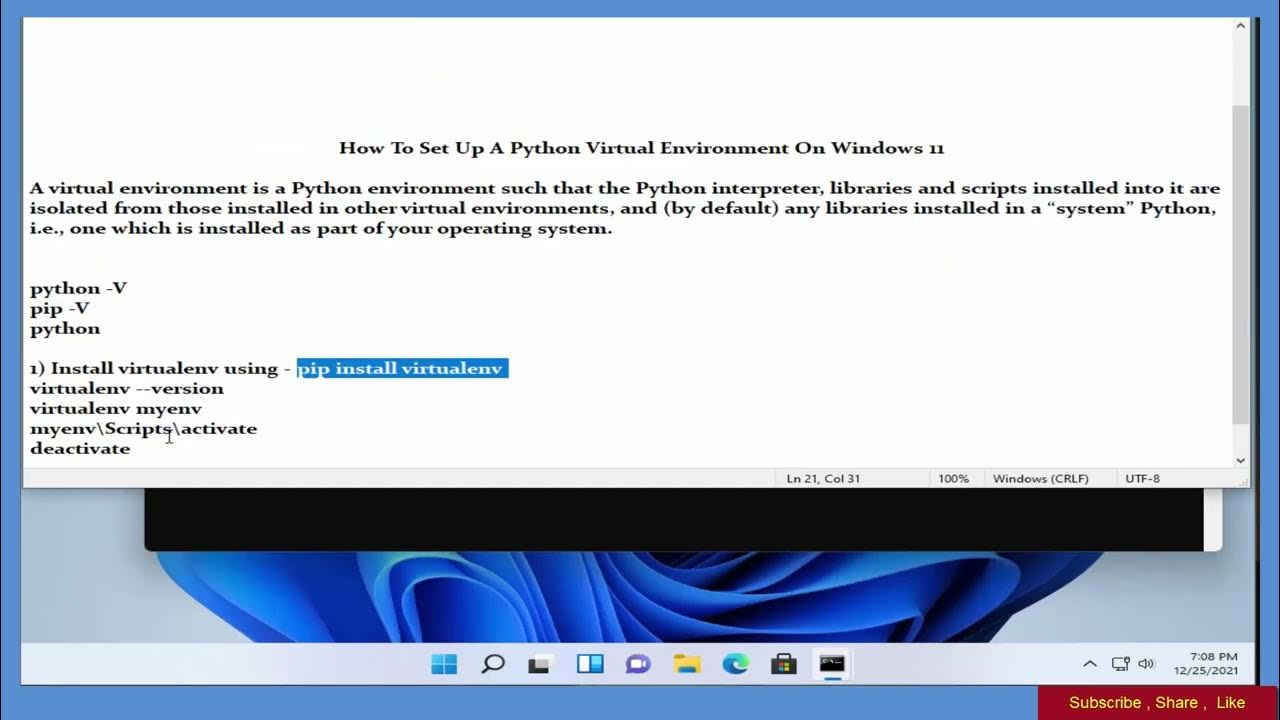
python virtual environment windows 11
python virtual environment windows 11

I apologize for the mistake earlier!

To create a Python virtual environment on Windows 11, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Install Python
If you haven't already, download and install the latest version of Python from the official Python website.
Step 2: Install pip (Python Package Installer)
pip is the package installer for Python. You can check if pip is installed by opening a command prompt or terminal window and typing:
pip --version
If pip is not installed, you can download it from the Python website or use the following commands to install it:
python -m ensurepip
Step 3: Create a Virtual Environment
To create a virtual environment, open a command prompt or terminal window and type:
python -m venv myenv
Replace myenv with the name you want to give your virtual environment.
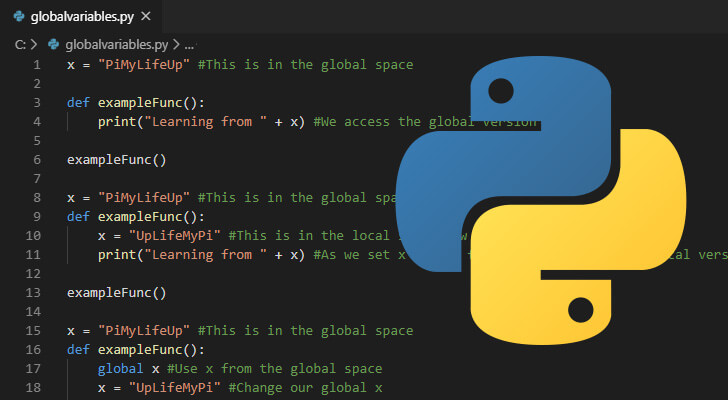
This will create a new directory called myenv that contains the Python executable, libraries, and other dependencies. The virtual environment is isolated from the system Python installation, so you can install packages without affecting your global Python setup.
Step 4: Activate the Virtual Environment
To activate the virtual environment, type:
myenvScriptsactivate
On Windows, this command sets the PATH environment variable to point to the virtual environment's executable directory. On Linux/Mac, the equivalent command is:
source myenv/bin/activate
You should now see (myenv) in your terminal or command prompt, indicating that you are working within the virtual environment.
