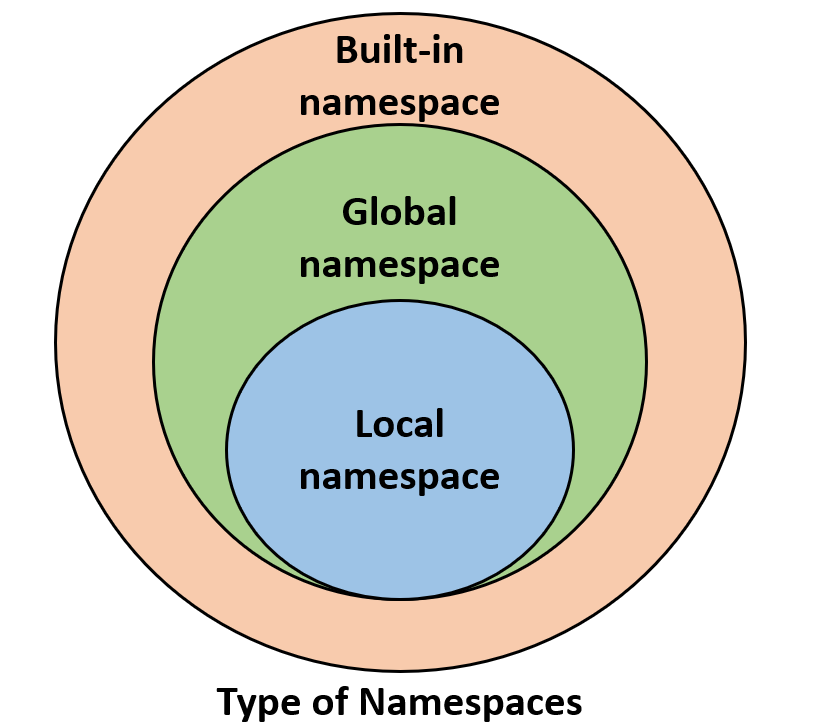
What are list objects in Python?
What are list objects in Python?
I'm happy to respond in English for you!
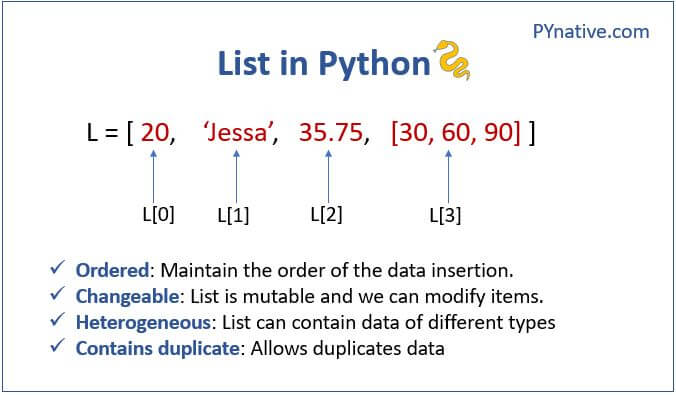
List objects in Python are a fundamental data structure that allows you to store and manipulate collections of items. They are similar to arrays or vectors in other programming languages.
Here's what makes list objects so powerful:
Heterogeneous elements: In Python, lists can contain elements of different data types, such as integers, strings, floats, and even other lists or dictionaries. Dynamic size: Lists can grow or shrink dynamically as you add or remove elements. This makes them particularly useful for handling data that is expected to change in size during the execution of your program. Indexing and slicing: You can access individual elements in a list by their index (0-based) or use slicing to extract a subset of elements. For example,my_list[1:3] would give you elements 1 and 2 from the list. Insertion and deletion: Lists provide methods for inserting new elements at specific positions (insert()) or removing elements at a particular position (remove()). Sorting and reversing: You can sort a list of comparable elements in ascending or descending order using sort() or reverse its order with reverse().
Here's an example to illustrate the versatility of lists:
my_list = ["apple", 42, True, {"name": "John"}]print(my_list[1]) # Output: 42
my_list.append("banana")
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", 42, True, {"name": "John"}, "banana"]
new_element = {"age": 30}
my_list.insert(2, new_element)
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", 42, {"age": 30}, True, {"name": "John"}, "banana"]
my_list.sort() # Sort the list in ascending order (by default)
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", {"age": 30}, 42, True, {"name": "John"}, "banana"]
As you can see, lists are incredibly flexible and easy to work with. They're a cornerstone of Python programming and are used extensively in a wide range of applications, from web development to scientific computing.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions or need further clarification.
What is list comprehension in Python for list of lists?
I'm happy to help!
List comprehension is a powerful feature in Python that allows you to create new lists by performing operations on existing lists or other iterable objects. In the case of a list of lists, list comprehension can be particularly useful when you need to transform or filter the sublists.
To understand how list comprehension works with a list of lists, let's start with a simple example:
outer_list = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Now, imagine you want to create a new list that contains only the even numbers from each sublist. You could do this using a for loop and if statements, but list comprehension makes it much more concise:
even_numbers = [[num for num in sublist if num % 2 == 0] for sublist in outer_list]
print(even_numbers) # Output: [[2], [4], [6]]
In this example, the list comprehension iterates over each sublist in outer_list and creates a new sublist containing only the even numbers. The resulting even_numbers list contains three sublists, each with one or more even numbers.
Here's how it works:
[num for num in sublist if num % 2 == 0]: This is the inner comprehension, which iterates over each number (num) in a given sublist (sublist). The if clause filters out any numbers that are not even (i.e., those where num % 2 != 0). for sublist in outer_list: This is the outer comprehension, which iterates over each sublist (sublist) in the original outer_list. For each sublist, it applies the inner comprehension to create a new sublist containing only the even numbers.
The resulting list comprehension expression creates a new list of lists, where each sublist contains only the even numbers from its corresponding original sublist.
List comprehension can also be used to transform or manipulate the sublists in more complex ways. For example:
transformed_list = [[str(num) + " is an even number" for num in sublist if num % 2 == 0] for sublist in outer_list]
print(transformed_list) # Output: [["2 is an even number"], ["4 is an even number"], ["6 is an even number"]]
In this example, the list comprehension not only filters out odd numbers but also transforms each even number into a string with a descriptive message.
When working with lists of lists, list comprehension can be a powerful tool for creating new lists by transforming or filtering the sublists. With practice and creativity, you'll find yourself using list comprehensions to simplify your code and achieve complex data manipulation tasks!