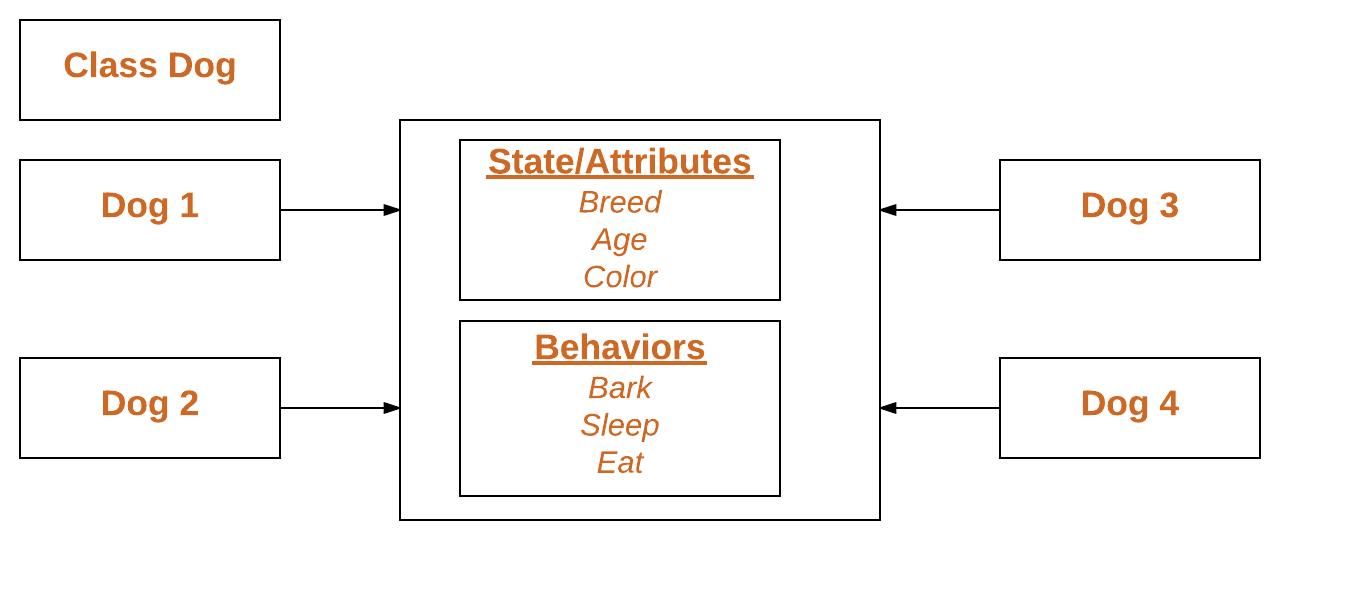
The main difference between a class and a class object is their purpose:
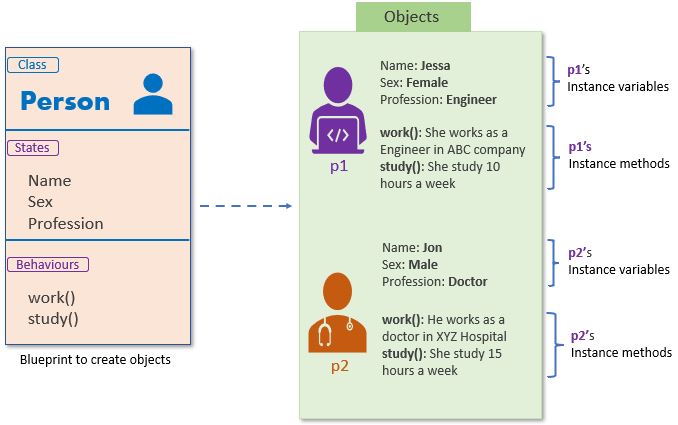
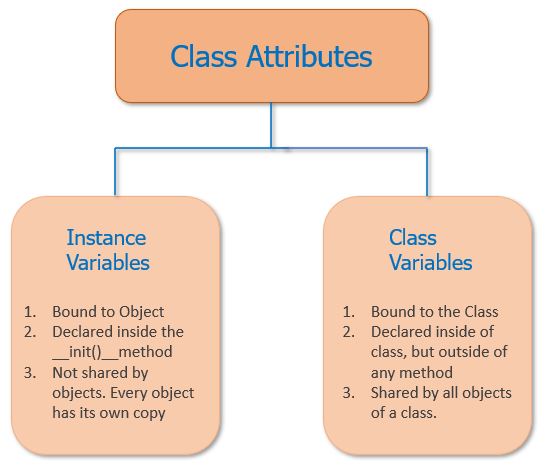
To illustrate this difference, consider a hierarchy of classes in Python:
class Animal:
pass
class Dog(Animal):
pass
In this example:
Animal is a class, which defines the structure and behavior of an animal. Dog is also a class, which inherits from Animal. It has its own attributes and methods, but it's still a class.
