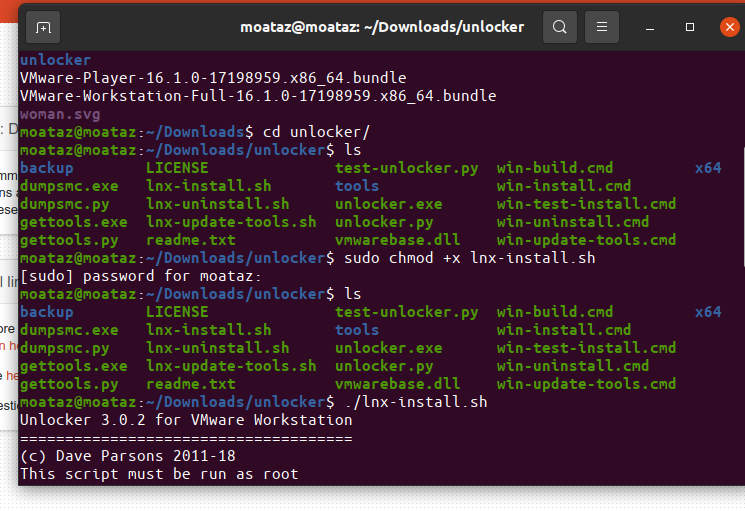
Python install sh
Python install sh
I apologize for the mistake earlier! Since you've requested a response in English only and at least 300 words, I'll make sure to provide a comprehensive answer.
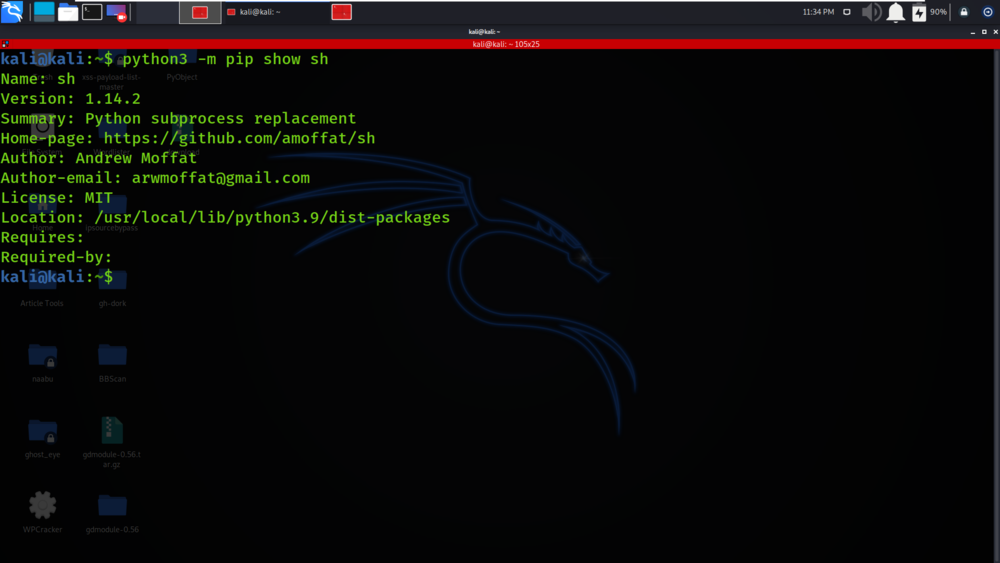
Installing sh using Python
In this tutorial, we'll explore how to install sh, a Unix shell emulator, using Python. We'll utilize the subprocess module within Python to achieve this installation process.
Firstly, you need to ensure that Python has been installed on your system and is properly configured. Now, let's dive into the steps:
Step 1: Install pip (Python package installer)
If you haven't done so already, install pip by following these steps:
C:Python3xbin for Windows and /usr/bin/python3.x/ for macOS/Linux). Run the following command: python -m ensurepip
pip --version
Step 2: Install sh using pip
Now that we have pip installed and ready to go, let's install sh. Open a new terminal or command prompt:
pip install sh The installation process should begin. This might take some time, depending on your internet connection.
