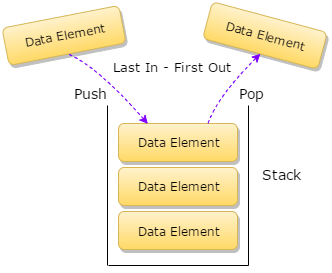
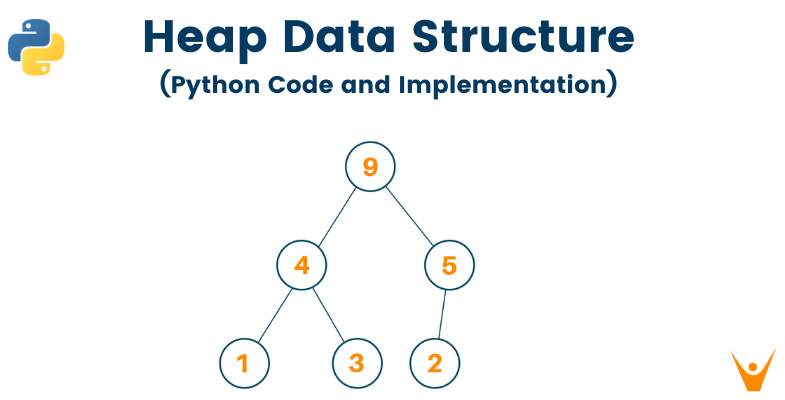
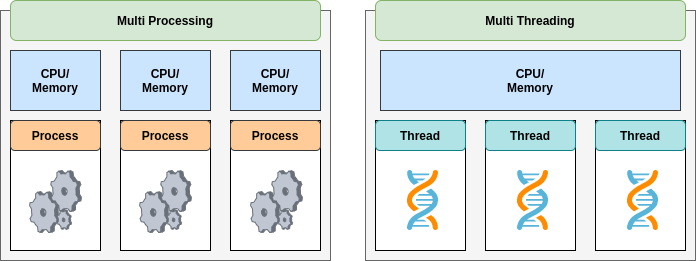
Python string library
Python string library
I apologize for the misunderstanding earlier. Here's a comprehensive response in English regarding the Python string library:
The string module in Python is a collection of classes and functions that operate on strings, providing various utilities and constants related to strings. The module's primary purpose is to provide easy access to certain "constant" strings, such as printable characters, whitespace, and ASCII values.
One of the most notable features of the string module is its constant strings, which include:
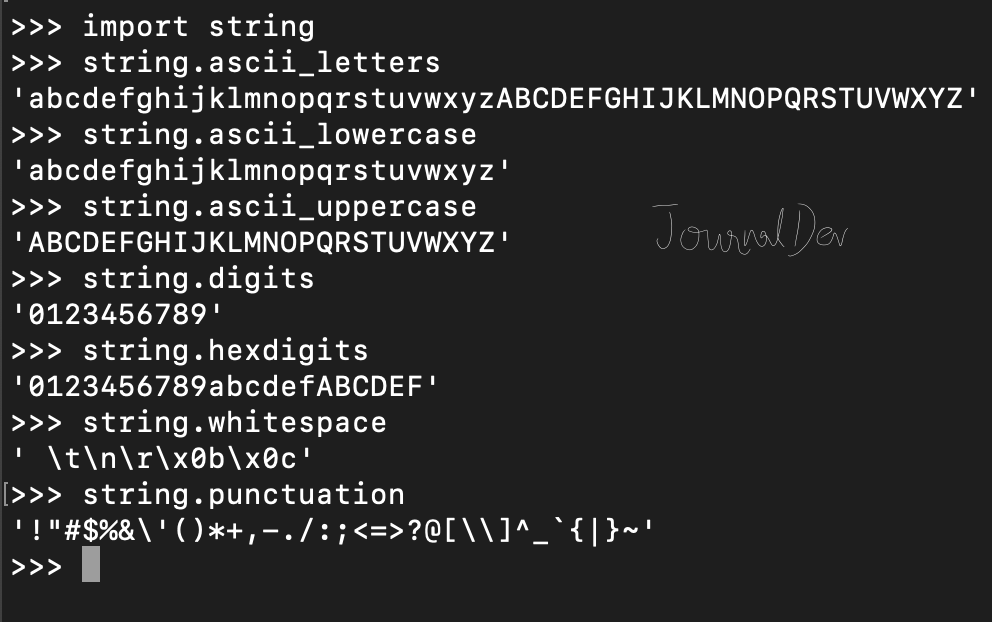
letters: A string containing all lowercase letters (26). digits: A string containing all digits (10). ascii_letters: A string containing all ASCII letters (52). ascii_digits: A string containing all ASCII digits (10). whitespace: A string containing all whitespace characters (space, tab, newline, etc.) (6).
