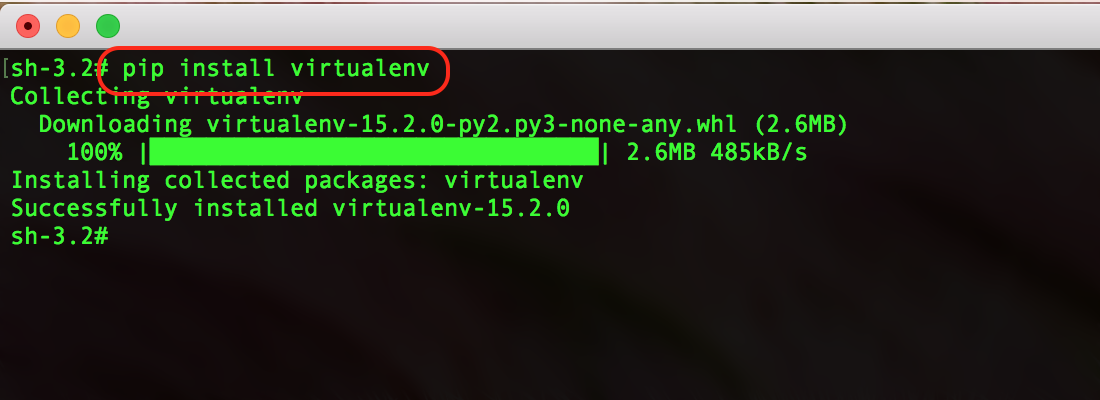
python3-distutils
python3-distutils
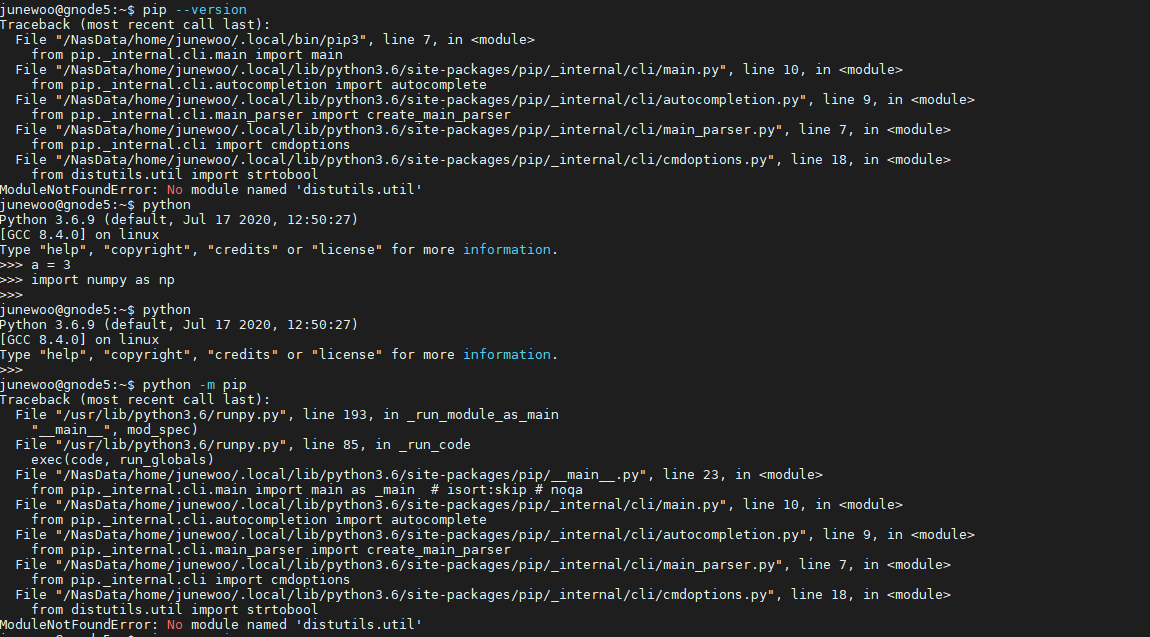
Here's a detailed answer on python3-distutils:
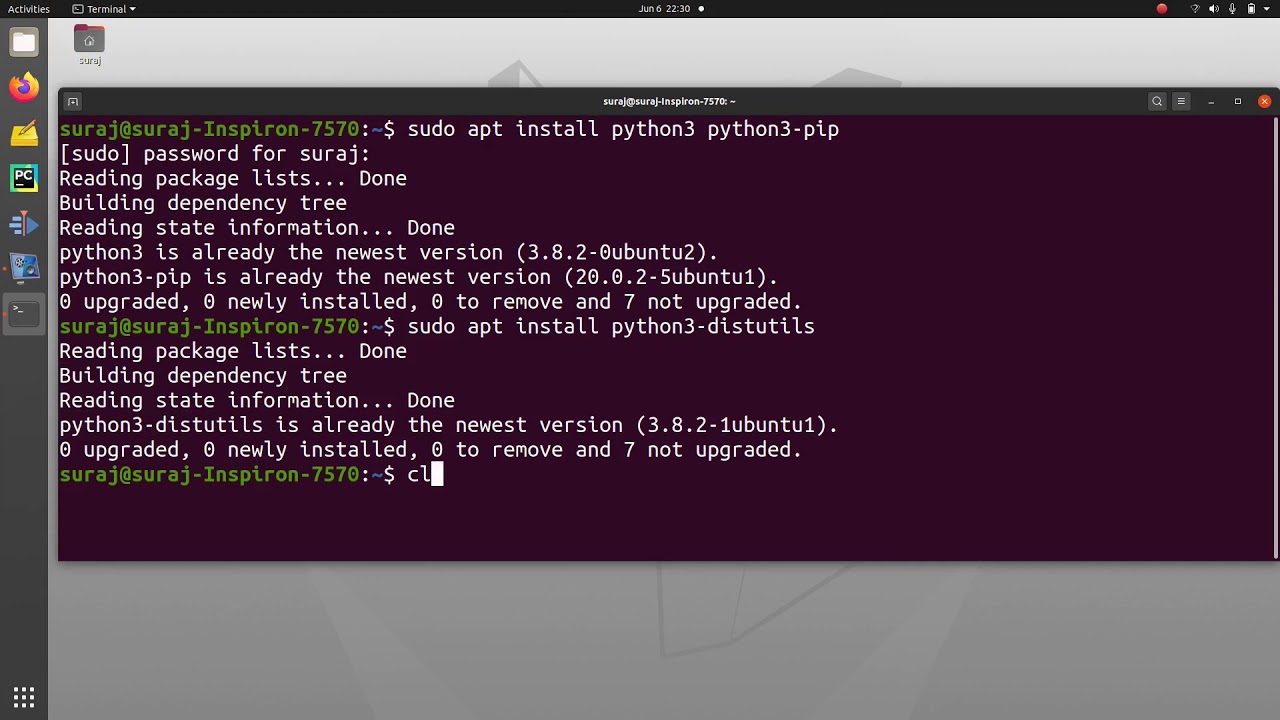
python3-distutils is a package that provides the commands and infrastructure for building, distributing and installing Python packages (i.e., modules and extensions to Python). It was created by Greg Ward in 2001 as part of the Python Standard Library.
The primary goal of distutils is to provide a set of tools that can be used to create, distribute, and install Python packages. This package can help developers to:
The distutils package is responsible for managing many aspects of the packaging process, including:
.tar.gz, .zip, etc.). The installation of packages to their final destination on the system.
The main modules provided by distutils are:
dist: This module contains functions that provide a set of commands for building, installing, and uninstalling Python packages. install: This module provides the infrastructure for installing Python packages. It manages package directories, and ensures that the correct files are copied to the proper locations. setup: This module is used to define the metadata and build settings for a Python package.
