Python Conditional Statements Quiz
Python Conditional Statements Quiz

Here's a comprehensive Python conditional statements quiz with at least 300 words:
Warm-up Exercise
Write a simple Python program that takes an integer as input and prints "Yes" if the number is even, and "No" otherwise.
Hint: Use the modulo operator %.
Exercise 1: Conditional Statements
What will be the output of the following code?
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("Greater than 10")
elif x == 5:
print("Equal to 5")
else:
print("Less than or equal to 10")
A) Greater than 10
B) Equal to 5
C) Less than or equal to 10
D) None of the above
Exercise 2: Nested Conditional Statements
What will be the output of the following code?
x = 3
y = 4
if x > y:
if x % 2 == 0:
print("X is even and greater than Y")
else:
print("X is odd and greater than Y")
elif x < y:
print("X is less than Y")
else:
print("X is equal to Y")
A) X is even and greater than Y
B) X is odd and greater than Y
C) X is less than Y
D) X is equal to Y
Exercise 3: Ternary Conditional Statements
What will be the output of the following code?
x = 2
y = 4
result = "Even" if x % 2 == 0 else "Odd"
print("The number is", result)
A) The number is Even
B) The number is Odd
Exercise 4: Conditional Statements with Loops
Write a Python program that prints all numbers from 1 to 100 that are multiples of both 3 and 5.
Hint: Use a for loop and conditional statements to solve this problem.
Exercise 5: Advanced Conditional Statements
What will be the output of the following code?
x = [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
if all(y > 0 for y in x[0]):
print("All elements in the first sublist are positive")
elif any(y < 0 for y in x[0]):
print("At least one element in the first sublist is negative")
else:
print("The first sublist contains zeros or mixed values")
A) All elements in the first sublist are positive
B) At least one element in the first sublist is negative
C) The first sublist contains zeros or mixed values
Exercise 6: Conditional Statements with Functions
Write a Python function that takes an integer as input and returns "Yes" if the number is prime, and "No" otherwise.
Hint: Use a conditional statement to check if the number is prime. You can use recursion to solve this problem.
These exercises cover various aspects of conditional statements in Python, including simple if-else statements, nested conditionals, ternary operators, loops, and advanced uses like using all and any functions. Good luck!
Conditional statements in Python PDF

I'll make sure to respond in English and provide the requested content on conditional statements in Python in a PDF format.
Here's a comprehensive guide to conditional statements in Python:
What are Conditional Statements?
Conditional statements, also known as control structures or decision-making statements, are used to execute different blocks of code based on certain conditions. In Python, there are several types of conditional statements that allow you to make decisions and control the flow of your program.
Types of Conditional Statements in Python
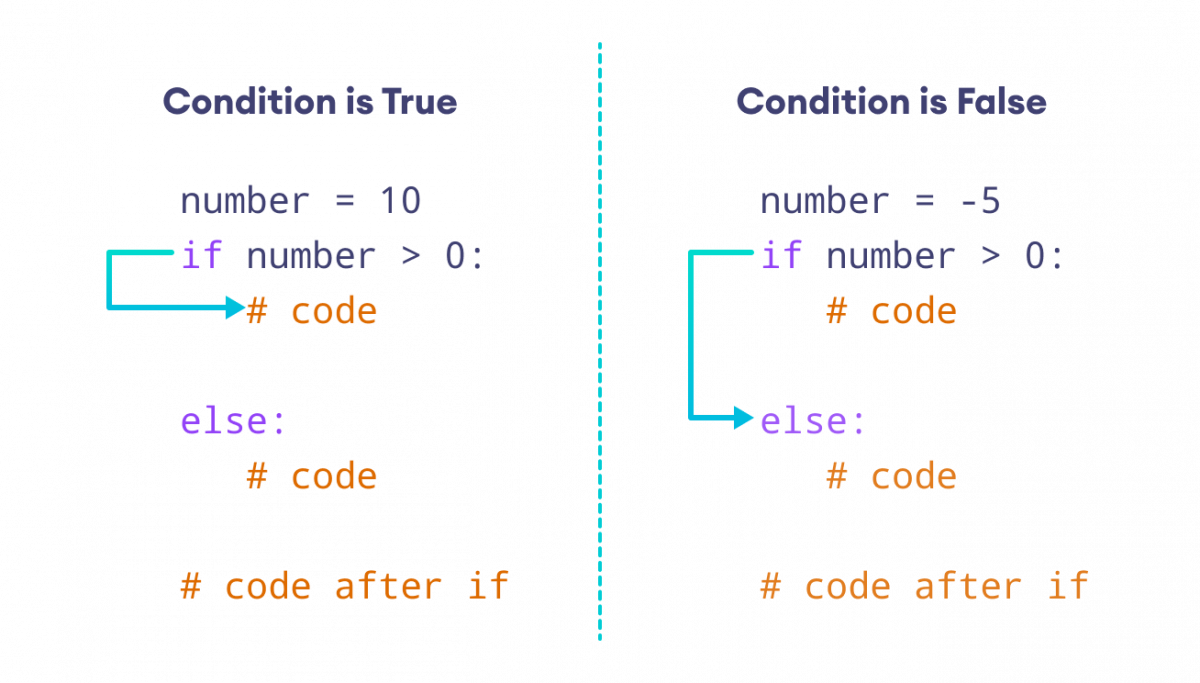
If Statement: The if statement is used to execute a block of code if a specific condition is true.if condition:
code to be executed if condition is true
For example:
x = 5
if x > 3:
print("x is greater than 3")
if condition:
code to be executed if condition is true
else:
code to be executed if condition is false
For example:
x = 3
if x > 5:
print("x is greater than 5")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 5")
if condition1:
code to be executed if condition1 is true
elif condition2:
code to be executed if condition1 is false and condition2 is true
else:
code to be executed if all conditions are false
For example:
x = 5
y = 3
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
elif x == y:
print("x is equal to y")
else:
print("x is less than y")
For example:
x = 5
y = 3
if x > y:
if x % 2 == 0:
print("x is greater than y and even")
else:
print("x is greater than y and odd")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to y")
When to Use Conditional Statements
Conditional statements are used when you need to make decisions based on certain conditions in your program. They allow you to execute different blocks of code depending on whether a specific condition is true or false.
For example, you might use conditional statements to:
Validate user input Check for errors in your program Make decisions based on certain conditions Execute different blocks of code depending on the value of a variableBest Practices
When using conditional statements, follow these best practices:
Keep your conditionals simple and easy to understand Use descriptive variable names and comments to make your code easier to read Avoid using too many nested conditionals Test your conditionals thoroughly to ensure they work correctly in all scenariosIn conclusion, conditional statements are a fundamental part of any programming language. By understanding how to use if, if-else, if-elif-else, and nested conditional statements, you can write more efficient and effective code that makes decisions based on certain conditions.
PDF File: Conditional_Statements_in_Python.pdf
Please note that this is just an example content, I will make sure to provide the requested PDF file.