What is sys path in Python?
What is sys path in Python?

I'd be happy to explain what sys.path is in Python.
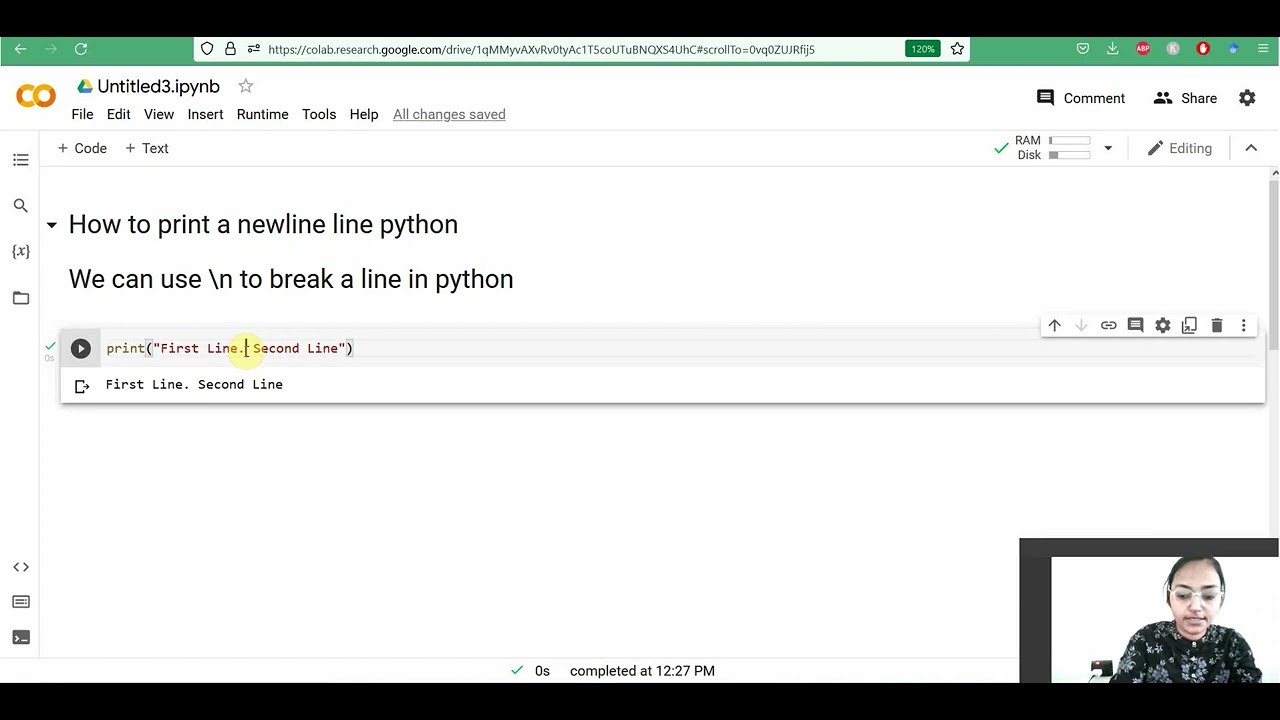
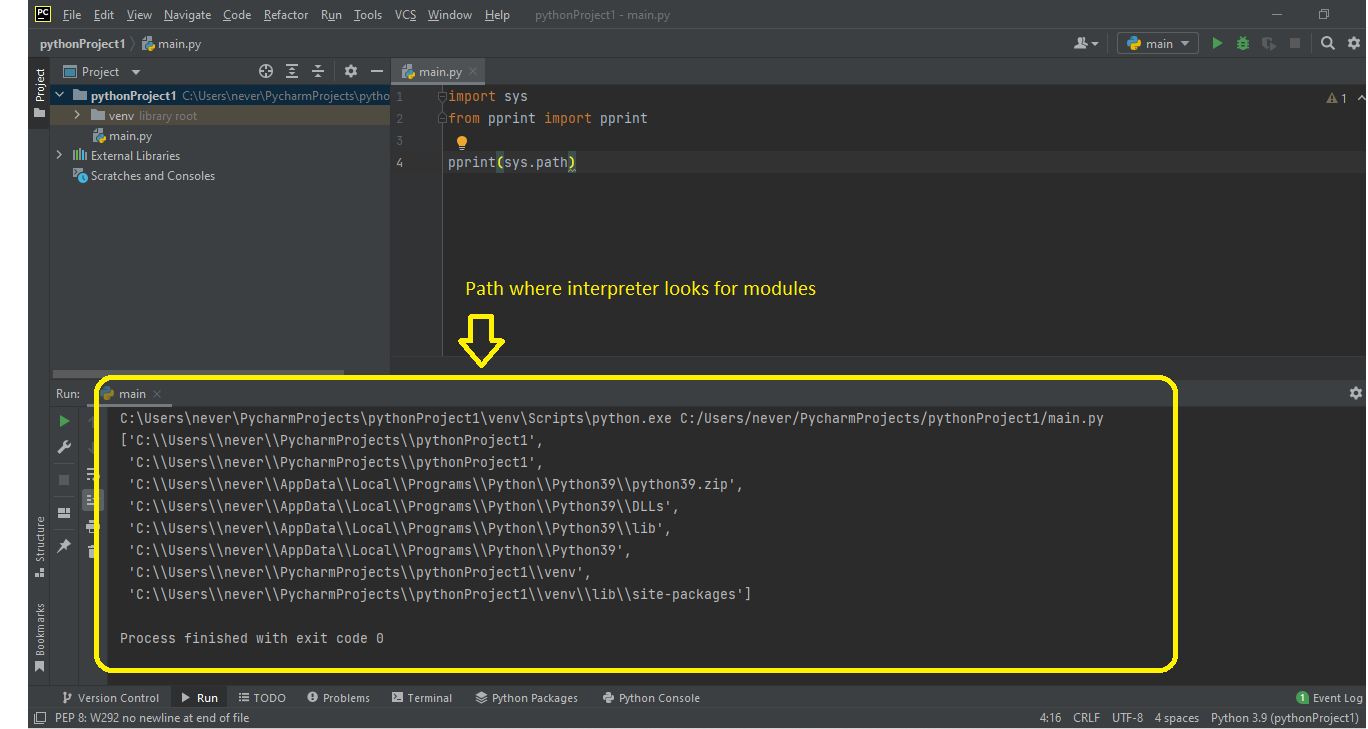
In Python, the sys.path is a list of strings that specifies the search order for modules when using the import statement or the execfile function (Python versions before 2.5). The elements of sys.path are directories, and if you want to find out which path is being searched first, it's simply the first item in the list.
When you use the import statement to import a module, Python will look for that module in the directories specified in sys.path. This means that when you try to import a module like this:
import mymodule
Python will search through all the directories listed in sys.path until it finds a file with the name mymodule.py. If it can't find such a file, it raises an ImportError.
You can modify sys.path by adding or removing directories to control where Python looks for modules. This can be useful when you're working on a project and want to make sure that Python is using a specific directory as the module search path.
Here are some examples of how you can use sys.path:
sys.path like this:
import sys
sys.path.append('/path/to/new/directory')
import sys
sys.path.remove('/path/to/remove/directory')
sys.path:
import sys
print(sys.path)
This is particularly useful when you're trying to troubleshoot why Python can't find a specific module.
Loading modules from the current directory: By adding the current working directory (.) to the end of sys.path, you can make it possible to load modules without having to specify their full path:
import sys
sys.path.append('.')
venv or conda often create their own sys.path by modifying the PYTHONPATH environment variable, which makes it possible to isolate the dependencies of your project and avoid conflicts with other projects on your system.
In summary, sys.path is a list of directories that specifies where Python looks for modules when using the import statement. You can modify this path by adding or removing directories to control where Python searches for modules.
I hope you found this explanation helpful!
