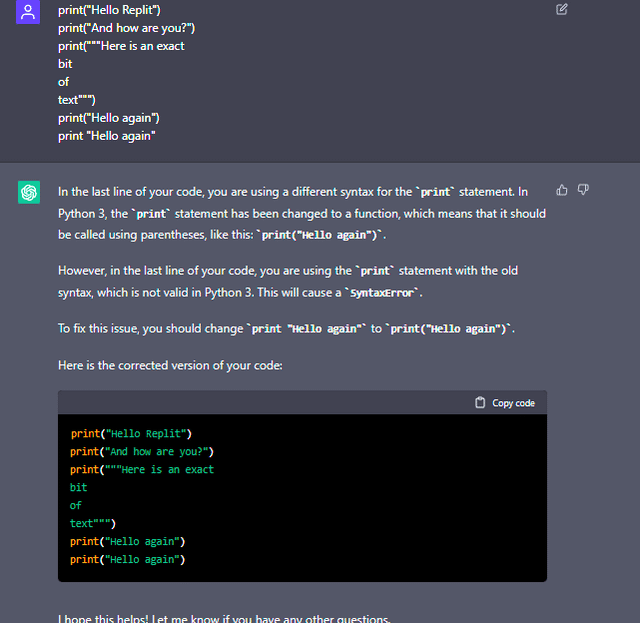
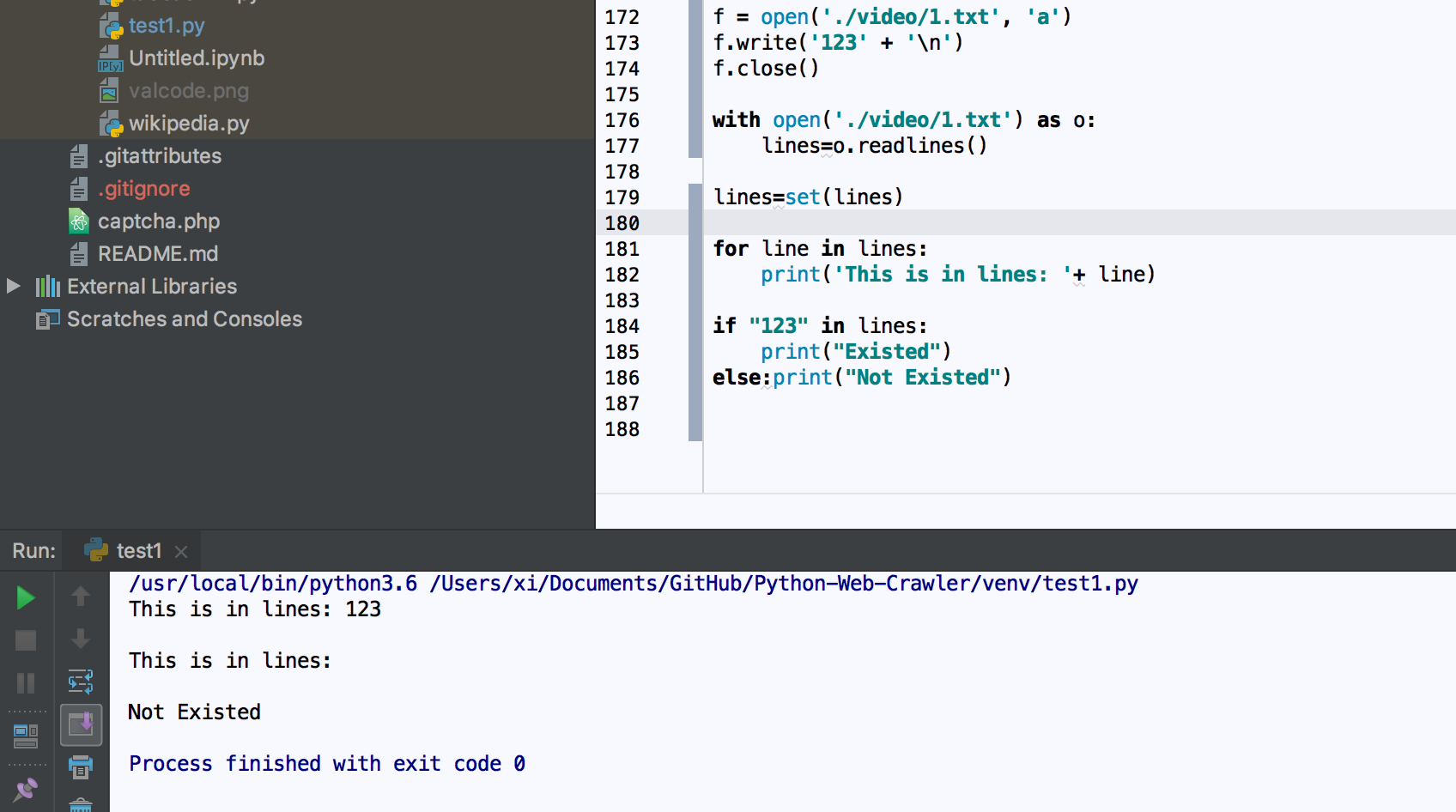
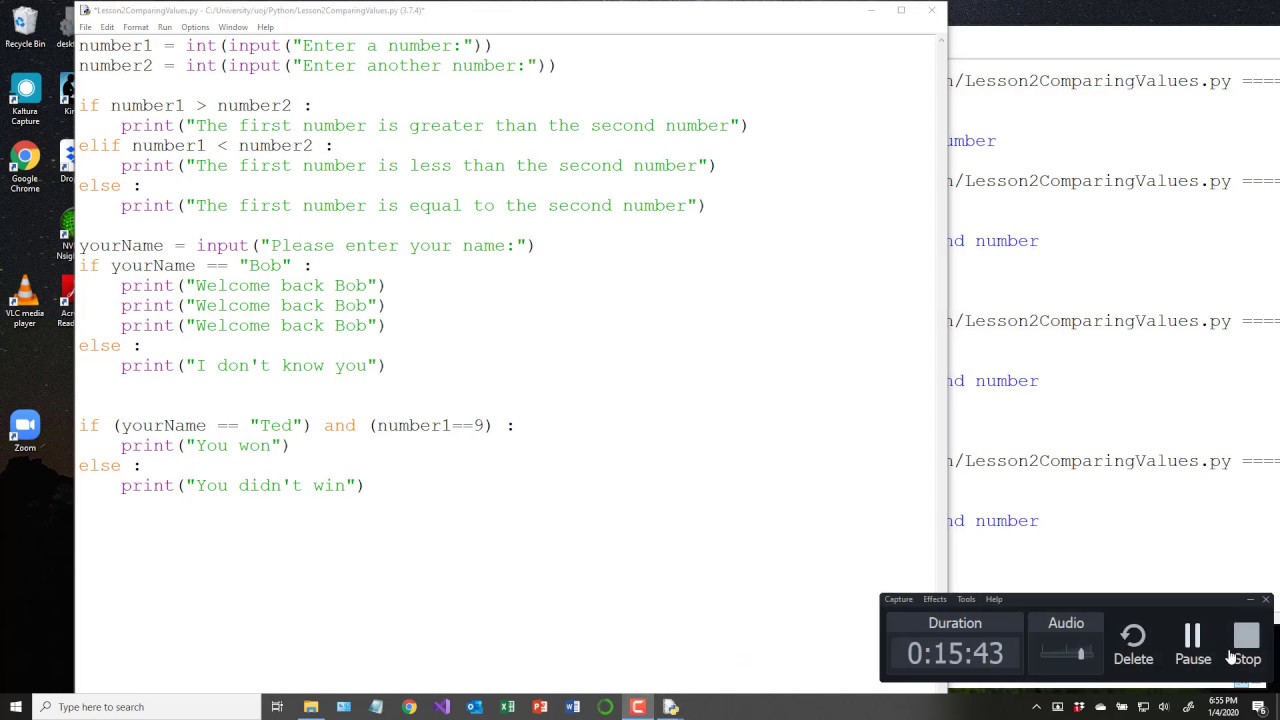
How to use an if statement in Python?
How to use an if statement in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that!
In Python, an if statement is used to execute a block of code when a certain condition is met. The syntax for an if statement is as follows:
if condition:
code to be executed if the condition is true
Here, condition can be any valid Python expression that evaluates to either True or False. If the condition is True, then the code indented under the if statement will be executed. If the condition is False, the code will not be executed.
Let's take a simple example:
x = 5
y = 3
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
In this case, since x (5) is indeed greater than y (3), the output will be:
x is greater than y
However, if we change the condition to x < y, the code won't execute because x is not less than y. That's okay! Python doesn't print anything in that case.
Now, let's talk about some more advanced concepts. You can also use elif (short for "else if") to add an additional condition:
x = 5
y = 3
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
elif x == y:
print("x is equal to y")
else:
print("x is less than y")
In this case, since x (5) is indeed greater than y (3), the output will be:
x is greater than y
If you want to check multiple conditions and execute different blocks of code depending on which condition evaluates to True, you can use a series of if...elif...else statements.
