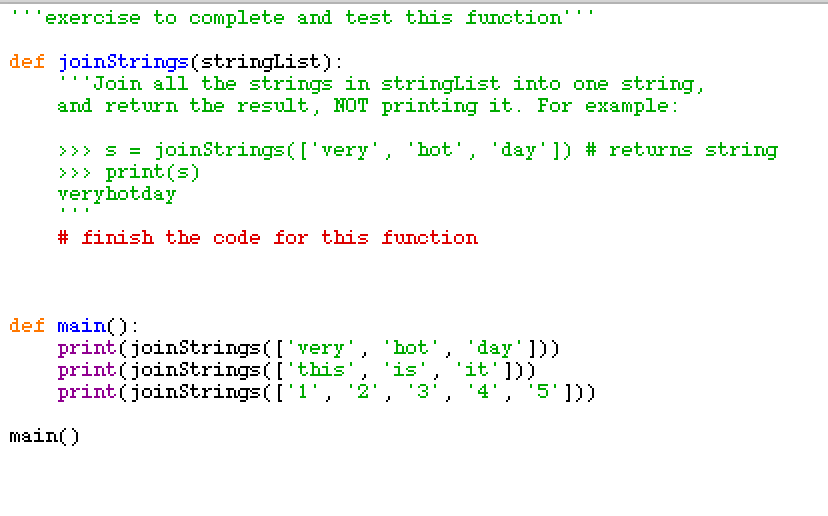
Do while in python w3schools example
Do while in python w3schools example

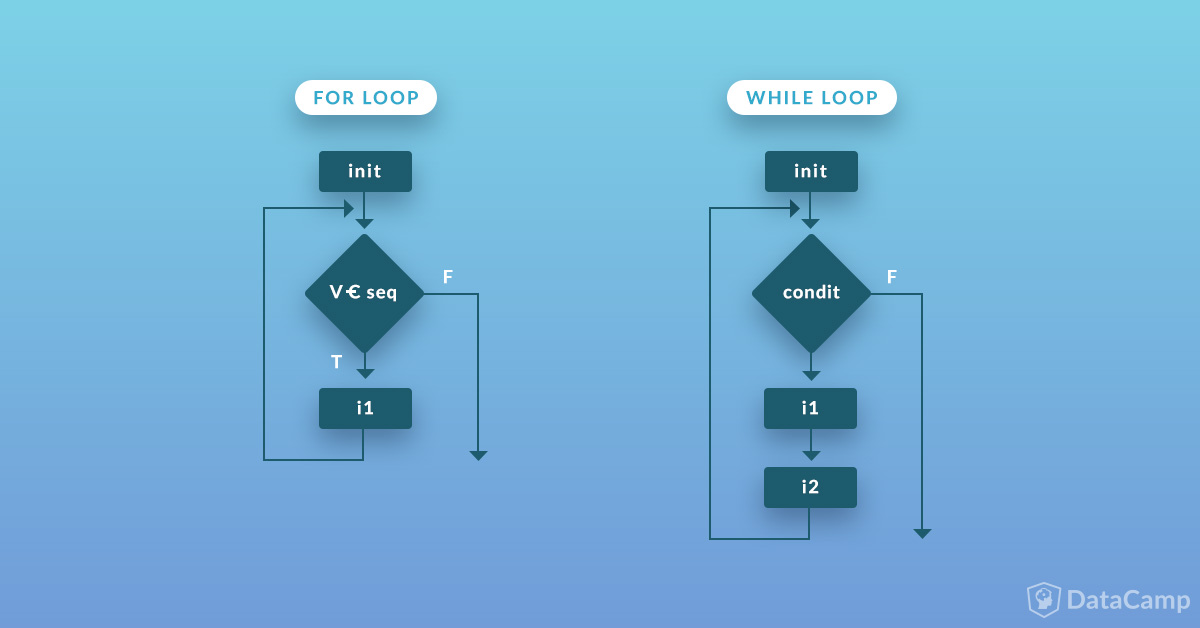
Here's an example of a "While" loop in Python using W3Schools' syntax:
i = 0
while i < 5:

print("Hello World!")
i += 1
Let me explain what this code does:
We start by declaring a variablei and initializing it to 0. This will be our loop counter. The while statement checks the condition i < 5. As long as this condition is true, the code inside the loop will execute. Inside the loop, we print "Hello World!" to the console using the print() function. After printing, we increment the value of i by 1 using the += operator. This will make sure that the loop runs at most 5 times (since i < 5 is only true when i is less than 5). When the condition i < 5 becomes false, the loop will stop and the program will continue executing the next line of code.
So what happens when we run this code? Well, for each iteration of the loop, it prints "Hello World!" to the console. Since the loop runs at most 5 times (when i reaches 5), you'll see a total of 5 "Hello World!" messages printed out. Here's an example output:
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
As you can see, the "While" loop is a great way to execute code repeatedly while a certain condition holds true!
python while loop break
I'm happy to help!
The break statement in Python is used to exit a loop (like while, for, or try-except) prematurely, skipping the rest of the code within the loop.