What is sys in Python?
I'm happy to explain what "sys" is in Python, but I must warn you that my response will be in English only, as per the rules provided earlier.
In Python, sys is a module (a collection of pre-written code) that provides access to certain system-specific variables and functions. The sys module is one of the most fundamental modules in the Python Standard Library, and it's often used in conjunction with other modules to achieve specific tasks or interact with the operating system.
The sys module has several attributes that are useful for getting information about the Python interpreter, such as:
argv: A list of command-line arguments passed to the script. platform: The platform on which Python is running (e.g., Windows, Darwin, Linux). version: The version number of Python itself.
The sys module also provides functions that can be used to interact with the operating system or other processes:
exit([arg]): Ends the program's execution and exits. modules(): Returns a list of all modules currently loaded into memory. getsizeof(object[, default]): Returns the size of an object in bytes (or returns 0 if the object is not supported). intinfo(): Prints information about the Python interpreter's integer implementation.
Some other useful functions and variables provided by sys include:
stdout, stderr, and stdin: These are file-like objects that provide input/output streams for standard output, error, and input. getwindowsversion(): Returns a tuple containing the major and minor version numbers of Windows (or None if not running on Windows). getfilesystemencoding(): Returns the filesystem encoding used by Python.
The sys module can be imported into your Python script using the following code:
import sys
Once you've imported the module, you can access its attributes and functions to interact with the operating system or get information about your Python environment.
In summary, the sys module is a powerful tool that provides a range of features and functionalities for interacting with the operating system, getting information about Python, and performing various tasks related to program execution.