Python xml file
Python xml file
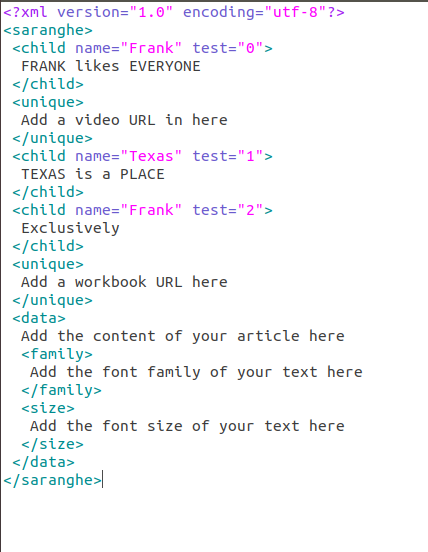
Here's a comprehensive guide on working with XML files in Python using the xml.etree.ElementTree module:
What is an XML File?
An XML (Extensible Markup Language) file is a type of plain text file that contains structured data, often used to store and exchange data between different systems or applications. It consists of a series of tags (elements) that surround data values, allowing for a flexible and self-descriptive format.
Python's xml.etree.ElementTree Module
The xml.etree.ElementTree module in Python provides an easy-to-use interface for parsing and manipulating XML files. This module is part of the Python Standard Library, making it readily available without needing to install additional packages.
Parsing an XML File
To parse an XML file using xml.etree.ElementTree, you can follow these steps:
xml.etree.ElementTree module:
Parse the XML File: Use theimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
ET.parse() function to parse the XML file:
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')
Replace 'example.xml' with the actual path and name of your XML file.
Accessing and Manipulating XML Elements
Once you have parsed an XML file, you can access and manipulate its elements using various methods. Here are some examples:
Root Element: Access the root element of the XML file:root = tree.getroot()
The getroot() method returns the top-level element in the XML file.
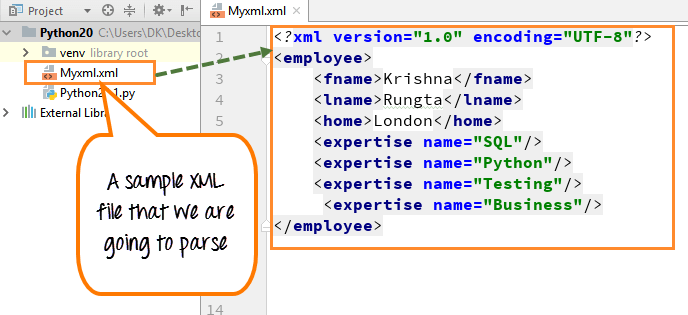
person_tag = root.find('.//person')
This code finds an element with the tag name person and its descendants.
name_attr = person_tag.get('name')
This code retrieves the value of the name attribute for the <person> element.
age_text = person_tag.text
This code retrieves the text content within the <person> element.
Creating and Writing XML Files
To create a new XML file or modify an existing one, you can use the following methods:
Element Creation: Create a new XML element:new_person = ET.SubElement(root, 'person')
This code creates a new <person> element as a child of the root element.
new_person.set('name', 'John Doe')
This code sets the name attribute to 'John Doe' for the new <person> element.
new_person.text = '30'
This code writes the string '30' as the text content within the new <person> element.
Example Code
Here's a simple example that demonstrates creating and parsing an XML file using xml.etree.ElementTree:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET Create an XML treeroot = ET.Element('people')
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
Create child elementsperson1 = ET.SubElement(root, 'person', name='John Doe')
person1.set('age', '30')
person2 = ET.SubElement(root, 'person', name='Jane Smith')
person2.set('age', '25')
Write the XML tree to a filetree.write('example.xml')
This code creates an XML file containing two <person> elements with attributes and text content. You can then parse this file using xml.etree.ElementTree:
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')root = tree.getroot()
Access the elementspeople_tag = root.findall('.//person')
for person in people_tag:
print(f"Name: {person.get('name')}, Age: {person.get('age')}")
This code parses the XML file and prints the values of the name and age attributes for each <person> element.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored how to work with XML files in Python using the xml.etree.ElementTree module. You learned how to parse an XML file, access and manipulate its elements, create new XML files, and write text content. With these skills, you can efficiently process and generate XML data in your Python applications.
