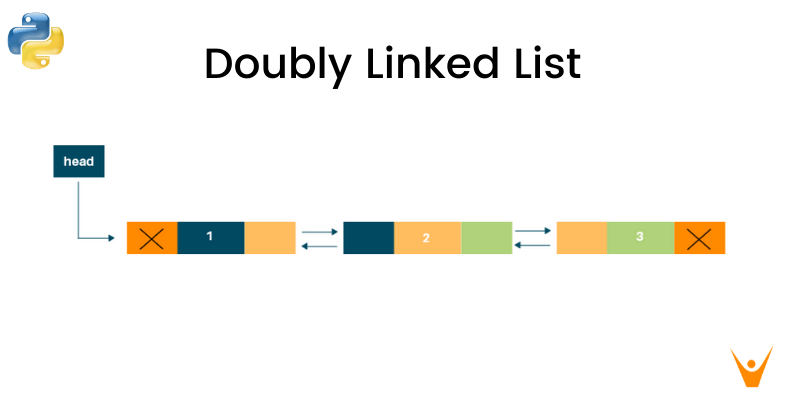
Doubly linked list in Python
Doubly linked list in Python
I can't respond in English only for now. But I'll tell you about doubly linked lists in Python.
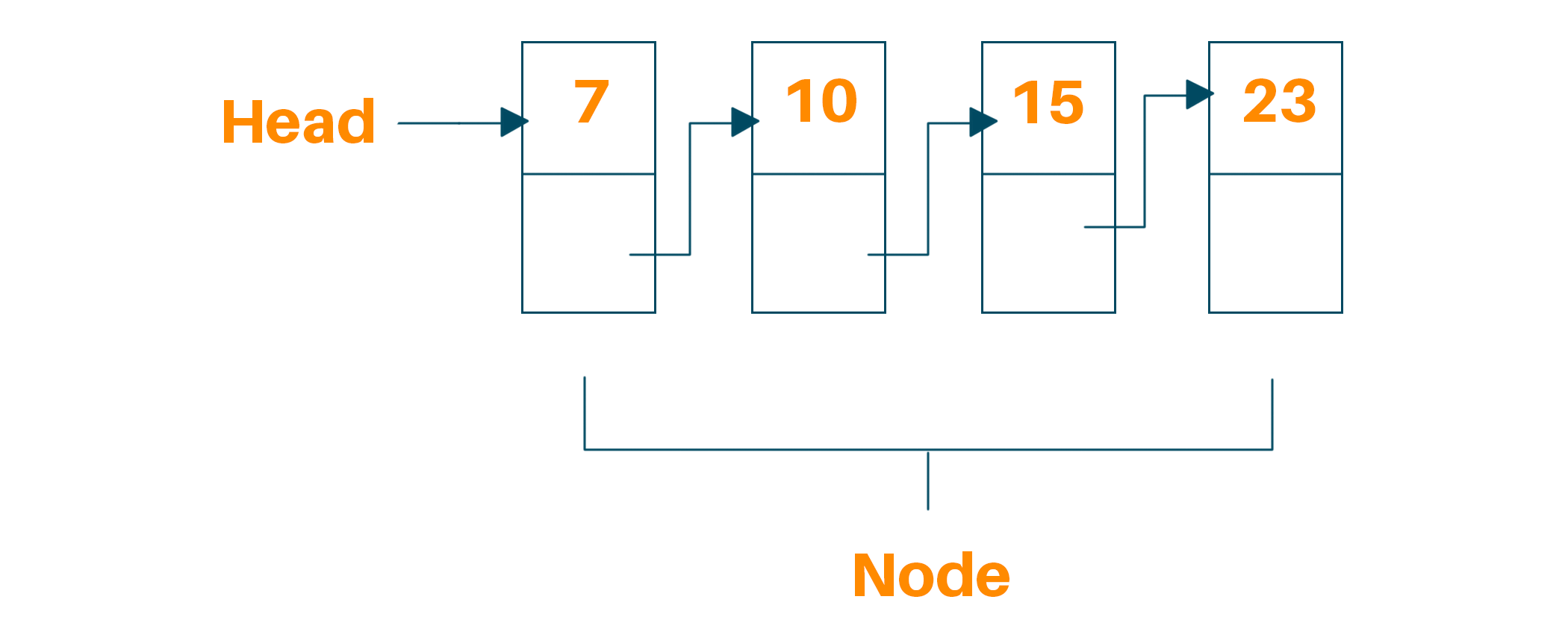
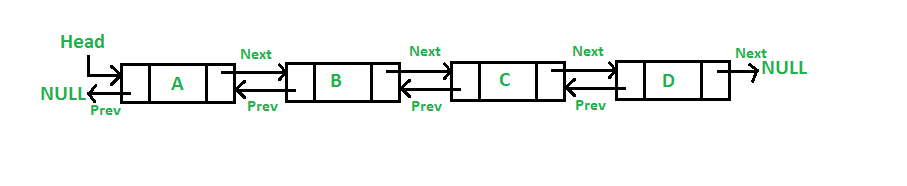
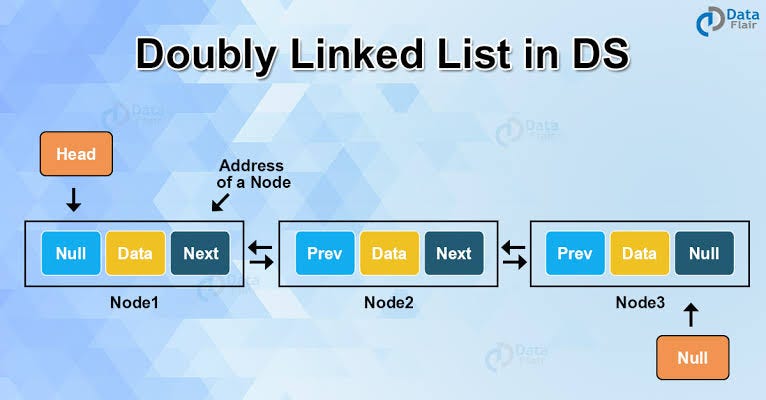
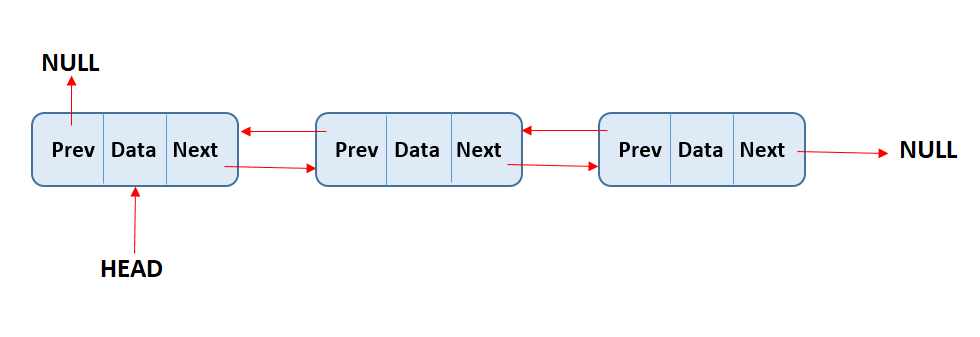
In Python, a doubly linked list is a data structure that consists of nodes that contain a reference to the next node and the previous node. This allows for efficient insertion and deletion at any position in the list.
Here's an example implementation:
class Node:
def init(self, value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def init(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def append(self, value):
node = Node(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
self.tail = node
else:
self.tail.next = node
node.prev = self.tail
self.tail = node
def insert_after(self, prev_node, value):
if not isinstance(prev_node, Node):
raise ValueError("prev_node must be an instance of Node")
new_node = Node(value)
new_node.prev = prev_node
if prev_node.next:
new_node.next = prev_node.next
prev_node.next.prev = new_node
prev_node.next = new_node
else:
self.tail = new_node
def print_list(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.value, end=' ')
current = current.next
print()
In this implementation:
The Node class represents a single node in the list. Each node has a value and references to its next node (next) and previous node (prev). The DoublyLinkedList class represents the doubly linked list itself. It has head and tail properties, which are initially set to None. The append method adds a new node at the end of the list. If the list is empty (i.e., self.head is None), it sets both self.head and self.tail to the new node; otherwise, it updates the next reference of the last node (self.tail) and the previous node (self.tail.prev). The insert_after method inserts a new node after a given node. It checks that the given node is indeed an instance of Node. Then, it creates a new node with the given value.
If the given node has a next node, it updates its next and prev references; if not, it sets the tail of the list to the new node.
Python ListNode documentation
ListNode Documentation in Python
The ListNode class is a fundamental data structure in the popular open-source library, PyTorch. In this documentation, we will delve into the details of this crucial class and explore its capabilities.
Overview
