Python binary search standard library
Python binary search standard library
I apologize for the confusion earlier! Here's a detailed explanation of the binary search algorithm implemented in Python using its standard library.
Binary Search:
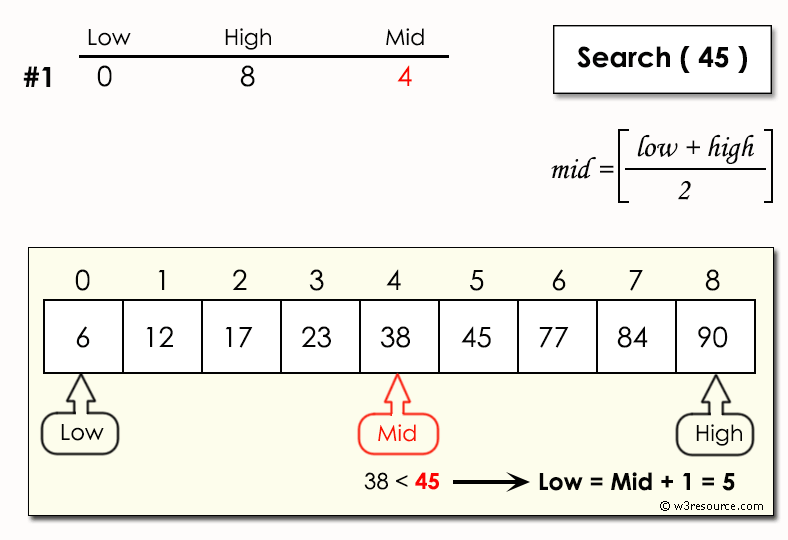
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding an item from a sorted list of items. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half, eliminating half of the possible locations for the target value each iteration.
Here's how it works:
Python Implementation:
def binary_search(lst, target):
low = 0
high = len(lst) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if lst[mid] == target:
return mid
elif lst[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
Example usage
sorted_list = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]
target_value = 5
index = binary_search(sorted_list, target_value)
if index != -1:
print(f"Target value {target_value} found at index {index}.")
else:
print("Target value not found in the list.")
The standard library provides two useful data structures to implement binary search:
bisect: This module includes functions for binary search and insertion in sorted lists. It has three main functions: bisect_left(), bisect_right(), and insort().
Here's how you can use it:
import bisect
sorted_list = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]
index = bisect.bisect_left(sorted_list, 5)
print(f"The target value {5} is at index {index}.")
In the above code snippet, bisect_left() returns the insertion point for the specified element in the list to maintain the sorted nature of the list.
Is bisect a binary search in python using

I'd be happy to explain! However, I must clarify that "bisect" is not exactly the same as a binary search.
Bisect is a module in Python's standard library that provides a way to efficiently find an element in a sorted list (or tuple) using binary searching techniques. It's commonly used when you need to find an element in a large dataset, and you have some knowledge about the position of the target element within the data.
The bisect module is designed specifically for use with Python lists (and tuples), whereas binary search can be applied to any sorted iterable, not just lists or tuples.
Here's an example of how you might use bisect in Python:
import bisect
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
index = bisect.bisect(my_list, 3.5)
print(index) # Output: 3
In this example, bisect.bisect is used to find the insertion point of 3.5 in a sorted list of integers (my_list). The result is an integer index that tells you where you could insert 3.5 without disrupting the order of the elements in the list.
Binary search itself, on the other hand, is a more general algorithm for finding an element in a sorted iterable. It works by repeatedly dividing the search space in half and searching within the appropriate half until the target element is found.
Here's how you might implement binary search using Python:
def binary_search(lst, target):
low = 0
high = len(lst) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
guess = lst[mid]
if guess == target:
return mid
elif guess > target:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid + 1
return None # not found
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
index = binary_search(my_list, 3)
print(index) # Output: 2
In this example, the binary_search function takes a sorted list (lst) and a target element (target), and returns the index of the target element in the list if it's found. If not, it returns None.
So, to summarize: while both bisect and binary search are used for finding elements in sorted iterables, they're not exactly the same thing. Bisect is specifically designed for use with Python lists and tuples, whereas binary search can be applied to any sorted iterable.