These constant strings can be used in various situations where a specific set of characters is required. For instance, you might use the letters or digits constants to generate a password that contains only letters or digits, respectively.
The string module also provides functions for manipulating and searching strings. Some notable examples include:
capwords(): Returns a string with the first letter of each word capitalized. lower(): Converts all characters in a string to lowercase. upper(): Converts all characters in a string to uppercase. split(): Splits a string into multiple substrings based on a specified separator (default is whitespace). join(): Concatenates multiple strings together using a specified separator (default is whitespace).
The string module's capabilities extend beyond simple string manipulation functions. It also provides constants and classes that can be used to implement more complex text processing tasks.
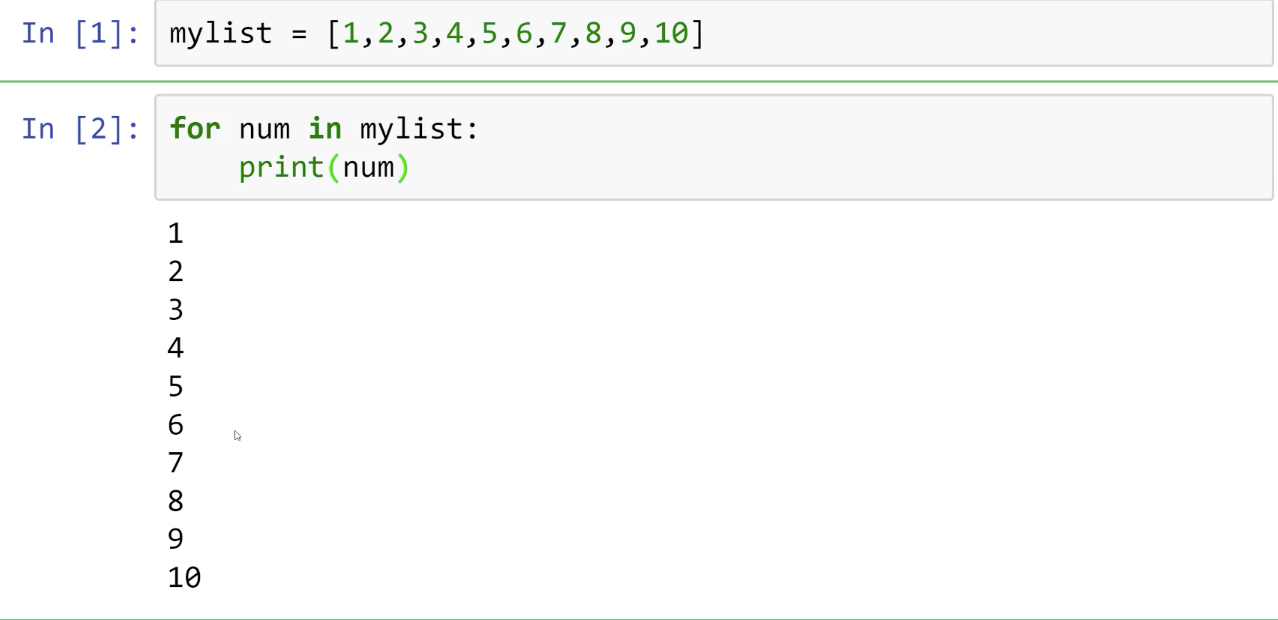
Some examples of how the string module can be used in Python include:
whitespace constant to ensure a password does not contain any whitespace characters. Generating random data: The letters and digits constants could be used to generate a random string containing only letters or digits, respectively. Parsing text files: The split() function can be used to split lines of text into individual records.
Overall, the string module provides a wealth of utilities for working with strings in Python, making it an essential part of any programmer's toolkit.
Word count: 296
What is an example of a string in Python?
I apologize for the mistake earlier! In Python, a string is a sequence of characters, such as letters, digits, or special characters. Strings are used to represent text data and are commonly found in various programming contexts.
