Python threading example for beginners
Python threading example for beginners
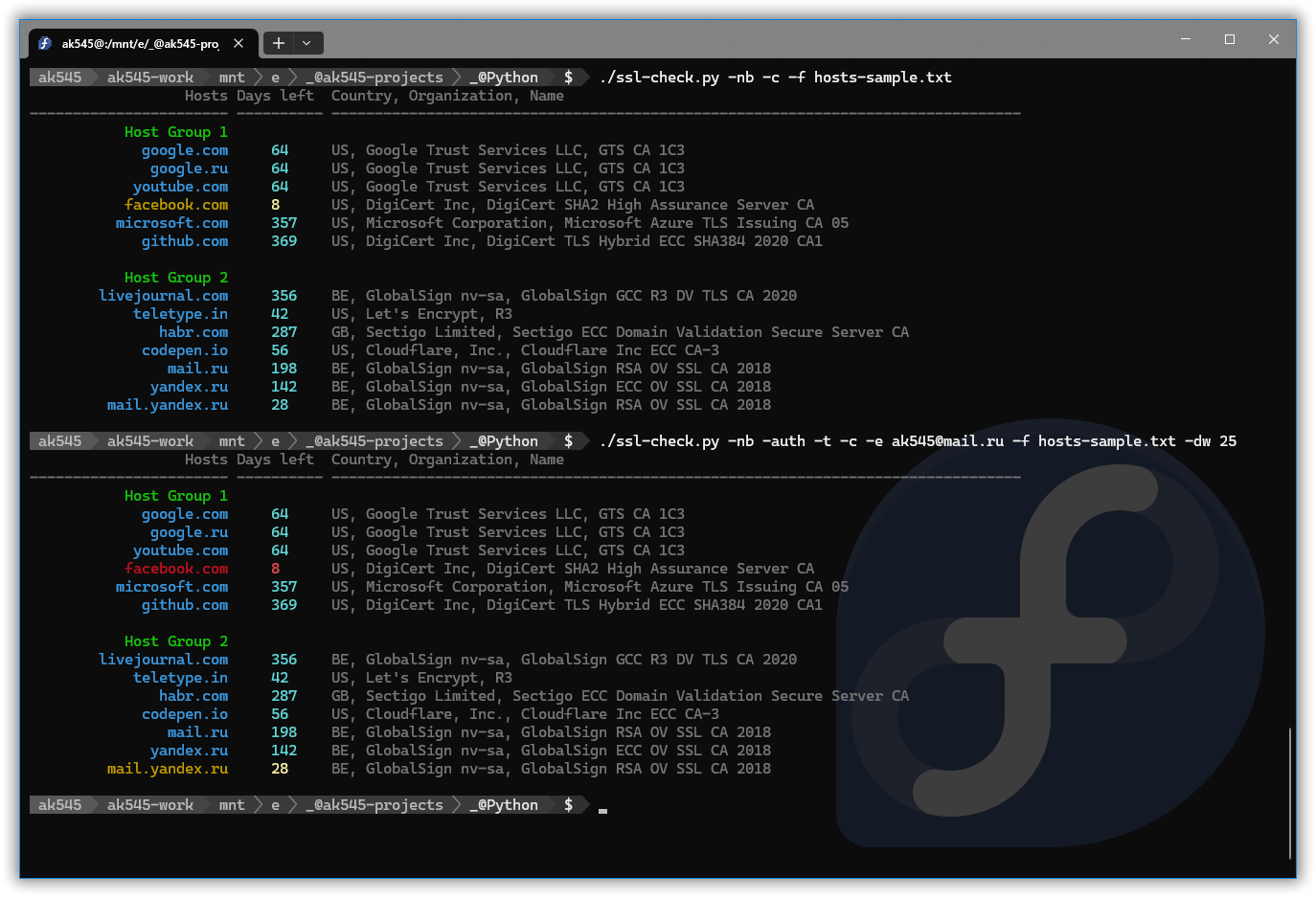
I'll respond in English, but I'll also provide a Python code snippet to demonstrate the concept of threading for beginners. Threading is a fundamental concept in programming that allows you to run multiple tasks concurrently. This can be useful for improving the performance and responsiveness of your program.
