How to use OAuth with Python?
How to use OAuth with Python?
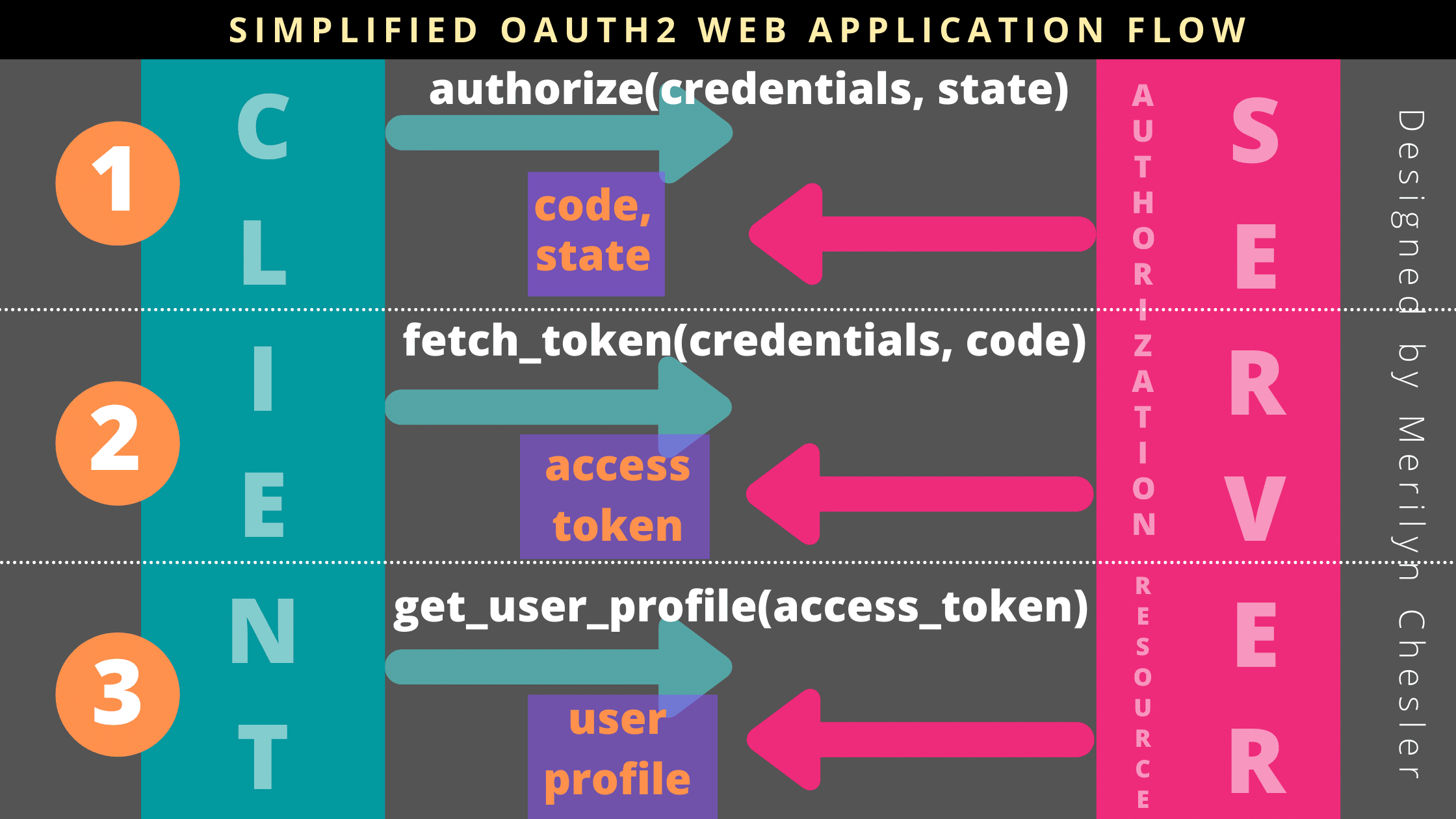
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an authentication protocol that allows users to grant third-party applications limited access to their resources without sharing their login credentials. In this article, we'll explore how to use OAuth with Python.
What is OAuth?
OAuth is a three-legged process:
Client Registration: The client (third-party application) registers itself with the Authorization Server (AS) and obtains a client ID. Authorization Request: The client redirects the user to the AS, requesting an authorization token (access token). Access Token Response: The user grants or denies access, and the AS responds with an access token if approved.Python OAuth Libraries
To use OAuth in Python, you can rely on popular libraries:
requests-oauthlib: A library that provides a simple interface for working with OAuth. oauthlib: A more comprehensive library that supports multiple OAuth flavors (e.g., OAuth 1.0a, OAuth 2.0). python-social-auth: A library that simplifies social media authentication using OAuth.For this example, we'll use requests-oauthlib.