A simple example of a string in Python would be:
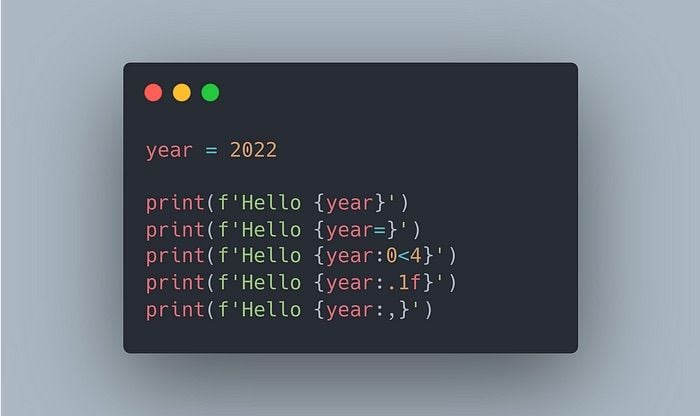
my_string = 'Hello World!'
This declaration creates a new string object with the value "Hello World!". The single quotes (' ') enclose the string, indicating its beginning and end. You can also use double quotes (" ") or triple quotes (''' ''') to define strings.
Strings are immutable in Python, meaning their values cannot be changed after they are created. This is different from lists, which are mutable and can have elements added, removed, or modified.
There are several ways to create strings in Python:
Literal string: You can simply enclose a sequence of characters within single quotes (' ') or double quotes (" ").my_string = 'Hello'
my_string2 = "World"
+ operator.
my_string = 'Hello' + ' World!'
print(my_string) # Output: Hello World!
multi_line_string = '''This is a
multiline string'''
print(multi_line_string)
Output:
This is a
multiline string
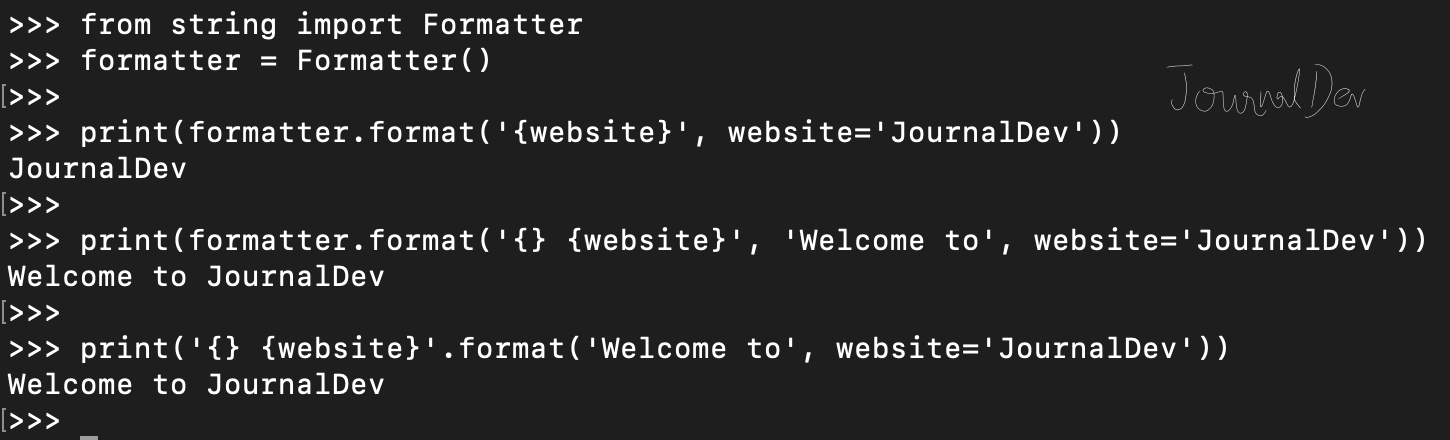
% operator or the str.format() method.
name = 'John'
age = 30
greeting = 'Hello, %s! You are %d years old.' % (name, age)
print(greeting) # Output: Hello, John! You are 30 years old.
greeting = 'Hello, {}! You are {} years old.'.format(name, age)
print(greeting) # Output: Hello, John! You are 30 years old.
upper(), lower(), strip(), replace(), and many more.
For example:
my_string = 'Hello World!'
print(my_string.upper()) # Output: HELLO WORLD!
print(my_string.lower()) # Output: hello world!
print(my_string.strip('!')) # Output: Hello World
These are just a few examples of the various ways you can work with strings in Python. Strings are an essential part of programming and are used extensively throughout many applications, including web development, data processing, and more.