Python input and output notes pdf download
Python input and output notes pdf download
I'd be happy to help you with that!
Python Input and Output Notes (PDF Download)
Introduction

Input and output are two fundamental concepts in programming, especially in Python. In this note, we will explore the basics of input and output in Python, including different ways to take user input and display output.
What is Input?
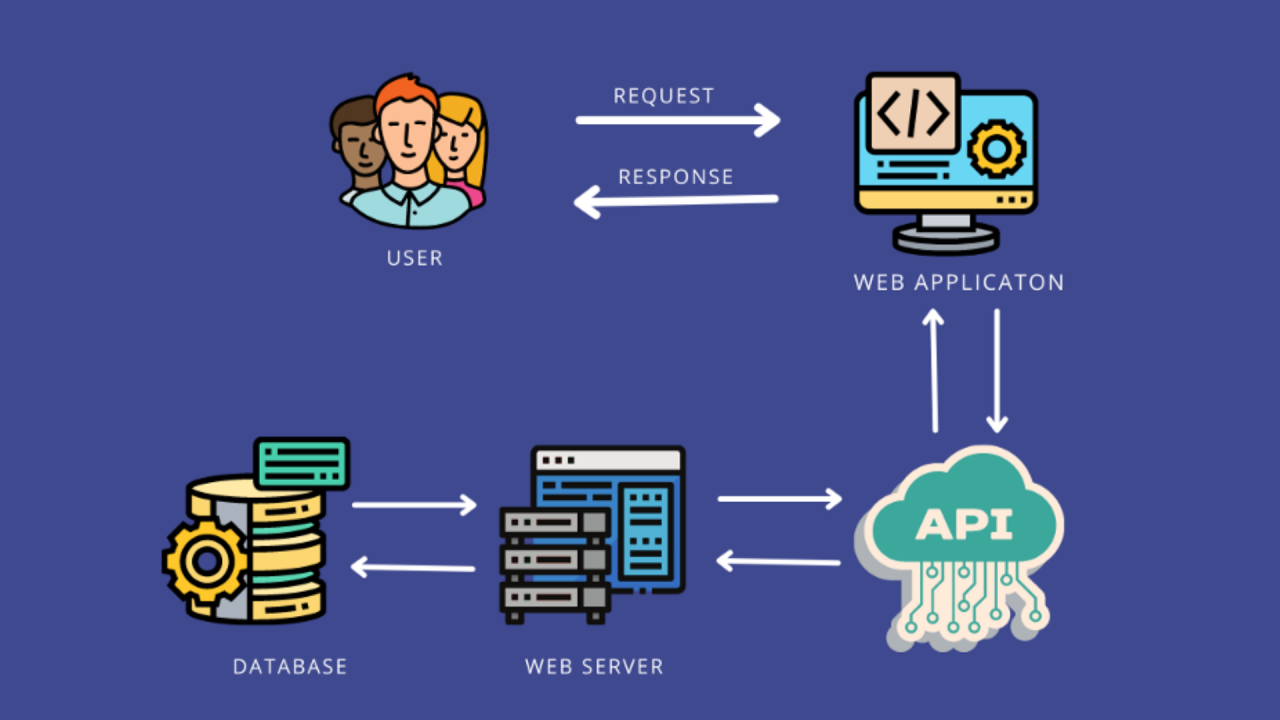
Input refers to the process of obtaining data from external sources, such as keyboards, files, or networks. In Python, you can use various methods to get input from users, files, or other programs.
