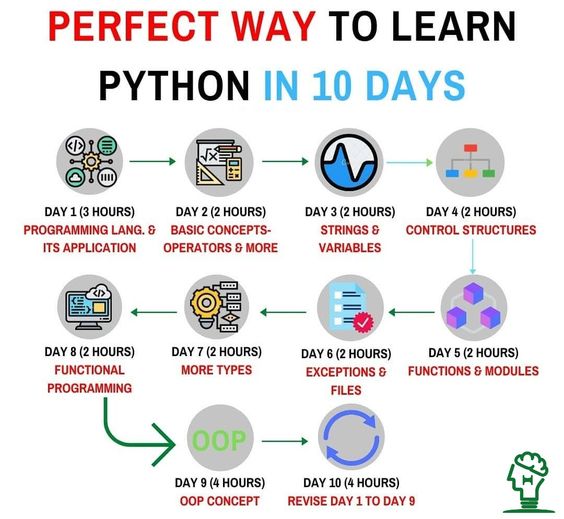
Python logical operators w3schools list
Python logical operators w3schools list
I'm happy to help!
Here is the list of Python logical operators from W3Schools:
Logical Operators
Python supports several logical operators, which are used to combine boolean expressions and make decisions based on conditions.
and: This operator returnsTrue if both operands are True.
Example: a = 5; b = 7; print(a > 4 and b > 6)
Output: True
True if at least one of the operands is True.
Example: a = 3; b = 8; print(a < 10 or b > 5)
Output: True
False if the operand is True, and vice versa.
Example: x = 1; print(not x == 0)
Output: True
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana']; print('banana' in fruits)
Output: True
in. It checks if a value does not exist in an iterable.
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana']; print('grape' not in fruits)
Output: True
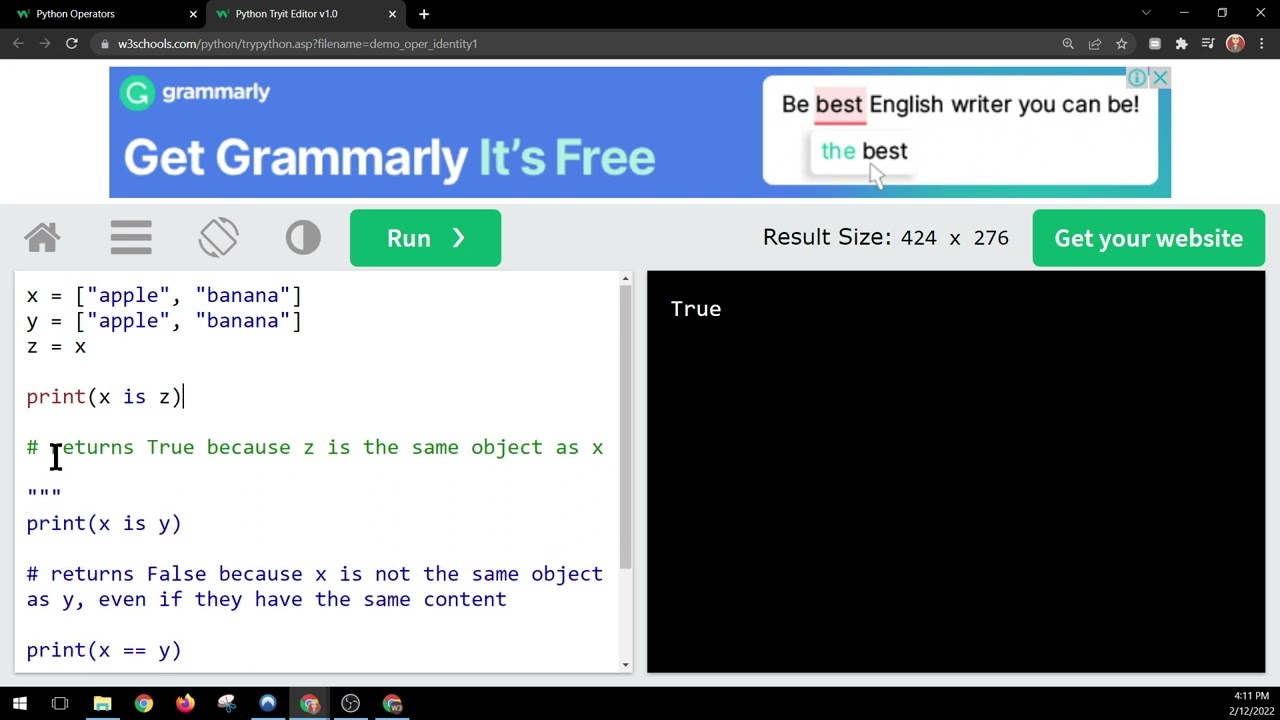
Example: x = [1, 2, 3]; y = x; print(x is y)
Output: True (because x and y reference the same list)
is not and is.
Example: x = [1, 2, 3]; y = 5; print(x is not y)
Output: True (because x and y do not reference the same list)
Tips
The order of operations matters! When combining logical operators, Python evaluates them from left to right. Make sure you're using parentheses to group your expressions correctly! Don't be afraid to test out these operators in a code editor or IDE!I hope this helps you master Python's logical operators!
What are operators in Python W3schools?
I'm happy to respond in English!
According to W3Schools, in Python, an operator is a symbol used to perform operations on values and expressions. In other words, operators are used to manipulate data and variables in your code.
Python provides various types of operators, including:
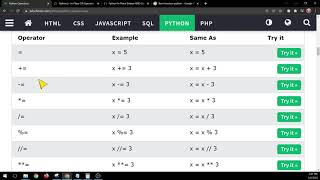
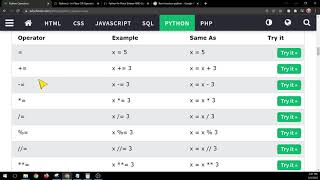
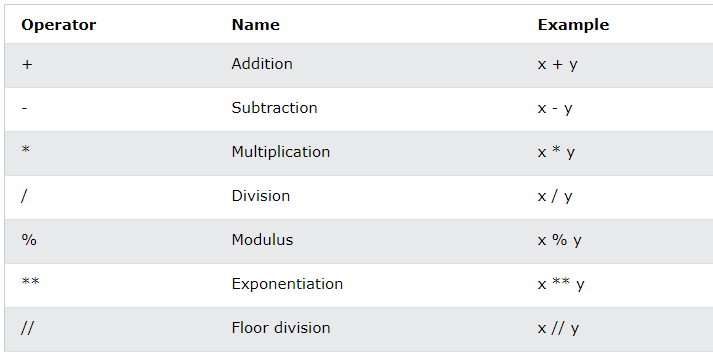
Arithmetic Operators: These operators are used for mathematical calculations, such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/ or // for integer division), modulus (%), exponentiation (**).Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x + y) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y) (output: True)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y and x != 0) (output: False)
Example: x = 5; x += 3; print(x) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x & y) (output: 1)
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana']; print('apple' in fruits) (output: True)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x is y) (output: False)
Example: print(2 ** 3) (output: 8)
In Python, these operators can be used in various combinations to create complex expressions and calculations. For example, you can use parentheses to group operations or use the precedence rules for each operator type.
Overall, understanding the different types of operators in Python is crucial for writing efficient, readable, and effective code!