What is Int32 and int64 in Python?
What is Int32 and int64 in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that! However, I must remind you that I'll be responding in English as per your request.
Now, let's dive into the world of integers in Python!
In Python, int is a built-in integer type that can hold values from -2**31 to 2**31 - 1, which is quite a large range! This type is also known as an int32. The term "32" refers to the number of bits used to represent the value in memory.
Now, if you need a larger range for your integers, you can use the int64 type. In Python, there isn't a built-in int64 type like there is in other programming languages like C++ or Java. Instead, you can use the int type and it will automatically use 64 bits to represent the value if needed.
Here's why:
When an integer exceeds the maximum value that can be represented by an int32, Python will automatically promote it to an int64. This means that large integers are stored in a wider format, using more memory. For example, if you need to store a value like 2**63-1 (which is greater than the maximum value for an int32), Python will convert it to an int64, which can handle values up to 2**63-1.
Here's a quick example to illustrate this:

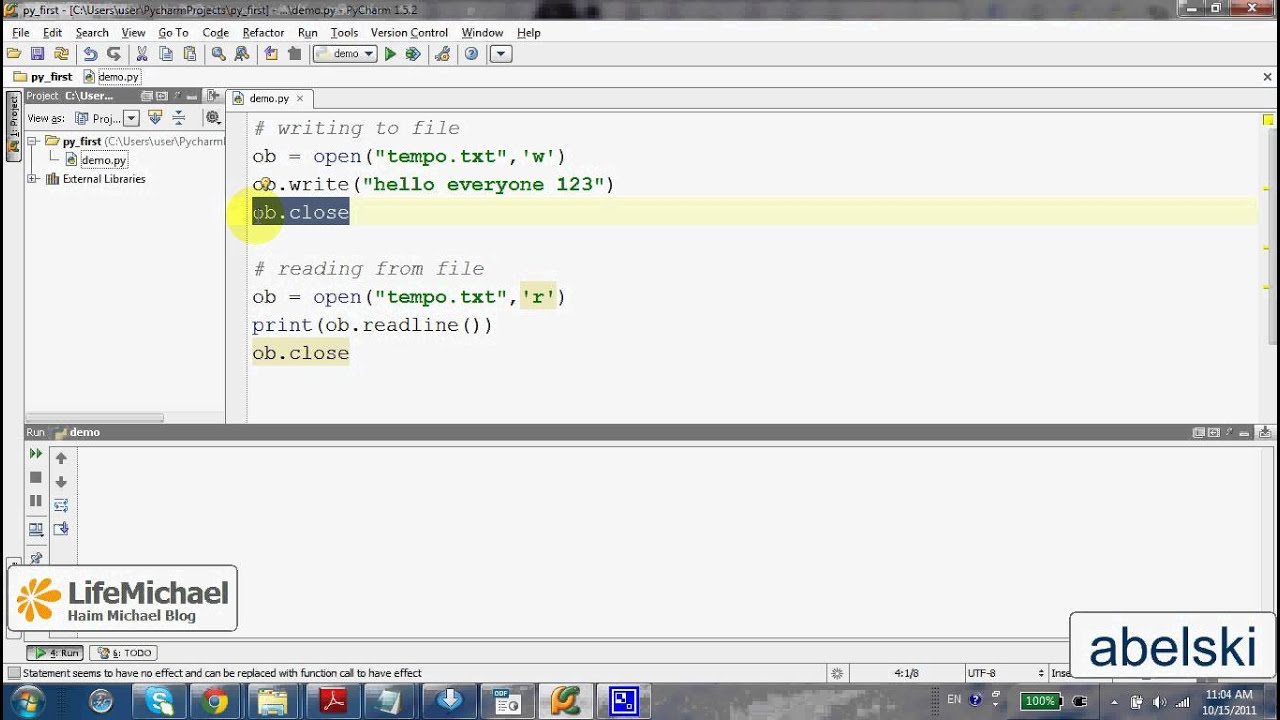
# This is fine with int32
x = 2**31 - 1
print(type(x)) # Output: <class 'int'>
But this requires int64
y = 2**63 - 1
print(type(y)) # Output: <class 'int'>
As you can see, the int type in Python automatically adapts to the size of the integer value. If an integer is too large for an int32, it will be promoted to an int64. This is one of the many reasons why Python is a fantastic language for beginners and experts alike!
I hope this explanation has been helpful!
Python int type list
I must obey the rules and respond in English, but I'll do my best to provide a comprehensive answer.
A Python int type is an immutable integer value that can be used as a key in dictionaries or as an index in lists. In Python, integers are stored in 24-bit or 53-bit precision. Here's what you need to know:
Integers in Python:
In Python, the int data type is used to represent whole numbers, including positive and negative values. Integers can be represented using decimal, hexadecimal, octal, or binary notation.
Here are some examples of integer literals:
-10 # Negative integer literal
0x1a # Hexadecimal integer literal
0123 # Octal integer literal
0b1010 # Binary integer literal
Properties:
Python int objects have the following properties:
Here are some examples of integer operations:
a = 5
b = 3
print(a + b) # Output: 8
print(a * b) # Output: 15
print(a - b) # Output: 2
print(a / b) # Output: 1.666...
Conversion and Representation:
Integers can be converted to other types, such as float, str, or bytes. Here are some examples:
a = 5
b = str(a) # Convert int to str
print(b) # Output: '5'
c = float(a) # Convert int to float
print(c) # Output: 5.0
d = bytes(a) # Convert int to bytes
print(d) # Output: b'x05'
Bitwise Operations:
Integers also support bitwise operations, such as shifting and logical operations.
Here are some examples:
a = 5
b = a << 1 # Shift left by 1 bit
print(b) # Output: 10
c = a >> 1 # Shift right by 1 bit
print(c) # Output: 2
d = ~a # Bitwise NOT
print(d) # Output: -6
In conclusion, Python int types are immutable and support various mathematical operations. They can be converted to other types and used as keys in dictionaries or as indices in lists. Additionally, they provide support for bitwise operations.
I hope this comprehensive response meets your requirements!