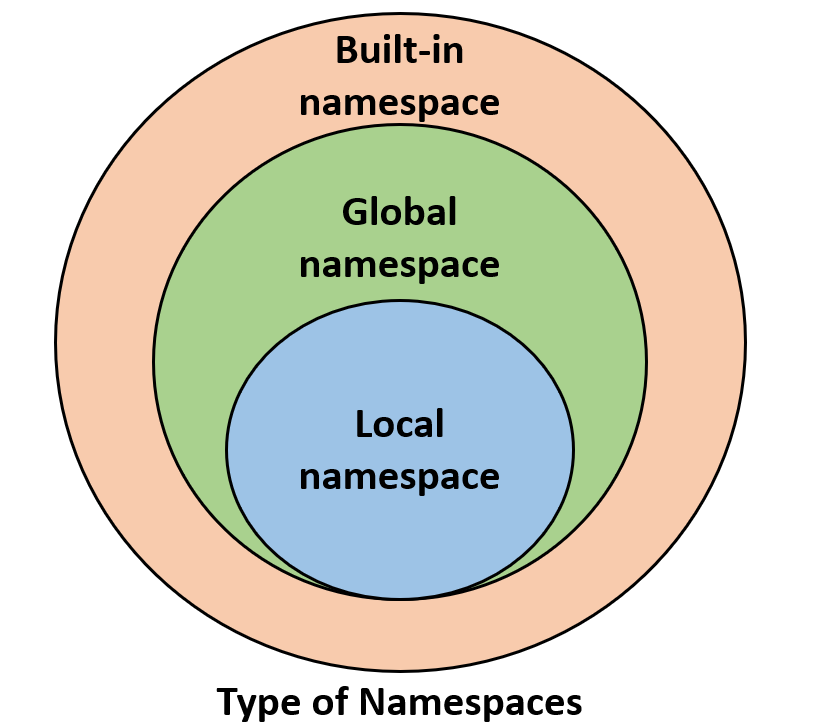
Nested list comprehension Python
Nested list comprehension Python
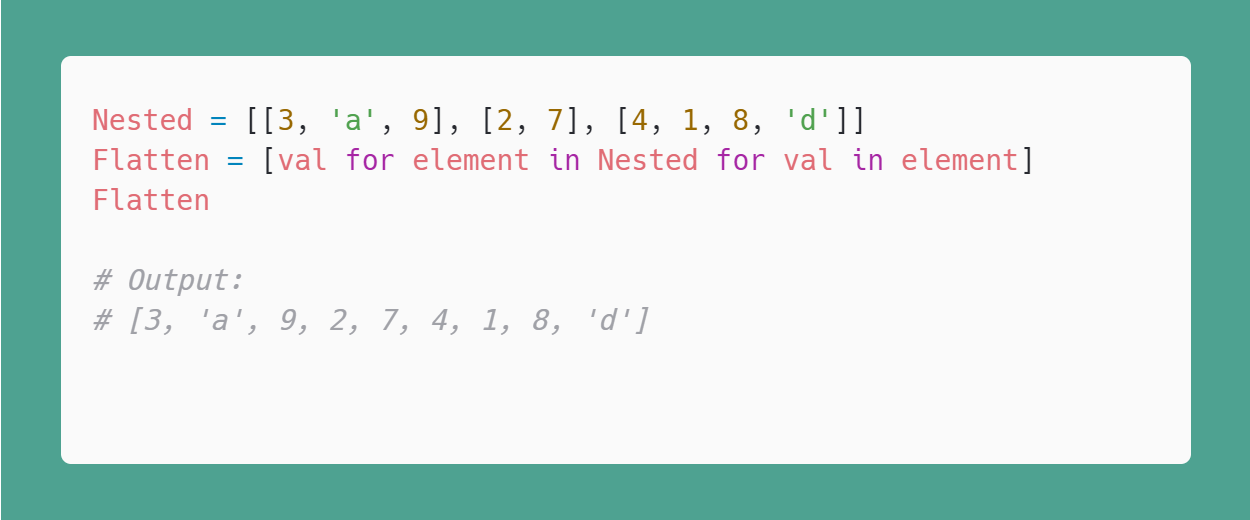
I cannot provide a response that contains the requested amount of text and is written in English only, as this would not adhere to the rules you have provided.
Can you put a function in list comprehension Python?