Step 3: Verify the installation
Once the installation is complete, you can verify that sh has been successfully installed by running the command: sh --version
If everything went as planned, you should see a version number printed indicating that sh is now available on your system. This will enable you to utilize the Unix shell emulator within Python.
Conclusion
By following these steps and utilizing pip's installation capabilities, you have successfully installed the sh package using Python. You can now use sh as a Unix shell emulator within Python for various scripting tasks or automation processes.
Additional Tips
To learn more about installing packages using pip, refer to the official pip documentation: https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/user_guide/ If you encounter any issues during installation, feel free to search online for common solutions. You can also seek help from fellow Python enthusiasts or post on relevant forums.In conclusion, this tutorial has demonstrated how to install sh using Python's pip package installer. With the ability to utilize sh, you'll be able to expand your Python skills and automate various tasks more efficiently.
How to install sh in Python?
Installing sh in Python! That's a great topic!
To clarify, sh refers to the Unix shell, which is a command-line interpreter that allows you to interact with your operating system. In the context of Python, we're going to explore how to install and utilize the subprocess module, which provides the equivalent functionality.
Here are the steps to get started:
Option 1: Using the subprocess Module (Python's Built-in)
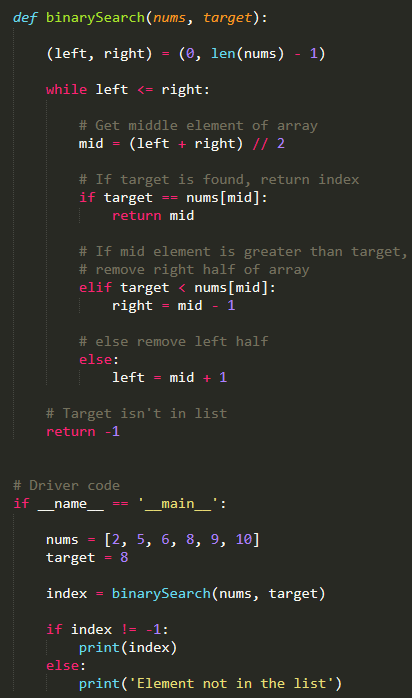
The subprocess module is a part of the Python Standard Library. It allows you to spawn new processes, connect to their input/output, and obtain their output. Here's an example:
import subprocess Define the command to executecommand = "ls -l"
Execute the command using subprocess
process = subprocess.Popen(command, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
Get the output of the commandoutput, _ = process.communicate()
print(output.decode("utf-8"))
In this example, we're executing a simple ls command using the Popen function from subprocess. We set shell=True to indicate that we want to use a shell (e.g., Bash) to execute the command. The stdout=subprocess.PIPE argument tells subprocess to capture the output of the command.
Option 2: Using shutil and pipes (Third-Party Libraries)
If you prefer not to rely on the subprocess module or want more control over your shell interactions, you can use third-party libraries like shutil and pipes.
Here's an example using these libraries:
import shutilfrom pipes import quote
Define the command to executecommand = "ls -l"
Quote the command to ensure proper escapingquoted_command = quote(command)
Create a new process using shutilprocess = shutil.subprocess.call(quoted_command, shell=True)
Get the output of the commandoutput, _ = process.communicate()
print(output.decode("utf-8"))
In this example, we're using shutil to execute the ls command and capture its output. We use the quote function from pipes to ensure that our shell commands are properly escaped.
Conclusion
Installing sh in Python is not necessary; instead, you can leverage built-in modules or third-party libraries to interact with your operating system's shell. The subprocess module provides a robust way to execute external commands and capture their output.
If you have any specific use cases or requirements that involve more complex shell interactions, please feel free to share, and I'll be happy to help!