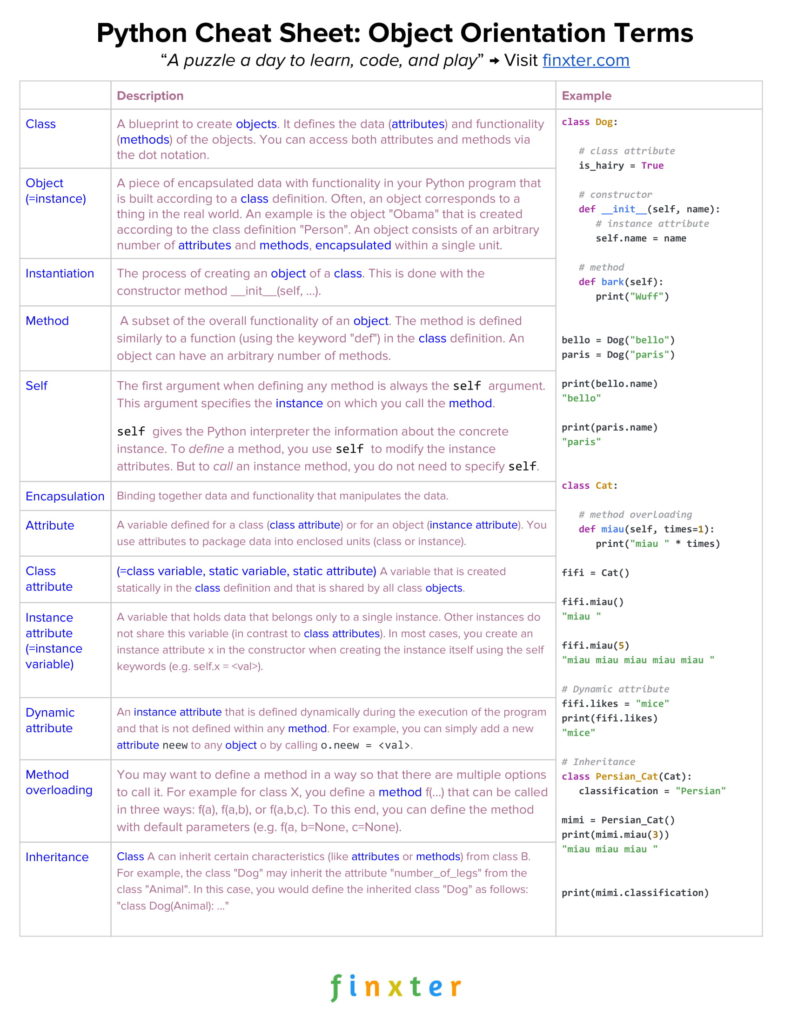
What is operator in Python
What is operator in Python
I'm happy to respond in English for you!
In the world of programming, particularly in Python, an operator is a symbol or phrase used to perform operations on values or variables. It's a crucial concept that allows programmers to manipulate data, make decisions, and control the flow of their code.
Python operators can be categorized into several groups:
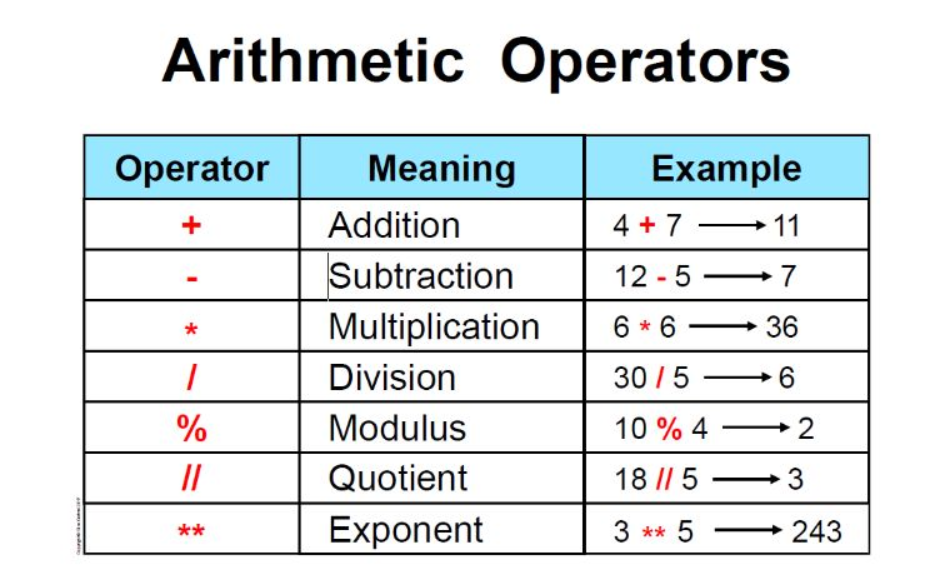
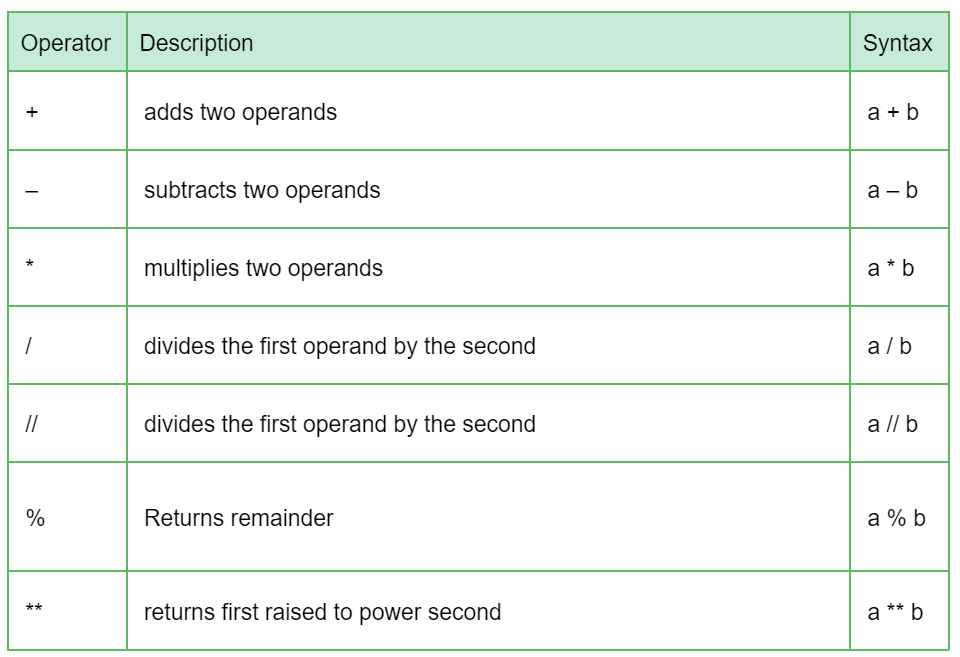
Arithmetic Operators: These are used for mathematical calculations, such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), modulus (%), exponentiation (**), and floor division (//).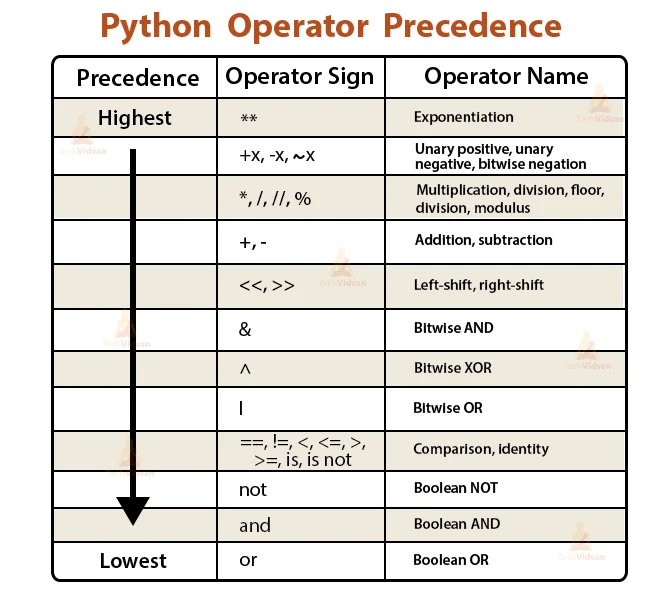
Example: a = 5; b = 3; c = a + b would result in c being assigned the value 8.
Example: if a == 5: would evaluate whether a is equal to 5, and if true, execute the code within the if block.
Example: if a > 0 and b < 10: would evaluate whether both conditions (a being greater than zero and b being less than ten) are true, and if so, execute the code within the if block.
Example: x = 5; y = x * 2 would set y equal to twice the value of x, which is 10.
Example: a = 3; b = a & 1 would set b equal to the result of performing a bitwise AND operation between a and the integer 1, which is 1.