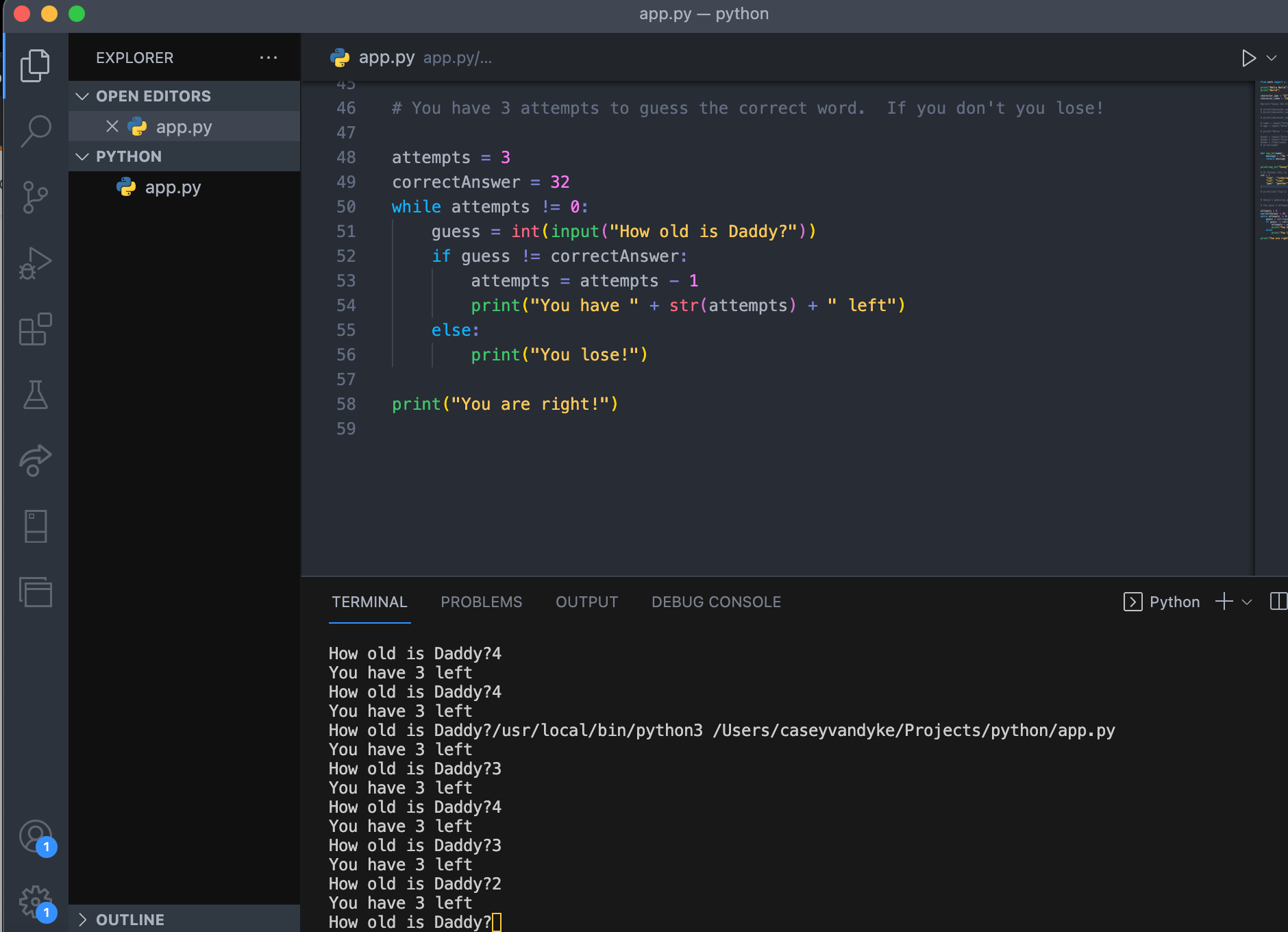
Here's an example of using break with a while loop:
i = 0while i < 5:
print(f"Current value: {i}")
if i == 3:
break
i += 1
print("Loop terminated!")
When you run this code, the output will be:
Current value: 0
Current value: 1
Current value: 2
Current value: 3
Loop terminated!
As you can see, the loop stopped at i == 3, even though it was supposed to go up to 5. The break statement effectively "killed" the loop, making it exit early.
Now, here are some scenarios where you might use break:
break to stop the loop and move on. Invalid input: When dealing with user input (e.g., from a file or console), you might encounter invalid data. You could use break to stop processing further if that happens. Detection of certain conditions: Let's say you're searching for a specific pattern in text, and when you find it, you can stop the search process.
Some important things to remember about break:
while, for, or try-except). If you use it outside a loop, Python will raise a SyntaxError. You should be careful when using break, as it can make your code less readable. Try to avoid breaking out of loops unless absolutely necessary. There's no equivalent to continue in other languages; if you're familiar with other programming languages, keep this in mind.
In conclusion, the break statement in Python allows you to exit a loop prematurely, giving you more control over the flow of your program. Just be mindful of its limitations and use it wisely!