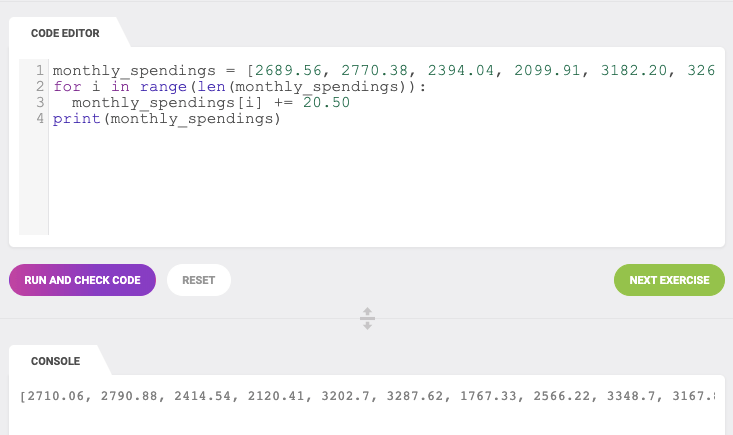
Python list vs array examples
Python list vs array examples

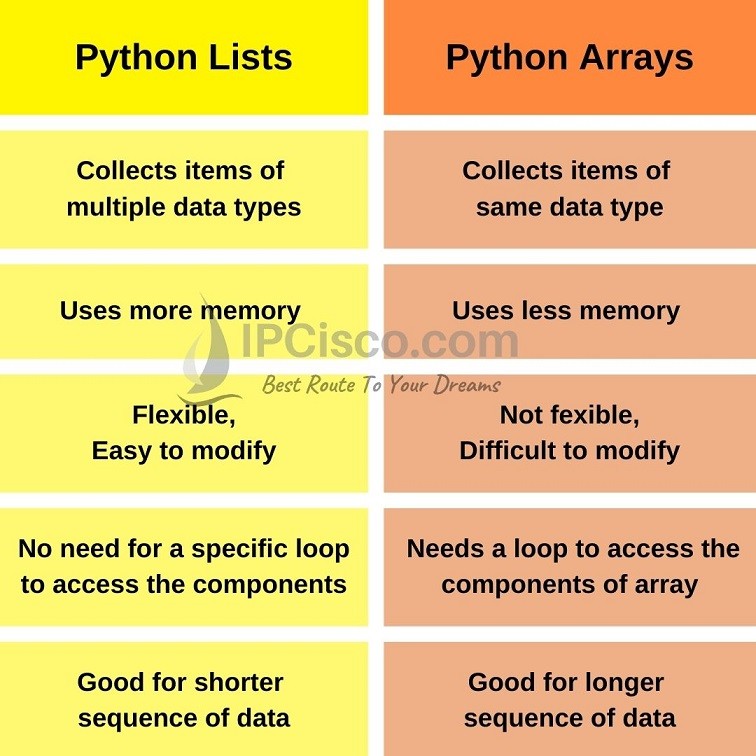
Here's a comprehensive comparison of Python lists and arrays:
In Python, you can store data in two main ways: Lists and Arrays. Both are data structures that allow you to store multiple values in a single variable. However, there are some significant differences between them.
Python List (List)
A Python list is an ordered collection of items. It allows you to store any type of object, including strings, integers, floats, dictionaries, and even other lists. Lists can be created using the square brackets [] or the list() function.