Example: if 'x' in ['a', 'b', 'c']: would evaluate whether the string 'x' is present in the given sequence, and if true, execute the code within the if block.
Example: if x is y: would evaluate whether both x and y reference the same object in memory, and if true, execute the code within the if block.
In conclusion, Python operators are an essential part of programming in this language. By mastering these symbols and phrases, you'll be able to write concise, expressive, and efficient code that accomplishes your tasks with ease!
What are the 7 arithmetic operators in Python?
I'd be happy to explain the 7 arithmetic operators in Python!
Python provides a set of basic arithmetic operators that allow you to perform calculations with numbers. These operators can be categorized into two main groups: binary operators, which take two operands (left and right), and unary operators, which operate on a single value.
Addition (+): The addition operator is used to add the values of two numbers together. This operator returns the sum of the left-hand operand and the right-hand operand.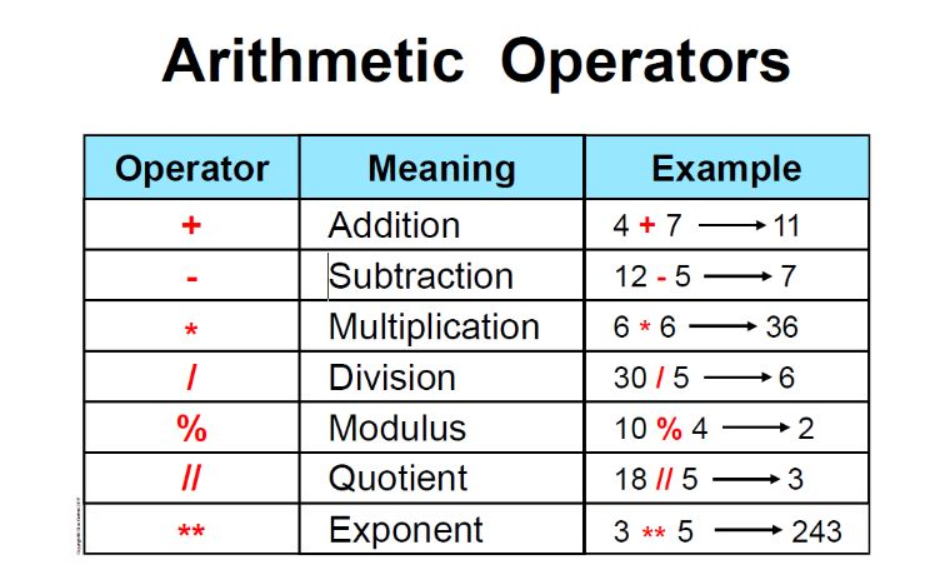
Example: a = 5; b = 3; c = a + b; print(c) will output 8.
Example: a = 5; b = 3; c = a - b; print(c) will output 2.
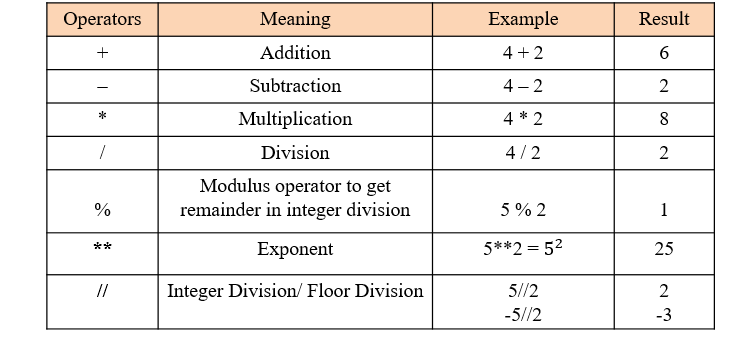
Example: a = 5; b = 3; c = a * b; print(c) will output 15.
Example: a = 5; b = 2; c = a / b; print(c) will output 2.5.
Note that in Python 3.x and later, the / operator performs "true division", which means it always returns a float, even if the operands are integers. To get integer division, you can use the // operator (see below).
Example: a = 5; b = 2; c = a // b; print(c) will output 2.
Example: a = 17; b = 5; c = a % b; print(c) will output 2, because 17 divided by 5 leaves a remainder of 2.
Example: a = 2; b = 3; c = a ** b; print(c) will output 8, because 2 raised to the power of 3 equals 8.
These arithmetic operators are essential for performing calculations in Python, and you'll likely use them frequently in your programming endeavors!