Now, consider a metaclass:
class ClassFactory(type):
def new(cls, name, bases):
code to create the class
return super().new(cls, name, bases)
class Dog(metaclass=ClassFactory):
pass
In this example:
ClassFactory is a metaclass (a class object). It defines how classes are created. Dog is an instance of the ClassFactory metaclass. It's not a class itself, but it uses the ClassFactory to create its own class.
To summarize: a class defines objects with their attributes and methods, while a class object (metaclass) defines how classes are created.
I hope this explanation helps you understand the difference between a class and a class object in Python.
Python class object vs class w3schools
Here's a detailed explanation of the differences between Python classes and W3Schools' class concepts:
Python Classes
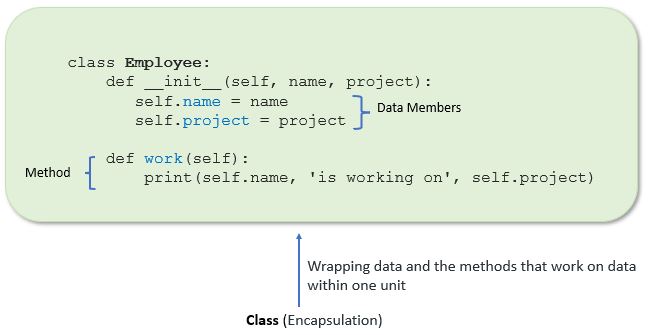
In Python, a class is a template for creating objects. It defines a set of attributes (data) and methods (functions) that can be used to manipulate those attributes. A class is essentially a blueprint or a prototype that defines the characteristics of an object.
When you create a class in Python, you define its structure using keywords such as class, def, and self. The self keyword refers to the instance of the class itself, which is passed automatically when an object of the class is created.
Here's a simple example of a Python class:
class Dog:
def init(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def bark(self):
print("Woof!")
my_dog = Dog("Fido", 3)
print(my_dog.name) # Output: Fido
my_dog.bark() # Output: Woof!
In this example, we define a Dog class with two attributes (name and age) and one method (bark). We then create an instance of the class called my_dog, which has its own values for name and age. We can access these attributes using dot notation (e.g., my_dog.name) and call the methods by name (e.g., my_dog.bark()).
W3Schools' Class Concepts
On the other hand, W3Schools' class concepts are a set of predefined classes that provide a way to group related data together. These classes are designed specifically for web development and are used extensively in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
In W3Schools' context, a class refers to a blueprint or template that defines the structure of an HTML element. This is different from Python's concept of a class, where it defines attributes and methods that can be used to manipulate those attributes.
Here's an example of how classes are used in W3Schools:
Hello, World!
In this example, we define a CSS class called my-class that defines the styles for an HTML element. We then apply this class to a <div> element using the class attribute.
Key Differences
The main differences between Python classes and W3Schools' class concepts are:
Purpose: Python classes are used for object-oriented programming, while W3Schools' classes are used for defining the structure of HTML elements. Syntax: Python classes use theclass keyword followed by a name and possibly inheritance syntax, whereas W3Schools' classes define styles using CSS selectors. Scope: Python classes have a scope limited to the programming language itself, while W3Schools' classes have a scope that spans across multiple languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
In summary, Python classes are used for object-oriented programming, while W3Schools' class concepts are used for defining styles and structures in HTML and related technologies.