Python how to check if file exists in directory
Python how to check if file exists in directory
To check if a file exists in a directory using Python, you can use various methods. Here are a few ways to do it:
Method 1: Using the os module
You can use the os.path.exists() function to check if a file exists at a specific path. This function returns True if the path refers to an existing path or file, and False otherwise.
Here's an example:
import os
file_path = '/path/to/file.txt'
if os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f"The file {file_path} exists.")
else:
print(f"The file {file_path} does not exist.")
Method 2: Using the os module with stat()
You can use the os.stat() function to check if a file exists. This function returns a dictionary-like object containing information about the file, including whether it exists.
Here's an example:
import os
file_path = '/path/to/file.txt'
try:
stats = os.stat(file_path)
print(f"The file {file_path} exists.")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"The file {file_path} does not exist.")
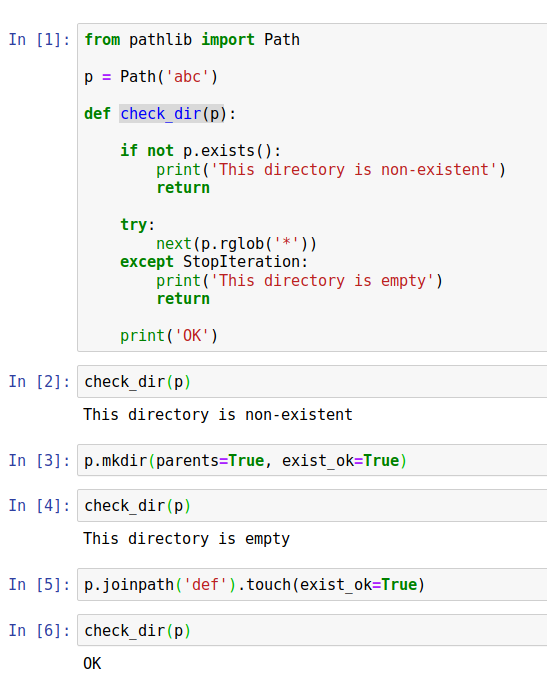
Method 3: Using the pathlib module
You can use the Path class from the pathlib module to check if a file exists. This module provides a more convenient way of working with paths than the os module.
Here's an example:
import pathlib
file_path = '/path/to/file.txt'
if pathlib.Path(file_path).exists():
print(f"The file {file_path} exists.")
else:
print(f"The file {file_path} does not exist.")
Method 4: Using a try-except block
You can use a try-except block to catch the FileNotFoundError exception if the file does not exist.
Here's an example:
import os
file_path = '/path/to/file.txt'
try:
open(file_path, 'r')
print(f"The file {file_path} exists.")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"The file {file_path} does not exist.")
All of these methods will allow you to check if a file exists in a directory using Python. You can choose the one that best fits your needs and coding style.
Best Practices
When working with files, it's important to follow best practices to ensure that your code is robust and reliable. Here are some tips:
Always use absolute paths instead of relative paths to avoid ambiguity. Use try-except blocks to catch exceptions that may occur when working with files. Check the existence of a file before trying to read or write it to avoid errors. Use context managers (e.g.,with statements) to ensure that files are properly closed after use.
By following these best practices, you can write Python code that is efficient and reliable when working with files.
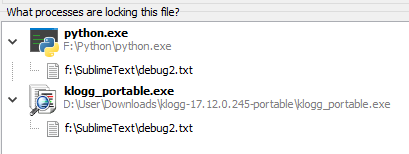
How to check if a file is locked in Python?

I'm glad you asked! Checking if a file is locked in Python can be achieved using various approaches, depending on the type of lock you're looking for and the platform you're working on. Here are some methods to help you detect file locks:
OS-Level Locks: On Unix-based systems (including macOS), you can use theos module's path.getmtime() function to check if a file has an open handle:
import os
file_path = "/path/to/locked/file.txt"
try:
os.lstat(file_path)
except OSError as e:
print(f"{e.strerror} - The file is likely locked!")
This method works by attempting to retrieve the file's last access time using os.lstat(). If the file is locked, you'll get an OSError with a specific error message.
win32file module from the pywin32 library:
import win32file
file_path = "C:pathtolockedfile.txt"
try:
win32file.GetFileStatus(file_path)
except win32file.error as e:
print(f"{e.strmessage} - The file is likely locked!")
This method uses the win32file.GetFileStatus() function to check if a file has an open handle. If it does, you'll get a win32file.error exception.
stat module's stat(), fstat(), or lstat() functions to check if a file is locked:
import stat
file_path = "/path/to/locked/file.txt"
try:
stat.lstat(file_path)
except OSError as e:
print(f"{e.strerror} - The file is likely locked!")
This method works by attempting to retrieve the file's inode information using stat.lstat() or one of the other stat functions. If the file is locked, you'll get an OSError with a specific error message.
fcntl: On Unix-based systems (including macOS), you can use the fcntl module to check if a file has a lock:
import fcntl
file_path = "/path/to/locked/file.txt"
try:
fcntl.flock(file(file_path, "r+"), fcntl.LOCK_EX)
except IOError as e:
print(f"{e.strerror} - The file is likely locked!")
This method uses the fcntl module's flock() function to attempt to lock the file. If the file is already locked, you'll get an IOError exception.
filelock or pyinotify to detect and manage file locks in Python.
Keep in mind that these methods might not work on all platforms or in all situations. It's essential to handle potential exceptions and errors when checking for file locks, as this information is not always available or reliable.
I hope this helps you detect those pesky file locks!