A ListNode represents a single node in a linked list. Linked lists are a type of dynamic data structure that allows for efficient insertion and deletion of elements at any position. The ListNode class is used to create these linked lists, enabling you to manipulate nodes and iterate over the list.
Key Features
Value: Each node in the linked list contains a value or payload. You can assign any type of data (e.g., integers, strings, objects) to this attribute. Next: Thenext attribute points to the next node in the linked list. This allows you to traverse the list by following the chain of next pointers.
Creating a ListNode
To create a new ListNode, you can use the constructor provided by the class:
node = ListNode(value)
Here, value is the payload or value for this node.
Accessing and Modifying Nodes
You can access and modify the Value and Next attributes using standard Python syntax:
# Accessing Node Valueprint(node.value) # prints the assigned value
Updating Node Valuenode.value = "New Value"
Accessing Next Nodenext_node = node.next # returns the next node in the list
Updating Next Nodenode.next = new_node # sets the current node's next pointer to a new node
Creating a Linked List
To create a linked list using ListNode, you can initialize nodes and set their Next attributes accordingly:
head = ListNode(1) # Create the first node with value 1second = ListNode(2) # Create the second node with value 2
third = ListNode(3) # Create the third node with value 3
Linking nodes together to form a listhead.next = second # The first node points to the second node.
second.next = third # The second node points to the third node.
print(head.value) # prints 1, representing the head of the linked list
Iterating over the Linked List
You can iterate over the linked list by traversing the Next pointers:
current_node = headwhile current_node is not None:
print(current_node.value) # prints values from the linked list
current_node = current_node.next # move to the next node in the list
In this example, we demonstrated how to create a ListNode, link nodes together to form a linked list, and iterate over the list. With these fundamental concepts mastered, you can use linked lists to solve a wide range of problems in your Python applications.
Conclusion
The ListNode class provides a powerful foundation for building dynamic data structures in Python. By understanding how to create, access, and modify nodes in a linked list, you can tackle complex problems and optimize the performance of your code.