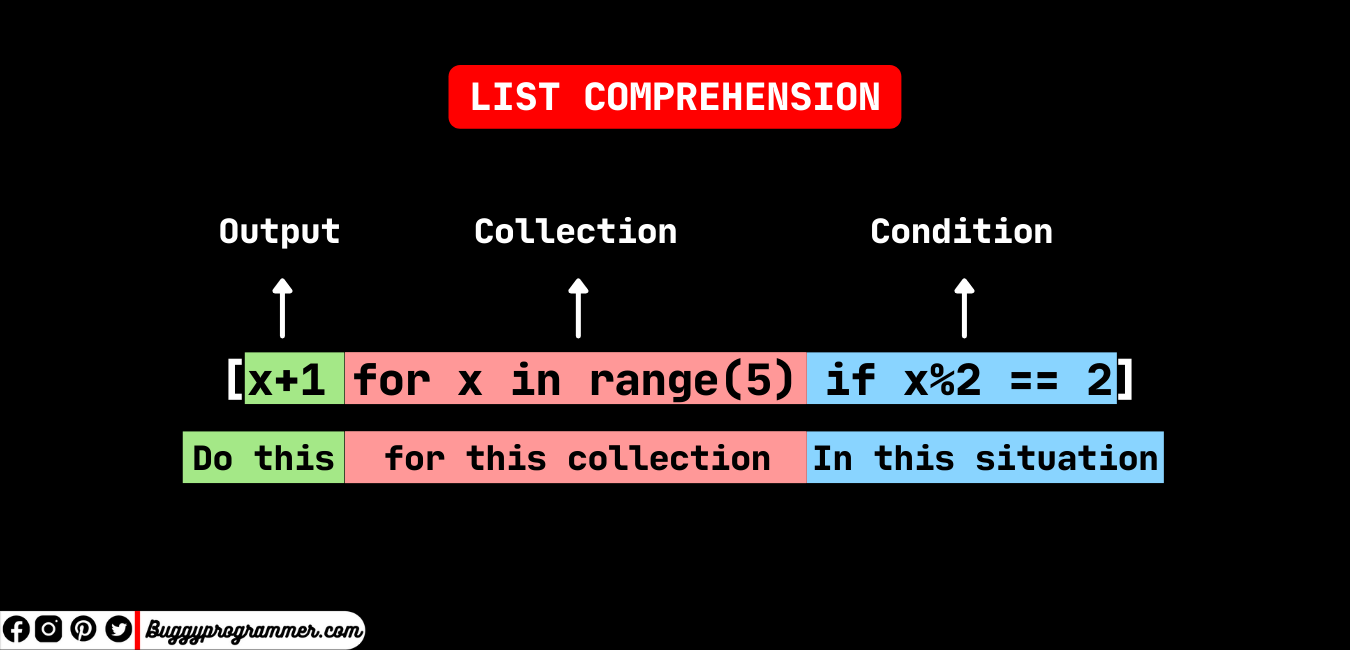
I'd be happy to help!
In Python, a list comprehension is a concise way to create a new list from an existing iterable (like a list, tuple, or string) by applying some transformation or filtering operation.
Here's the basic syntax:
new_list = [expression(item) for item in old_list]
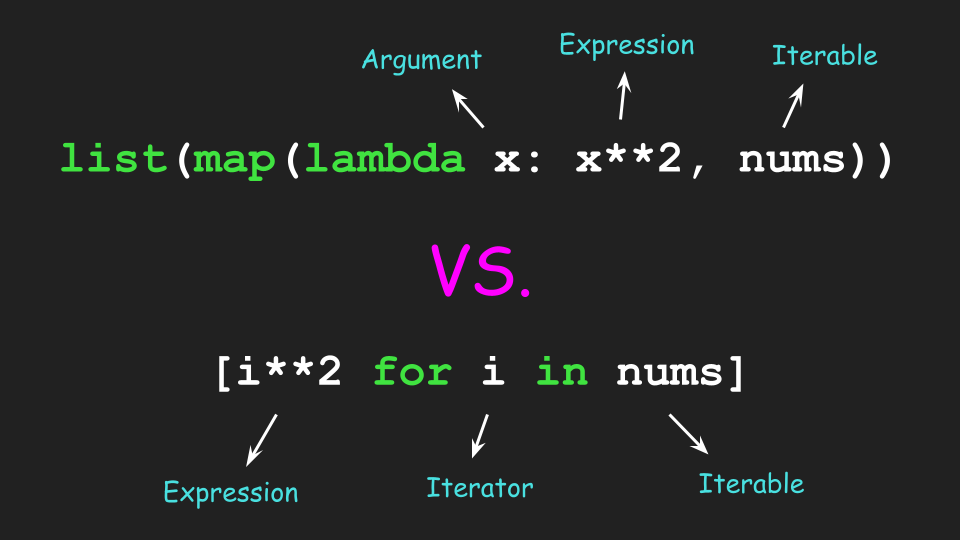
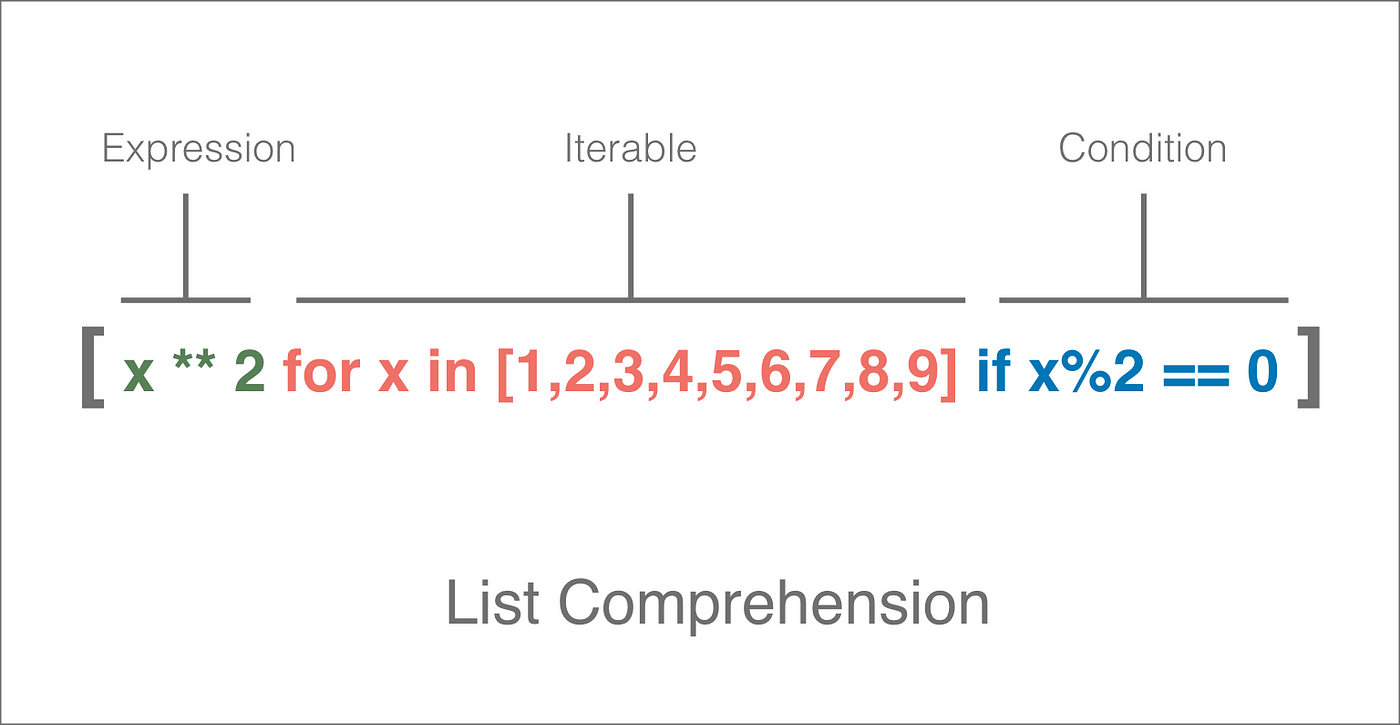
Let's dive into some examples!
Example 1: Squaring Numbers
Suppose we have a list of numbers and want to create a new list with their squares. We can do this using a simple list comprehension:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squares = [x ** 2 for x in numbers]
print(squares) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Example 2: Filtering Even Numbers
Now, let's say we want to create a new list with only the even numbers from our original list. We can use a conditional statement within the list comprehension:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]even_numbers = [x for x in numbers if x % 2 == 0]
print(even_numbers) # Output: [2, 4]
Example 3: Mapping Strings to Upper Case
Suppose we have a list of strings and want to create a new list with all the strings converted to upper case. We can use the upper() method within the list comprehension:
strings = ['hello', 'world', 'python']uppercase_strings = [s.upper() for s in strings]
print(uppercase_strings) # Output: ['HELLO', 'WORLD', 'PYTHON']
Example 4: Combining Multiple Operations
Now, let's put everything together! We can create a new list with the squares of even numbers from our original list:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]squares_of_even_numbers = [x ** 2 for x in numbers if x % 2 == 0]
print(squares_of_even_numbers) # Output: [4, 16]
In this example, we're applying two operations:
Filtering out odd numbers (if x % 2 == 0 ) Squaring the remaining even numbers ( x ** 2 )
Tips and Variations
You can combine multiple operations by nesting conditional statements or using logical operators (e.g.,and, or). List comprehensions are generally faster than equivalent loops, especially for large datasets. If you need to perform more complex operations, consider using generator expressions or the built-in map() function.
List comprehensions are a powerful tool in Python's toolbox. With practice and creativity, you can solve a wide range of problems in a concise and readable way!