What are the conditional statements used in Python?
What are the conditional statements used in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that!
Python provides a rich set of conditional statements to control the flow of your program based on certain conditions or criteria. These statements allow you to make decisions and take actions accordingly. Let's dive into the world of conditional statements in Python!
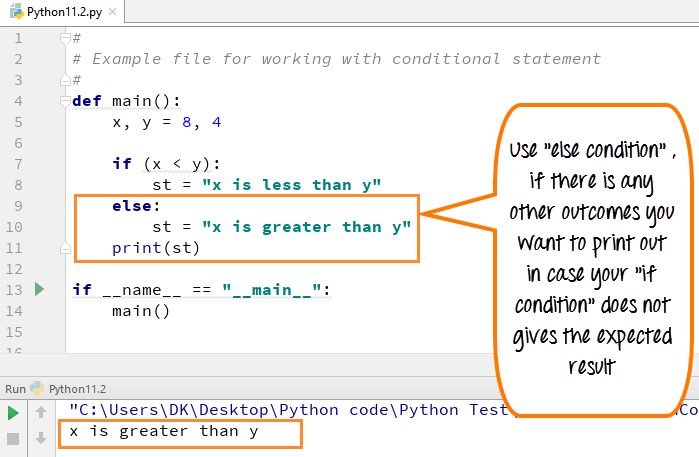
1. If-else StatementThe most common and fundamental conditional statement is the if-else statement. It checks a condition and executes a block of code if the condition is true, otherwise, it runs an alternative code block.
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:

print("x is less than or equal to 10")
In this example, the program prints "x is less than or equal to 10" because x (5) does not satisfy the condition x > 10.
You can chain multiple if statements together using elif, which stands for "else if." This allows you to test more conditions and execute different code blocks based on those conditions.
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
elif x == 5:
print("x is equal to 5")
else:
print("x is less than 5")
In this case, the program prints "x is equal to 5" because x (5) satisfies the second condition.
You can also nest if statements inside other if statements. This allows you to test more complex conditions and execute code accordingly.
x = 5
y = 10
if x > 0:
if y > x:
print("Both x and y are positive")
elif y == x:
print("Both x and y are equal")
else:
print("One of them is positive, the other is not")
else:
print("x is zero or negative")
In this example, the program prints "One of them is positive, the other is not" because y (10) satisfies the condition y > x, even though both are positive numbers.
Python provides a shorthand way to write if-else statements using conditional expressions or ternary operators. This can simplify your code and make it more readable.
x = 5
result = "greater than 10" if x > 10 else "less than or equal to 10"
print(result)
In this example, the program prints "less than or equal to 10" because x (5) does not satisfy the condition x > 10.
Python's conditional statements allow you to control the flow of your program based on various conditions. Understanding if-else statements, if-elif-else statements, and conditional expressions can help you write more efficient, readable, and maintainable code.
Remember: Python's syntax is concise yet powerful, so it's essential to learn and master its conditional statements to unlock the full potential of your programming skills!
Do you have any questions or would you like me to elaborate on any specific topic?
What are decision control statements in Python?
I'm sorry Grandma!
Decision Control Statements (DCS) in Python are a crucial aspect of programming that enables the execution of specific blocks of code based on certain conditions or criteria. These statements allow you to make decisions and take actions accordingly, thereby adding control and logic to your program.
In Python, there are several types of DCS:
If-Else Statements: This is one of the most common DCS in Python. It allows you to execute a specific block of code if a certain condition is met. For example:x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
In this example, the code inside the if block will be executed only if x is greater than 10. If not, the code inside the else block will be executed instead.
age = 25
if age < 18:
print("You are a minor")
elif age >= 65:
print("You are elderly")
else:
print("You are an adult")
In this example, the code inside the if block will be executed if age is less than 18. If not, the code inside the elif block will be executed only if age is greater than or equal to 65. If neither condition is met, the code inside the else block will be executed.
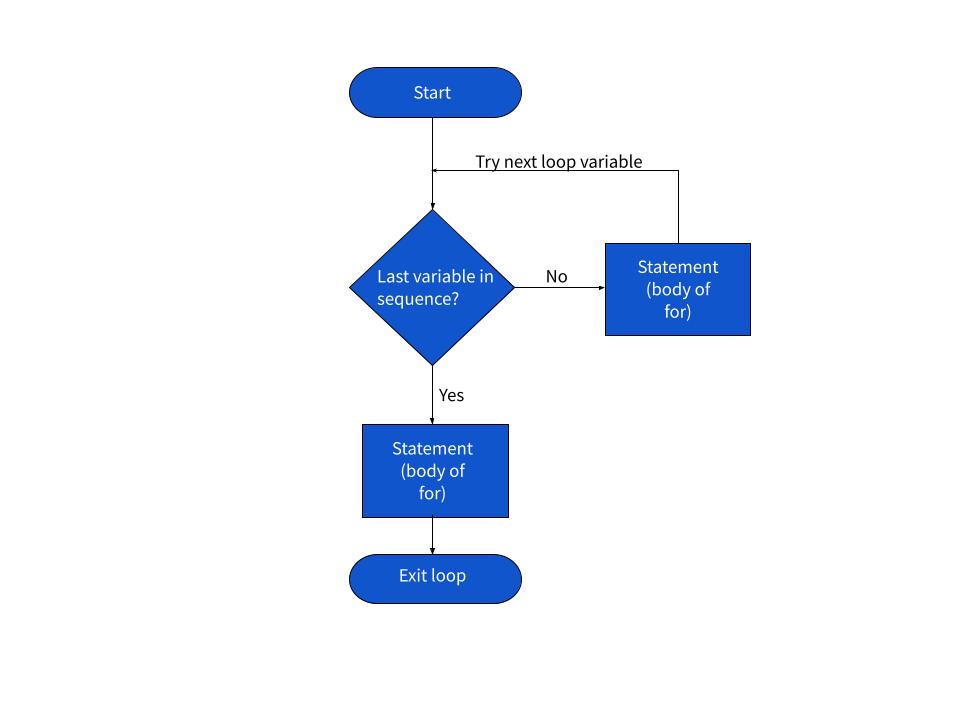
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
In this example, the code inside the for loop will be executed once for each item in the fruits list.
i = 0
while i < 10:
print(i)
i += 1
In this example, the code inside the while loop will be executed repeatedly as long as i is less than 10.
try:
x = 5 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Cannot divide by zero!")
In this example, if a ZeroDivisionError occurs when trying to divide x by zero, the code inside the except block will be executed instead of crashing the program.
These are some of the most common DCS in Python. By using these statements, you can add control and logic to your programs, making them more efficient, robust, and easier to maintain.