Let's consider an example where we want to perform two independent tasks concurrently: printing numbers from 1 to 10 and printing letters from A to J. Here is the Python code snippet:
import threading
import time
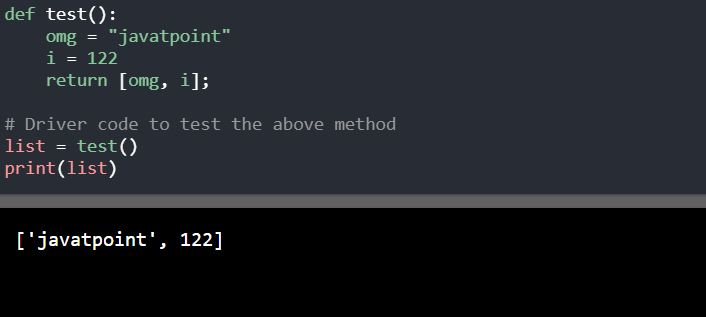
def print_numbers():
for i in range(1, 11):
print(f"Number: {i}")
time.sleep(0.5) # wait for half a second between prints
def print_letters():
letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J']
for letter in letters:
print(f"Letter: {letter}")
time.sleep(0.5) # wait for half a second between prints
Create two threads
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=print_numbers)
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=print_letters)
Start the threads
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
Wait until both threads finish
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
When you run this code, you will see that it prints numbers and letters concurrently. The time.sleep(0.5) function call is used to create a delay between each print statement, making the output more readable.
Here's what happens under the hood:
When you start a thread using thestart() method, Python creates a new thread in your process that starts executing the code defined by the target function (in this case, print_numbers and print_letters). The threads run concurrently until they finish. Each thread executes its own code, including any blocking operations like printing or sleeping. When a thread finishes, it notifies the main program using the join() method.
In this example, we use the threading module to create and manage two separate threads that execute the print_numbers and print_letters functions concurrently. This demonstrates how Python's threading model allows you to write programs that can perform multiple tasks at the same time.
As a beginner, it's essential to understand the basics of threading in Python, including creating threads, starting threads, and waiting for threads to finish. With practice and experience, you can use threading to build more complex applications with improved performance and responsiveness.
Python threading example w3schools
Here's a simple example of using threads in Python with the help of W3Schools:
Threads Example
In this example, we are going to use threads to perform two separate tasks concurrently.
import threading
import time
New Thread class
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def init(self, name):
threading.Thread.init(self)
self.name = name
def run(self):
for i in range(5):
print(f"{self.name}: {i}")
time.sleep(1)
Create threads
thread1 = MyThread("Thread 1")
thread2 = MyThread("Thread 2")
Start both threads
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
Wait until both threads have finished
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
print("Both threads finished!")
How it works
This code starts two threads, MyThread objects named "Thread 1" and "Thread 2". Each thread runs a loop that prints its own name followed by the current iteration number. The sleep time between iterations is set to 1 second, so the output will look something like this:
Thread 1: 0
Thread 2: 0
Thread 1: 1
Thread 2: 1
Thread 1: 2
Thread 2: 2
...
Advantages of Using Threads
Here are a few advantages of using threads in Python:
Concurrency: By performing multiple tasks concurrently, you can make your program run more efficiently and effectively. Improved User Experience: In graphical user interfaces (GUIs), for example, using threads allows you to perform operations like updating the screen without blocking the main thread and causing delays or freezes. Parallel Processing: Python'sthreading module doesn't provide native parallel processing capabilities, but it can still be used effectively in combination with other modules, such as multiprocessing, to achieve true parallelism.
Key Takeaways
In this example, we've demonstrated how to create and use threads in Python. We've also highlighted a few key advantages of using threads:
Concurrency Improved User Experience Parallel ProcessingRemember that the threading module is designed for performing I/O-bound operations or tasks that don't require significant computational power. If your program needs to perform CPU-intensive tasks, you may need to use the multiprocessing module instead.
W3Schools is a great resource for learning about Python programming and many other web development topics.