Here are some key features of Python lists:
Ordered: Lists maintain their order. You can access elements by their index (position). Heterogeneous: You can store different data types in a list.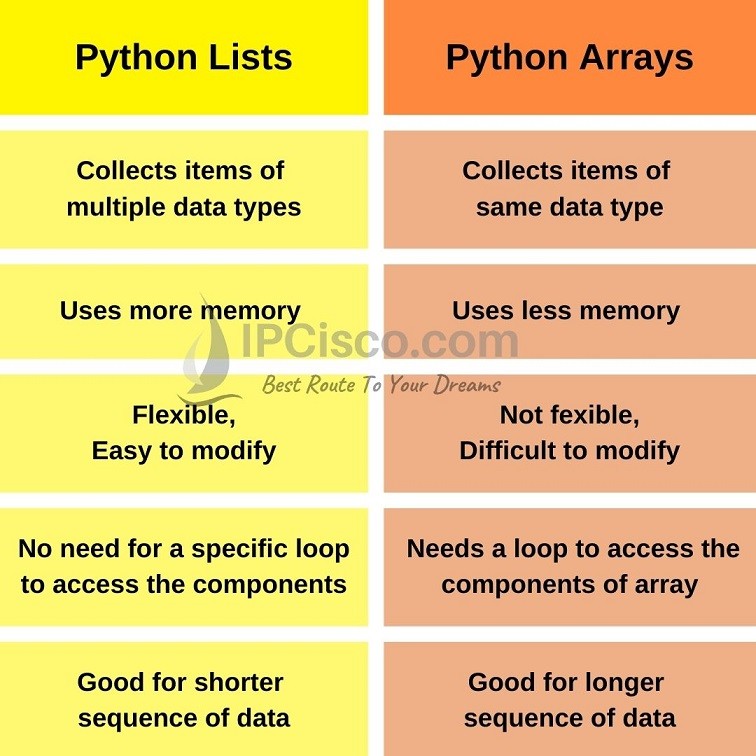
Example:
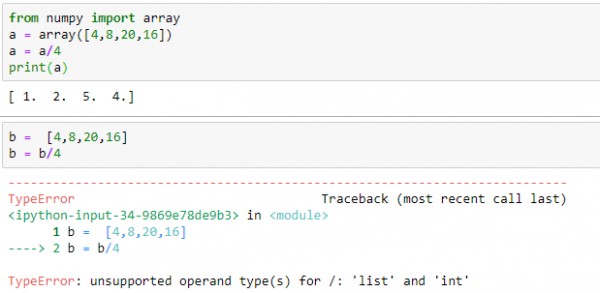
my_list = ["apple", "banana", 1, 2.5]
print(my_list) # Output: ['apple', 'banana', 1, 2.5]
NumPy Array (Array)
A NumPy array is a multi-dimensional data structure that allows you to store large amounts of numerical data. Arrays are designed for efficient numerical computations and are particularly useful when working with scientific and engineering applications.
Here are some key features of NumPy arrays:
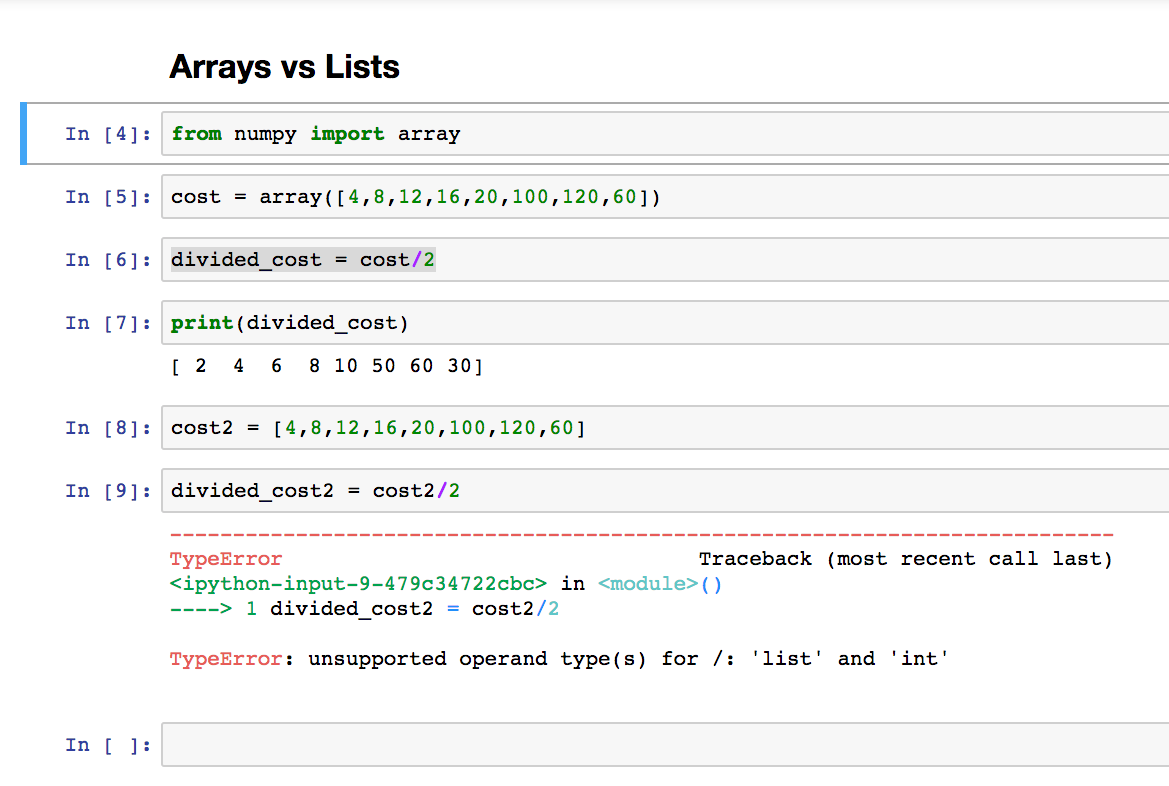
Ordered: Arrays maintain their order, just like lists. Homogeneous: All elements in an array must be the same type (e.g., all integers or all floats). Fixed size: The size of an array is fixed when it's created and cannot change afterwards. Efficient: NumPy arrays are implemented as contiguous blocks of memory, which makes them extremely efficient for numerical computations.Example:
import numpy as npmy_array = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(my_array) # Output: [[1 2]
[3 4]]
When to use each
Here are some guidelines on when to use Python lists and NumPy arrays:
Use Python lists when you need a flexible data structure that can store different types of objects, or when you need to dynamically change the size of your data. Use NumPy arrays when you're working with large amounts of numerical data and require efficient numerical computations. This is particularly useful in scientific computing, machine learning, and engineering applications.Conclusion