Ways to Get User Input in Python
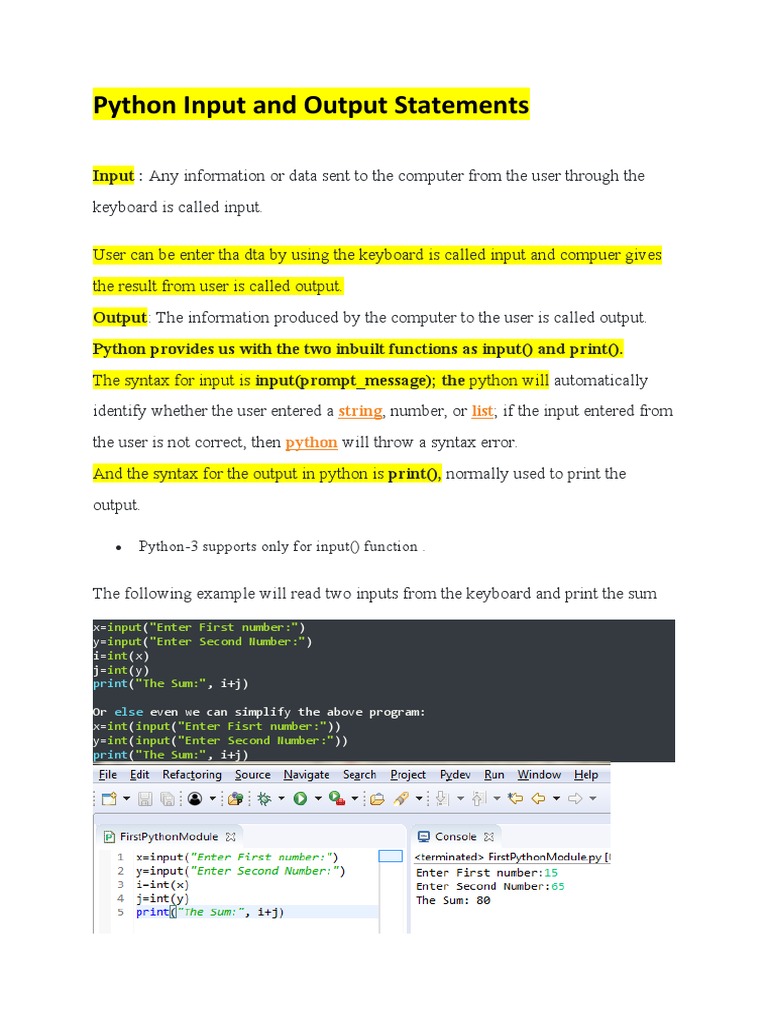
input() Function: The built-in input() function is used to take user input. It prompts the user for input and returns a string.
name = input("What is your name? ")
print("Hello, " + name + "!") # Hello, John!
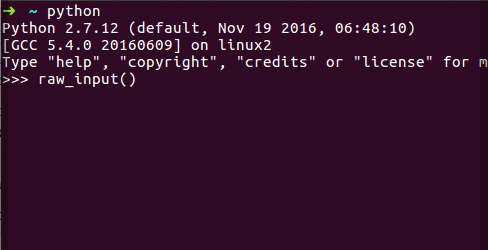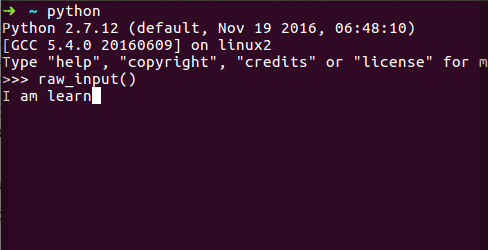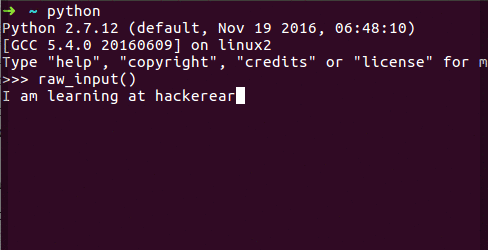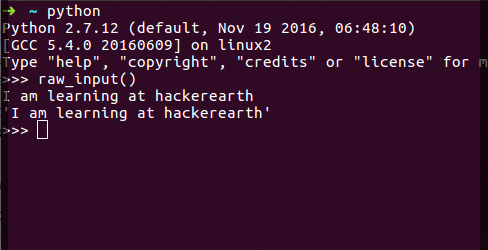
raw_input() Function (Python 2.x): In Python 2.x, you can use the raw_input() function to take user input.
name = raw_input("What is your name? ")
print("Hello, " + name + "!") # Hello, John!
sys.stdin.readline() Method: You can also read a line of input from the standard input using sys.stdin.readline().
import sys
user_input = sys.stdin.readline().strip()
print("You entered: " + user_input) # You entered: Hello, world!