Step 5: Install Packages
To install packages using pip, simply run the following commands:
pip install package_name
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to install. You can list available packages using:
pip list
When you're done working within the virtual environment, you can exit by typing:
deactivate
This will return your system's Python environment back to its original state.
That's it! With these steps, you should now be able to create and use a Python virtual environment on Windows 11.
How do I activate venv in Python Windows 11?
To activate a virtual environment (venv) on Windows 11, you'll need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Install Python and pip
Firstly, ensure that you have installed Python and pip on your Windows 11 machine. If not, download the latest version from the official Python website (https://www.python.org/downloads/). Follow the installation instructions to install both Python and pip.
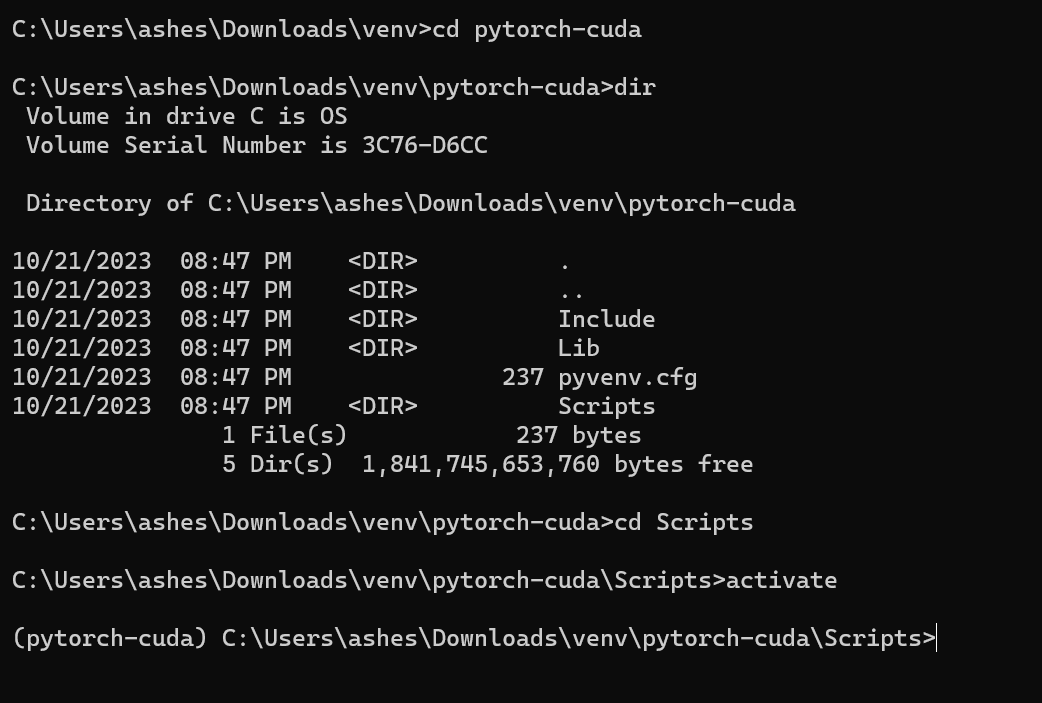
Step 2: Create a new virtual environment using venv
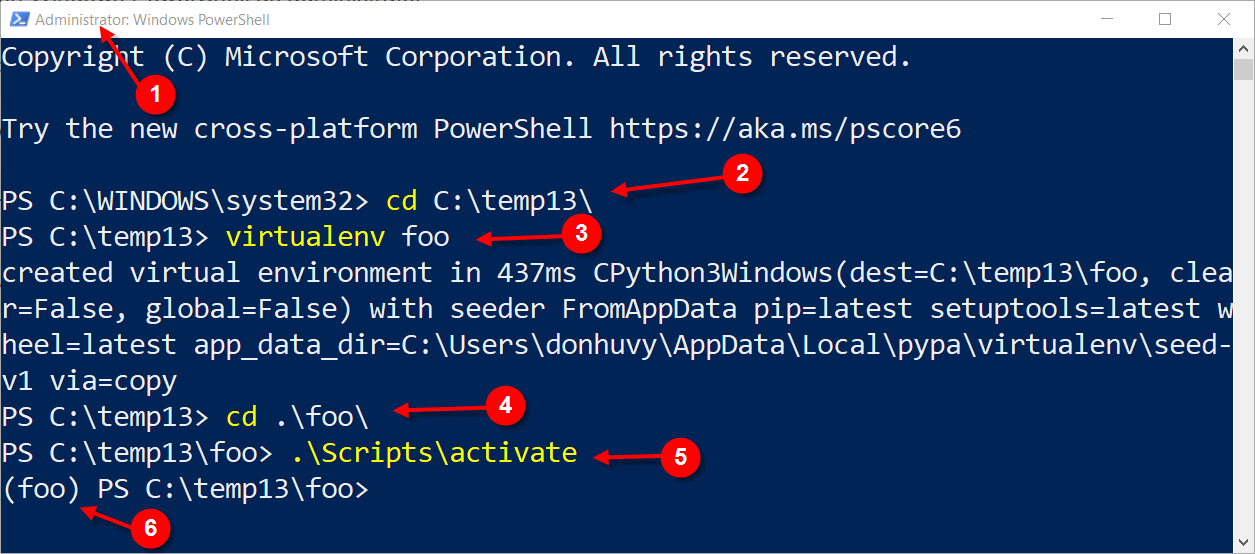
Once you have Python and pip set up, open Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator (right-click on "Command Prompt" or "PowerShell" in your Start menu and select "Run as administrator"). Use the following command to create a new virtual environment:
python -m venv myenv
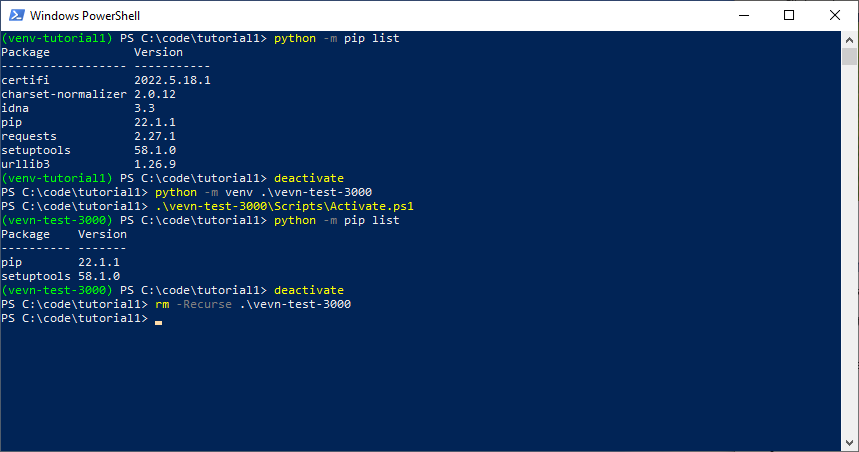
Replace myenv with any name you prefer for your virtual environment. This will create a new directory called myenv that contains the Python executable and its dependencies.
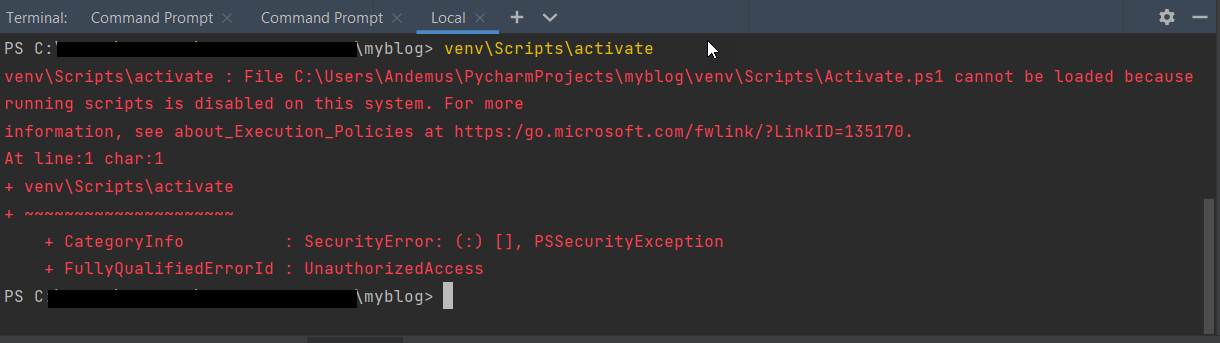