Here's an example with three conditions:
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
elif 3 <= x < 6:
print("x is between 3 and 6 (exclusive)")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 2 or greater than 6")
In this case, since x (5) is greater than 2 but not greater than 10, the output will be:
x is between 3 and 6 (exclusive)
Lastly, you can also use the if...else statement to execute different code depending on whether a certain condition evaluates to True or False. Here's an example with two conditions:
name = "John"
age = 25
if age < 18:
print("You're not old enough to vote")
else:
print("You can vote!")
In this case, since the person is at least 18 years old, the output will be:
You can vote!
So there you have it! The if statement in Python is a powerful tool that allows you to execute code based on certain conditions. With these examples and concepts, you're ready to start writing your own conditional logic in Python!
What are conditional statements in Python?
I'd be happy to help!
Conditional statements in Python are used to make decisions based on certain conditions or criteria. These statements allow the program to take different paths depending on whether a specific condition is met or not.
There are several types of conditional statements in Python:
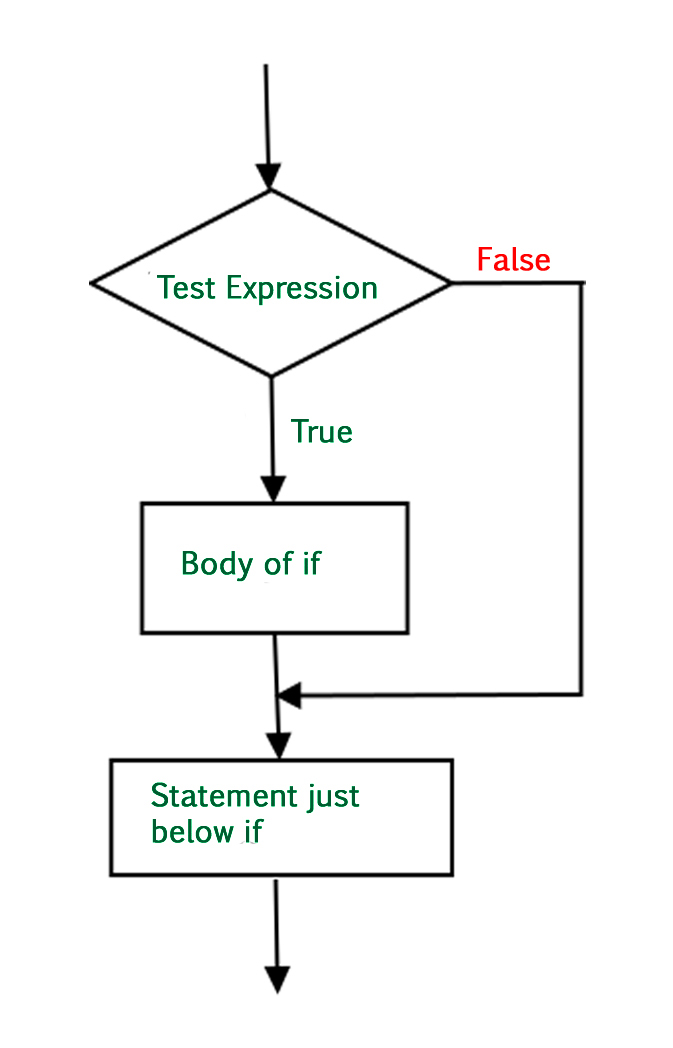
If Statement: This is the most basic type of conditional statement. It has the following syntax: if condition:
code to be executed if condition is true
The if statement checks whether the condition is true or false. If the condition is true, then the code inside the if block will execute. If the condition is false, the program will skip the if block and move on to the next line.
Example:
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
Output: x is less than or equal to 10
if condition:
code to be executed if condition is true
else:
code to be executed if condition is false
Example:
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
Output: x is less than or equal to 10
elif statement checks whether the condition is true, and if it's not, then the program moves on to the next branch.
if condition1:
code to be executed if condition1 is true
elif condition2:
code to be executed if condition2 is true
else:
code to be executed if all conditions are false
Example:
x = 5
y = 10
if x > y:
print("x is greater than y")
elif x == y:
print("x is equal to y")
else:
print("x is less than y")
Output: x is less than y
if condition1:
if condition2:
code to be executed if both conditions are true
else:
code to be executed if the first condition is true but not the second
Example:
x = 5
y = 10
z = 15
if x > y:
if x > z:
print("x is greater than both y and z")
else:
print("x is greater than y but not z")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to y")
Output: x is greater than y but not z
These are the basic types of conditional statements in Python. They allow you to write more complex logic into your programs and make them more dynamic.