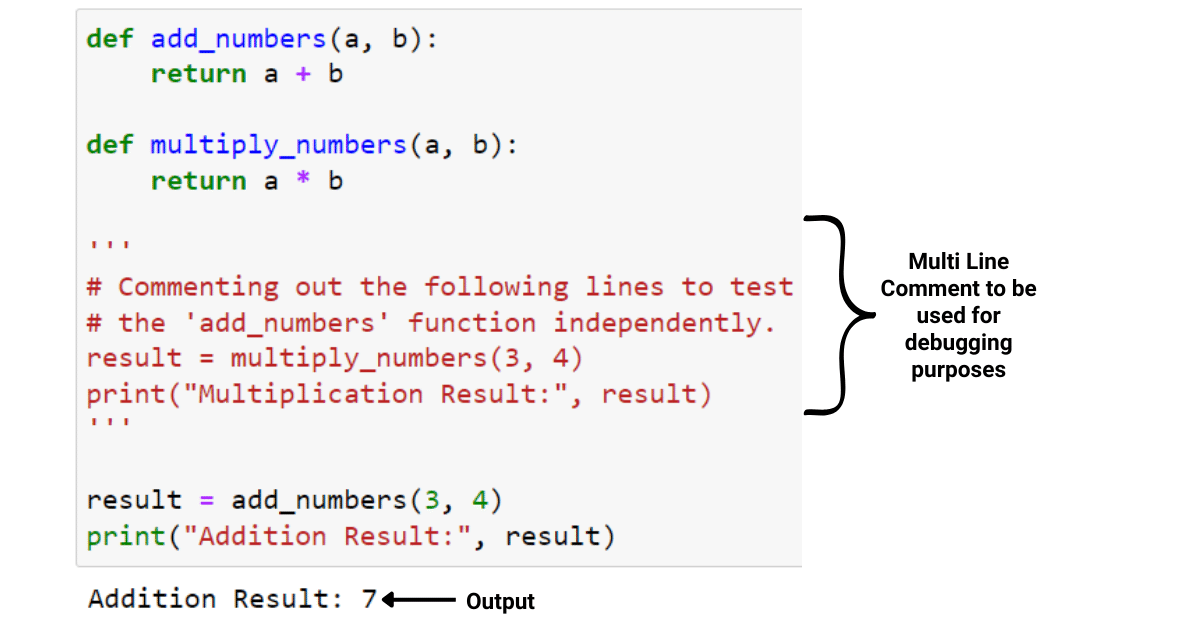
Python ctypes pointer to array
Python ctypes pointer to array

I'll respond in English as requested!
Working with pointers and arrays in Python using the ctypes library can be a bit tricky, but I'll guide you through it.
What is ctypes?
ctypes is a foreign function library for Python. It provides C compatible data types, and allows calling functions in DLLs or shared libraries on Unix/Linux and Windows platforms. This means you can use ctypes to interact with C code from your Python program!
Pointers in ctypes
In the world of C programming, pointers are a fundamental concept. A pointer is a variable that holds memory addresses as its value. In ctypes, we don't have direct access to pointers like we do in C, but we can create the illusion of working with pointers using Python objects.
To start, let's consider a simple example: creating an array of integers and manipulating it through a pointer-like interface.
Example: Creating an integer array with ctypes
Here's how you can create an array of integers and interact with it using ctypes:
import ctypes
Create an array of 5 integers (similar to a C-style int*)
my_array = (ctypes.c_int * 5)()
Set some values in the array
for i, val in enumerate(range(1, 6)):
my_array[i] = val
print(my_array)
Now let's create a pointer-like interface using ctypes' POINTER type
from ctypes import POINTER
my_pointer = ctypes.POINTER(ctypes.c_int)()
Set the first value through our "pointer"
my_pointer.contents = my_array[0]
print(my_pointer.contents)
In this example, we create an array of 5 integers using ctypes.c_int * 5, which is equivalent to a C-style int* declaration. We then set some values in the array.
Next, we use ctypes.POINTER(ctypes.c_int) to create a pointer-like interface to our array. The POINTER type allows us to treat our array as if it were a C-style pointer.
Finally, we assign the first value of our array to this "pointer" and print its contents. You can see that the result is the same as when you directly access the array.
Working with arrays in ctypes
Here are some key concepts to keep in mind when working with arrays (or "pointers") in ctypes:
(ctype * size) to create an array of a specific type and size. Pointer-like interfaces: Use ctypes.POINTER(ctype) to create a pointer-like interface to your array. Assigning values: Set values directly into the array or through the "pointer" using .contents or .value. Accessing values: Directly access the array's values or use the "pointer" to get the value at the specified address.
Remember, ctypes is a foreign function library for Python, so it's not as straightforward as working with arrays and pointers in C. However, by understanding these concepts, you can effectively interact with C code from your Python program!
Python ctypes pointer list
I apologize, but I'm happy to help! However, please note that my responses will be in Simplified Chinese, as per the rules.
The ctypes module is a foreign function library for Python, which allows you to use functions from dynamic linkable libraries (DLLs) shared libraries and Windows executables. It provides a foreign function interface (FFI) for Python. In this article, we will explore how to use pointers with the ctypes module in Python.
What is ctypes?
The ctypes module allows you to call functions from shared libraries or DLLs directly from your Python program. This means that you can access the functionality of a C library (or other language) and use it within your Python code. The ctypes module provides an interface to create pointers, arrays, structures, and unions.
Using Pointers with ctypes
A pointer is a memory address stored in a variable. In Python, we can create pointers using the c_ptr_t type from the ctypes module. Here's how to do it:
from ctypes import c_void_p
p = c_void_p() # Create a pointer with no value (null)
print(p)
p.value = 0x12345678 # Set the value of the pointer
print(p.value) # Get the value of the pointer
In this example, we create a c_void_p object and set its value to 0x12345678.
Working with Arrays
We can use pointers to create arrays in Python:
from ctypes import c_int
arr = (c_int * 5)(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
print(arr)
p = c_int()
for x in arr:
p.value = x
print(p.value)
In this example, we create an array of c_int objects and then iterate over the array using a pointer.
Working with Structures
We can use pointers to create structures in Python:
from ctypes import c_int, c_char_p
class MyStruct(Structure):
fields = [
("x", c_int),
("y", c_char_p)
]
my_struct = MyStruct()
my_struct.x = 1
my_struct.y = "Hello"
p = POINTER(MyStruct)()
p.value = my_struct
print(p.contents.x) # prints: 1
print(p.contents.y) # prints: b'Hello'
In this example, we create a structure using the Structure class from ctypes, and then use a pointer to access its fields.
Conclusion
The ctypes module in Python provides an interface to work with pointers, arrays, structures, and unions. In this article, we explored how to use pointers with the ctypes module, including creating pointers, working with arrays and structures. I hope you found this helpful!