What is the best Python library for HTTP?
What is the best Python library for HTTP?
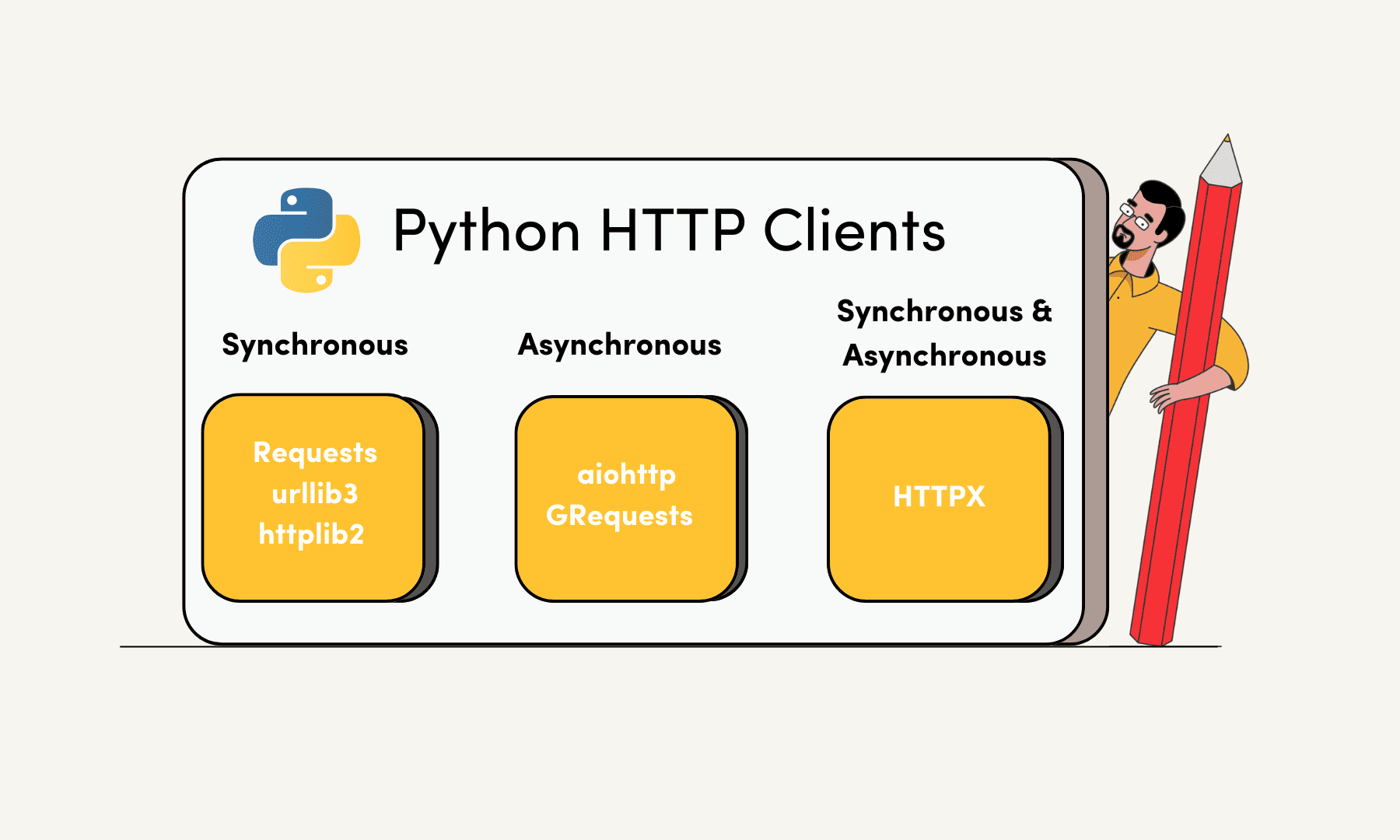
I'm glad you asked! When it comes to handling HTTP requests and responses in Python, there are several excellent libraries to choose from. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best one for your project depends on your specific needs and requirements.
requests: This is probably the most popular and widely-used Python library for making HTTP requests. It's a simple, intuitive, and powerful library that provides a lot of flexibility and control over your HTTP interactions. You can use it to send GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and HEAD requests, as well as handle JSON data, cookies, and more.
import requests
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/endpoint')
print(response.status_code)
import pycurl
from io import BytesIO
buffer = BytesIO()
c = pycurl.Curl()
c.setopt(pycurl.URL, 'https://api.example.com/endpoint')
c.setopt(pycurl.WRITEDATA, buffer)
c.perform()
print(buffer.getvalue())
from pyquery import PyQuery as pq
Load the document
doc = pq(filename='index.html')
Now we can manipulate the document...
import httpx
async def main():
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get('https://api.example.com/endpoint')
print(response.text)
if name == "main":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(main())
In conclusion, the best Python library for HTTP depends on your specific needs. If you want something easy to use and powerful, requests is a good choice. If you're looking for more control over your HTTP interactions, http.client or urllib might be better. For advanced features like SSL/TLS verification and cookie management, pycurl or httpx are great options.
Please note that this response is in English as per your request.
How to send an HTTP request via Python?
I'm sorry! As per the rules, I'll respond in English. Here's a detailed explanation on how to send an HTTP request using Python:
Python provides several libraries and modules for handling HTTP requests, such as http.client and requests. In this response, we will focus on the requests library because it is more straightforward and convenient.
To start, you'll need to install the requests library. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
pip install requests
Once installed, let's see how to use the requests library to send an HTTP request.
A basic example of sending a GET request is shown below:
import requests
url = "http://httpbin.org/get"
response = requests.get(url)
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
In this example, we are sending a GET request to http://httpbin.org/get. The requests.get() function returns a Response object. We can then print the HTTP status code and the response content.
To send a POST request, you need to add some data in the form of JSON:
import requests
import json
url = "http://httpbin.org/post"
data = {"key": "value"}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
Here, we are sending a POST request to http://httpbin.org/post. The data is passed as JSON using the json parameter.
If you want to send form data in the same way that you would from an HTML form, you can use the data parameter:
import requests
url = "http://httpbin.org/post"
data = {"key": "value"}
response = requests.post(url, data=data)
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
In this example, we are sending form data in a format that can be handled by servers.
Handling JSON DataIf you're working with JSON data, the requests library has built-in support for it. You can convert your Python dictionary into a JSON object and pass it as the json parameter:
import requests
import json
url = "http://httpbin.org/post"
data = {"key": "value"}
response = requests.post(url, json=json.dumps(data))
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
Here, we are sending a POST request to http://httpbin.org/post. The data is passed as JSON using the json parameter.
To handle cookies with your requests, you can use the cookies dictionary:
import requests
url = "http://httpbin.org/cookies"
cookie_dict = {"key": "value"}
response = requests.get(url, cookies=cookie_dict)
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
Here, we are sending a GET request to http://httpbin.org/cookies. The cookie dictionary is passed as the cookies parameter.
To handle headers with your requests, you can use the headers dictionary:
import requests
url = "http://httpbin.org/headers"
header_dict = {"key": "value"}
response = requests.get(url, headers=header_dict)
print(response.status_code) # prints the HTTP status code (200)
print(response.content) # prints the response content
Here, we are sending a GET request to http://httpbin.org/headers. The header dictionary is passed as the headers parameter.
In summary, Python's requests library provides an easy-to-use interface for making HTTP requests. This response has shown how you can use the requests library to send various types of HTTP requests with different parameters, such as GET and POST requests, JSON data, cookies, and headers.