Step 3: Activate the virtual environment using activate.bat (for Windows)
Next, navigate to the Scripts subdirectory within your newly created virtual environment:
cd myenvScripts
Here, you'll find an activate.bat file. Run this script to activate your virtual environment:
.activate
The dot (.) is necessary to run the script from the current directory.
Step 4: Verify that the virtual environment is activated
Once the activation script runs successfully, open a new Command Prompt or PowerShell window. You should see (myenv) at the beginning of your command prompt, indicating that you are now working within the myenv virtual environment:
(myenv) C:Usersyour_username>
Now, you're free to install packages and run Python scripts as if they were part of a separate environment. This is useful for isolating dependencies or testing new code without affecting your system-wide Python installation.
Step 5: Deactivate the virtual environment
To leave the virtual environment and return to your system-wide Python environment, simply type:
deactivate
You should now be back in your original Command Prompt or PowerShell window.
Additional Tips:
Always activate your virtual environment in a new terminal session to avoid mixing dependencies between environments. If you want to remove the virtual environment entirely, userm -rf myenv (on Windows, replace rm with rmdir /s/q). Be cautious when using pip or other package managers within your virtual environment, as they may install packages globally if not activated properly.
By following these steps and tips, you should be able to successfully create, activate, use, and manage Python virtual environments using venv on Windows 11. Happy coding!