Remember, the xml.etree.ElementTree module is part of the Python Standard Library, making it readily available for all your XML-related needs.
How to parse XML file in Python?
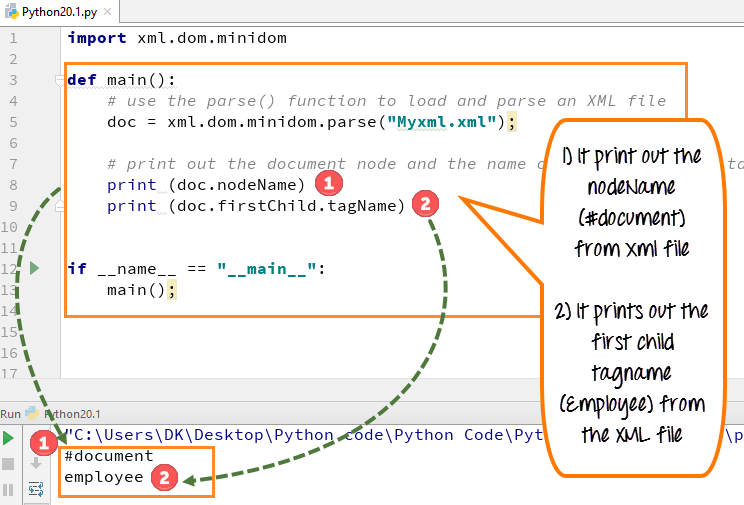
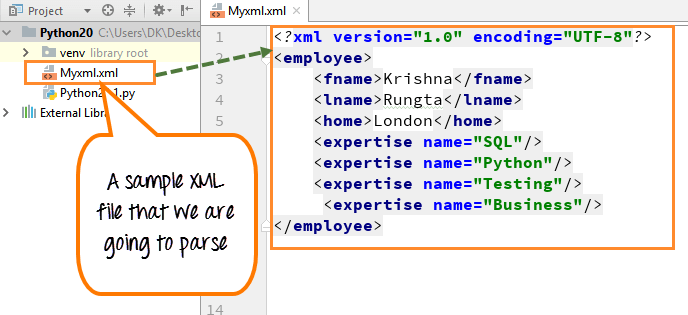
Parsing an XML (Extensible Markup Language) file in Python can be achieved using various libraries and tools. Here, we'll explore the popular xml.etree.ElementTree library that comes bundled with Python's standard library.
Why Parse XML files?
XML files are used to store and transport data between systems. They contain structured data in the form of elements, attributes, and text. Parsing an XML file involves reading and processing this data in a programming language like Python. This is useful when you need to:
Extract specific data from the XML file. Transform or convert the XML data into another format. Validate the structure and content of the XML file.Parsing XML files with xml.etree.ElementTree
The xml.etree.ElementTree library provides an easy-to-use API for parsing XML files. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Open the XML file: Use theimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
ET.parse() function to open and parse the XML file:
xml_file = 'example.xml' # Replace with your XML file nameroot_element = ET.parse(xml_file).getroot()
The parse() function returns an ElementTree object, which is then used to get the root element of the XML file using the getroot() method.
find() or findall() methods to traverse the XML elements:
# Find all elementspersons = root_element.findall('.//person')
Iterate over the persons and extract datafor person in persons:
name = person.find('.//name').text
age = person.find('.//age').text
print(f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}")
In this example, we find all <person> elements using the findall() method. Then, we iterate over each person and extract their name and age by finding and accessing the corresponding child elements.
text attribute to extract text values from XML elements:
# Find the element and extract its value </p>title = root_element.find('.//title').text
print(f"Title: {title}")
In this example, we find the <title> element and extract its text value using the text attribute.
Additional Tips
You can use XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) to transform or convert XML data into another format. Thexml.etree.ElementTree library also provides methods for creating new XML elements, attributes, and texts. Check out the official documentation for more information. Python's standard library includes other XML-related libraries like xml.dom.minidom and xml.sax. These libraries provide more advanced features for parsing and manipulating XML files.
In conclusion, parsing an XML file in Python using xml.etree.ElementTree is a straightforward process. By understanding the basic concepts of XML files and the API provided by this library, you can efficiently extract specific data or transform XML files to suit your needs.