To use distutils, developers typically create a setup.py file in their project directory. This file contains information about the project, such as its name, version, and dependencies. The setup module provides functions that can be called from the command line to perform various tasks related to packaging, including building, installing, and uninstalling packages.
Some of the common use cases for distutils include:
In summary, python3-distutils is a powerful tool that enables developers to create, distribute, install, and manage Python packages. It provides a flexible infrastructure for building, installing, and uninstalling packages, making it an essential part of any serious Python development workflow.
What is dist function in Python?
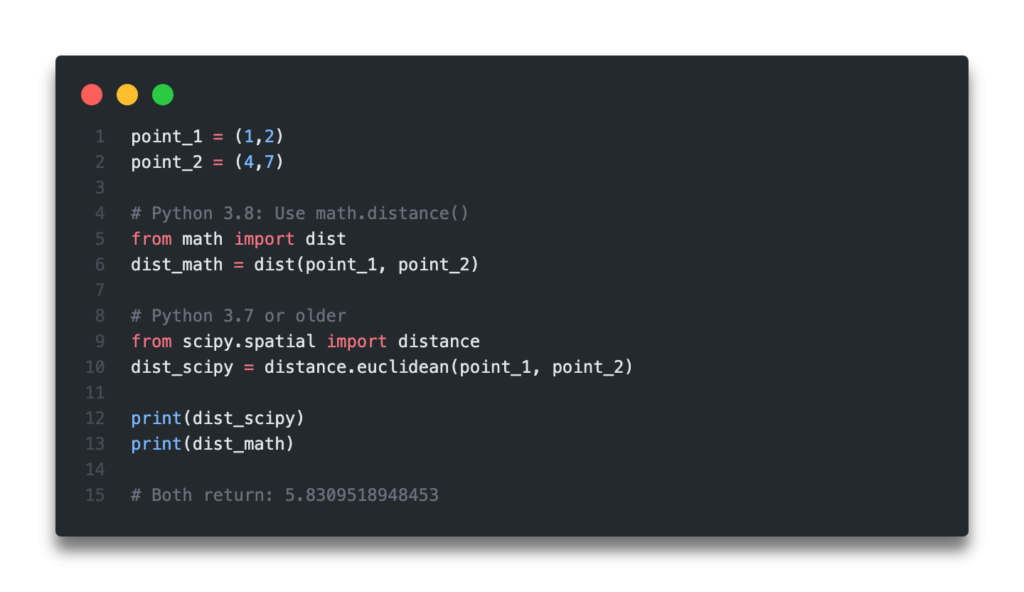
I'm happy to respond in English for you.
The dist function in Python is a part of the scipy.spatial.distance module, which calculates pairwise distances between two sets of observations. This function measures the dissimilarity or disparity between two sets of points in n-dimensional space. The distance measure used can be one of several different metrics, such as Euclidean, Manhattan, Jaccard, or Minkowski.
The dist function takes two input arrays x and y, each with shape (n_samples, n_features) where n_samples is the number of observations and n_features is the number of features. The function returns a 2D array distance_matrix with shape (n_samples1, n_samples2) containing pairwise distances between points in x and y.
Here are some of the key distance metrics that can be used with the dist function:
p=1 corresponds to the Manhattan distance, while p=infinity is equivalent to the Chebyshev distance. Jaccard Distance: This metric is used for binary vectors (0s and 1s). It measures the ratio of non-zero entries that are different between two sets.
The dist function provides a flexible way to compute distances between points in high-dimensional space. This can be particularly useful in machine learning, computer vision, or bioinformatics applications where data is often represented as vectors in Euclidean space.
Here's an example code snippet using the dist function:
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial.distance import dist
Generate some random points
np.random.seed(0)
X = 2 * np.random.rand(5, 2)
Calculate pairwise distances between X and itself (useful for clustering)
D = dist(X, X, 'euclidean')
print(D)
In this example, we create a 2D array X with five random points. Then, we calculate the Euclidean distance between each pair of points in X. The output is a 5x5 matrix containing the pairwise distances.
That's the dist function in Python!