In summary, Python lists are suitable for general-purpose programming tasks that require flexible data structures, while NumPy arrays are ideal for numerical computations where efficiency and speed are crucial. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one depends on the specific requirements of your project.
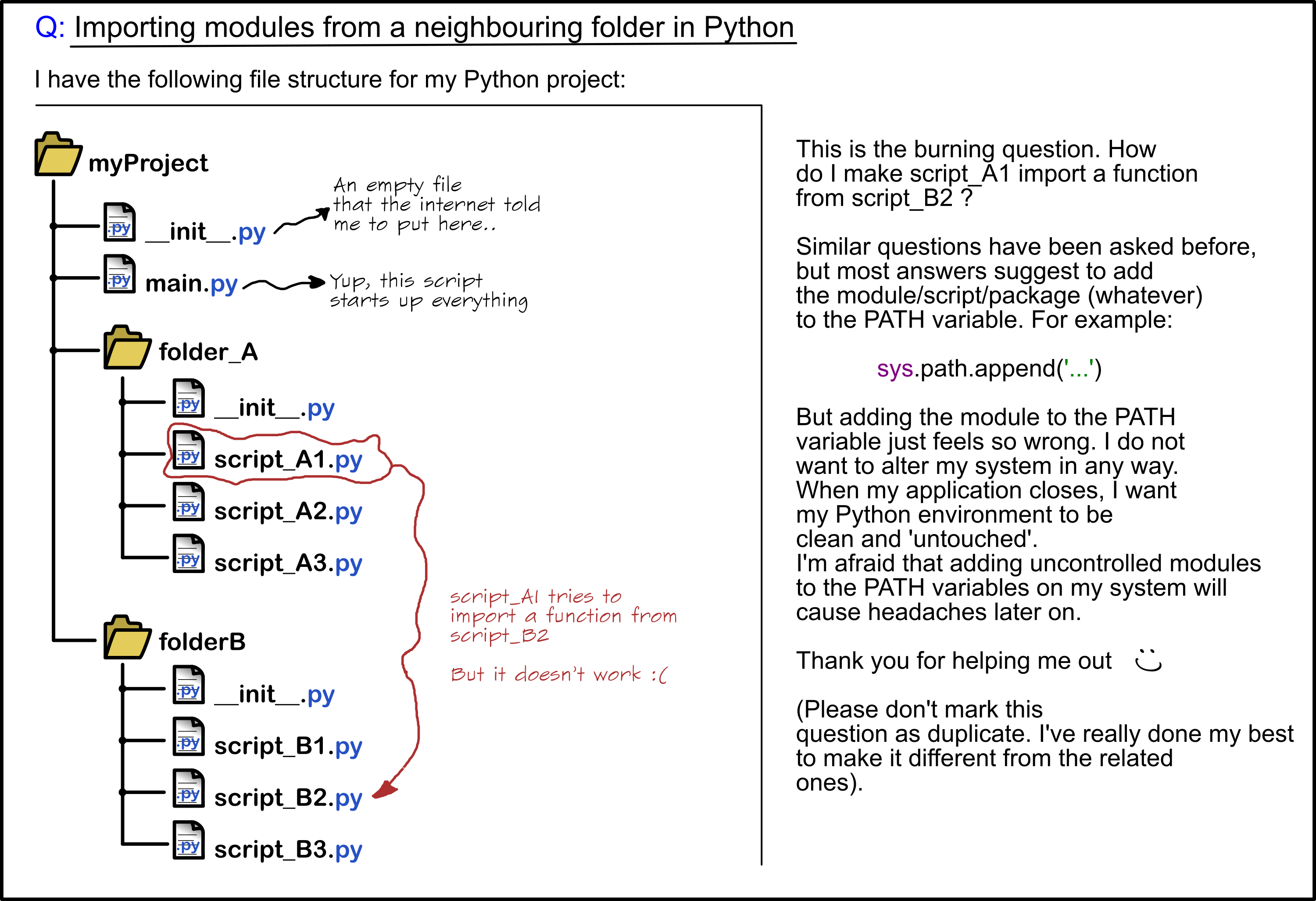
Python list vs C array

I'll respond in English as you requested.
Python's built-in list data structure and C's array are both used to store collections of items, but they have different characteristics and use cases. Understanding the differences between them can help you make informed decisions when working with these data structures in Python and C.
Dynamic Memory Allocation vs Static Memory Allocation
One significant difference between Python lists and C arrays is how memory is allocated for storing elements. In C, when you declare an array, a fixed amount of memory is allocated at compile-time. This means that the size of the array is known before the program starts executing. On the other hand, Python lists use dynamic memory allocation, which means that the memory is allocated at runtime based on the size of the list.
In C, when you declare an array with a specific size, you cannot change its size after compilation. You need to create a new array and copy the elements from the original array if you want to add or remove elements. In Python, you can easily add or remove elements from a list using various methods like append(), insert(), or remove().
Type Safety
C arrays are strongly typed, meaning that each element in the array must be of the same type. You cannot store different types of data in the same array without explicitly converting them to the correct type. Python lists, on the other hand, are dynamically typed, which means that you can store elements of any type (integers, strings, floats, etc.) in a list.
Memory Management

C arrays require manual memory management using pointers and malloc(), which can be error-prone and lead to memory leaks if not handled correctly. Python lists handle memory management internally, freeing the programmer from worrying about allocating or deallocating memory for each element.
Performance
When it comes to performance, C arrays are generally faster than Python lists because they are closer to the machine's native representation of data (memory layout, cache efficiency, etc.). However, in most cases, the difference in performance is negligible and may not be a significant concern unless you're working on high-performance, memory-bound applications.
Use Cases
C arrays are suitable for:
Performance-critical applications where manual memory management is acceptable. Applications that require strict type safety and control over data storage. Working with low-level system programming or embedded systems development.Python lists are suitable for:
Rapid prototyping, scripting, and development where ease of use and flexibility matter. Applications that don't require explicit memory management or type safety. Data analysis, scientific computing, or machine learning tasks where Python's NumPy library provides an efficient way to work with large arrays.In summary, while both C arrays and Python lists can be used for storing collections of items, their differences in dynamic vs static memory allocation, type safety, memory management, performance, and use cases make them suitable for distinct application domains.