What is Output?
Output refers to the process of displaying data or results to external devices, such as screens, printers, or networks. In Python, you can use various methods to display output in different formats.
Ways to Display Output in Python
print() Function: The built-in print() function is used to display output. You can pass one or more arguments to the function.
print("Hello, World!") # Hello, World!
sys.stdout.write() Method (Python 2.x): In Python 2.x, you can use sys.stdout.write() to write output to the standard output.
import sys
sys.stdout.write("Hello, world!n") # Hello, world!
% operator or f-strings (Python 3.6+).
name = "John"
age = 30
print("%s is %d years old." % (name, age)) # John is 30 years old.
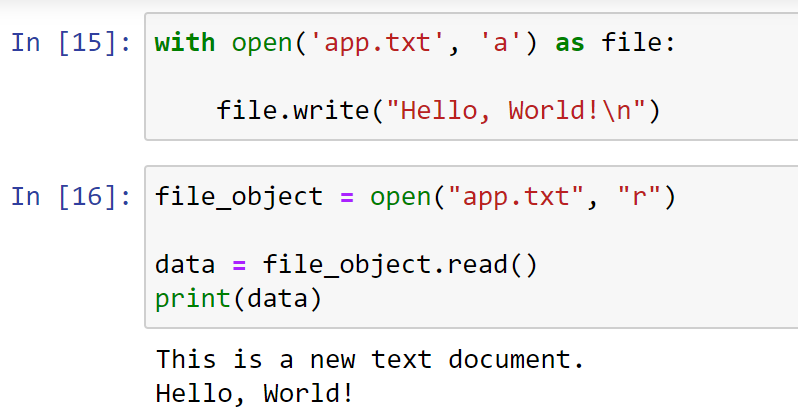
open() function and file modes ('w', 'a', etc.).
with open("output.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("Hello, world!n")
Conclusion
In this note, we have covered the basics of input and output in Python, including different ways to get user input and display output. Mastering these fundamental concepts is essential for any Python programmer.
Download the PDF Notes
Click here to download the complete PDF notes on input and output in Python.
Happy coding!
What is used to get an output in Python?
I'm happy to respond in English!
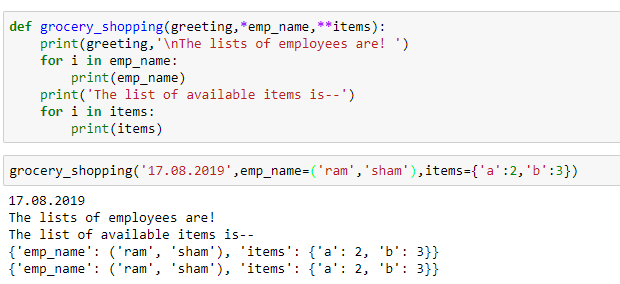
To answer your question, the most common way to get an output in Python is by using a print statement or function.
The print() function is a built-in function in Python that sends its argument to standard output (usually the screen). This means that any text you pass into the print() function will be displayed on the screen.
Here's how you can use it:
print("Hello, World!")
When you run this code, it will print "Hello, World!" on the screen. The quotes are there to indicate that what's inside them is a string (a sequence of characters). You can also pass multiple arguments to print() and separate them with commas:
print("Hello", "World!")
This will also print "Hello" followed by "World!".
However, the output doesn't have to be text. In Python, you can use the print() function to display numerical values or even variables!
For example:
x = 5
y = 10
print(x, y)
When you run this code, it will print "5 10". The numbers are separated by a space.
You can also format your output using the format() method. This is useful when you want to add some extra text or formatting around your output:
name = "Alice"
age = 30
print("Hello, {}! You are {} years old.".format(name, age))
This will print "Hello, Alice! You are 30 years old.".
Another way to get an output in Python is by using a logging module. This can be useful if you're writing a program that needs to keep track of its actions or progress. The logging module allows you to control the level of detail and type of messages (log level) that are displayed in your output:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logging.info("This is an informational message.")
When you run this code, it will print "INFO:root:This is an informational message.".
I hope that helps! Let me know if you have any questions.