OAuth Flow in Python
Let's assume you're building a Twitter-based chatbot using Python:
import requests
from requests_oauthlib import OAuth2Session
Client ID and secret from Twitter Developer Dashboard
client_id = "your_client_id"
client_secret = "your_client_secret"
Redirect URI (where the user will be redirected after authorization)
redirect_uri = "http://localhost:8000/callback"
Scope for our chatbot (e.g., read-only access to tweets)
scope = ["read"]
Create an OAuth2Session instance
oauth = OAuth2Session(client_id, redirect_uri=redirect_uri, scope=scope)
Redirect the user to Twitter's authorization page
authorization_url, state = oauth.authorization_url(
"https://api.twitter.com/oauth/authorize"
)
print(f"Please go to: {authorization_url}")
Handling the Authorization Response
After the user grants or denies access, they will be redirected back to your application with an authorization code. You'll need to exchange this code for an access token:
# Handle the callback from Twitter (authorization code)
token = oauth.fetch_token(
"https://api.twitter.com/oauth/token",
client_secret=client_secret,
authorization_response=requests.get("http://localhost:8000/callback")
)
Use the access token to make requests on behalf of the user
access_token = token["access_token"]
Making Requests
Now that you have an access token, you can use it to make requests to Twitter's API:
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}"}
response = requests.get("https://api.twitter.com/1.1/statuses/user_timeline.json", headers=headers)
Handle the response (e.g., print tweets)
print(response.json())
In this example, we used requests-oauthlib to handle the OAuth flow and exchange the authorization code for an access token. We then used the access token to make a request to Twitter's API.
Security Considerations
When working with OAuth in Python, keep the following security best practices in mind:
Secure Client Secrets: Store your client ID and secret securely (e.g., environment variables, encrypted files). Validate Tokens: Verify the authenticity of received tokens using a token validation service. Handle Token Revocation: Implement a mechanism to revoke access tokens when necessary (e.g., user revokes consent).By following these guidelines and leveraging Python libraries like requests-oauthlib, you can efficiently integrate OAuth into your application.
How to get access token from authorization code in Python?
I'd be happy to help you with that!
To get an access token from an authorization code in Python, you'll need to use the requests library and a bit of OAuth2 magic. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Step 1: Obtain the Authorization Code
First, your users will need to authenticate with your application using their client ID and secret key. You can then redirect them to an authorization URL that includes the code parameter. The URL should look something like this:
https://example.com/authorize?client_id=your_client_id&response_type=code&redirect_uri=https://example.com/callback&scope=profile+email
The user will enter their credentials and, if successful, will be redirected back to your application with an authorization code. For example:
https://example.com/callback?code=special_code_123&state=some_random_state_value
Step 2: Exchange the Authorization Code for an Access Token
Now that you have the authorization code, you can use it to exchange it for an access token. You'll need to send a POST request to your authorization server's token endpoint with the following parameters:
import requeststoken_url = 'https://example.com/token'
client_id = 'your_client_id'
client_secret = 'your_client_secret'
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
data = {
'grant_type': 'authorization_code',
'code': 'special_code_123',
'redirect_uri': 'https://example.com/callback',
'client_id': client_id,
'client_secret': client_secret
}
response = requests.post(token_url, headers=headers, data=data)
Step 3: Handle the Token Response
The token endpoint will respond with a JSON payload containing an access token, a refresh token, and some additional metadata. You should handle this response by extracting the access token and using it to authenticate further requests:
if response.status_code == 200:token_response = response.json()
access_token = token_response['access_token']
Use the access token for subsequent requests...else:
print(f"Failed to obtain access token: {response.text}")
Putting it All Together
Here's a complete example of how you might use Python to get an access token from an authorization code:
import requeststoken_url = 'https://example.com/token'
client_id = 'your_client_id'
client_secret = 'your_client_secret'
def get_access_token(redirect_uri, code):
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
data = {
'grant_type': 'authorization_code',
'code': code,
'redirect_uri': redirect_uri,
'client_id': client_id,
'client_secret': client_secret
}
response = requests.post(token_url, headers=headers, data=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
token_response = response.json()
access_token = token_response['access_token']
return access_token
else:
print(f"Failed to obtain access token: {response.text}")
return None
redirect_uri = 'https://example.com/callback'
code = 'special_code_123'
access_token = get_access_token(redirect_uri, code)
print(access_token)
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions or need further clarification.





























