python virtual environment windows 11
python virtual environment windows 11

I apologize for the mistake earlier!

To create a Python virtual environment on Windows 11, you can follow these steps:
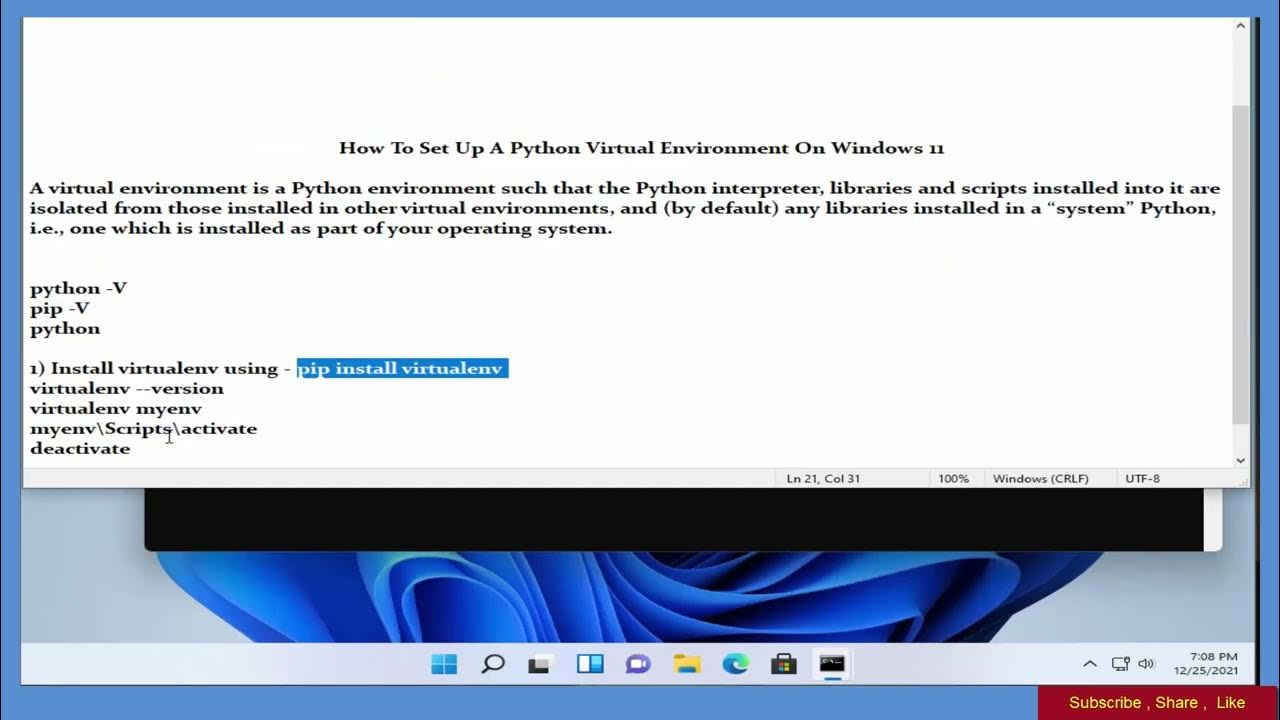
Step 1: Install Python
If you haven't already, download and install the latest version of Python from the official Python website.
Step 2: Install pip (Python Package Installer)
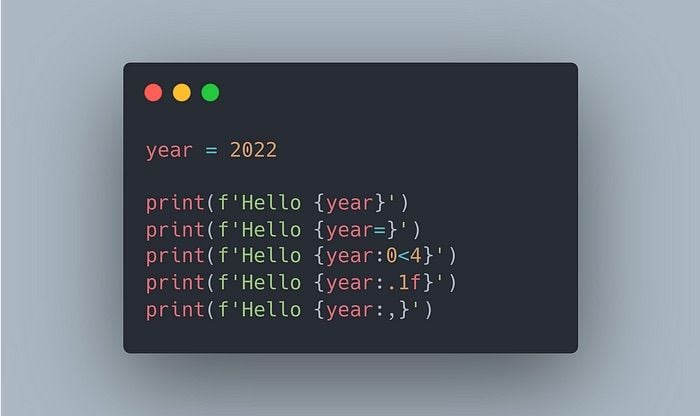
pip is the package installer for Python. You can check if pip is installed by opening a command prompt or terminal window and typing:
pip --version
If pip is not installed, you can download it from the Python website or use the following commands to install it:
python -m ensurepip
Step 3: Create a Virtual Environment
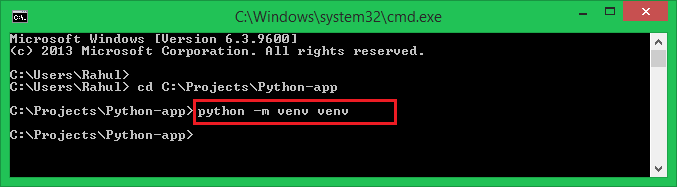
To create a virtual environment, open a command prompt or terminal window and type:
python -m venv myenv
Replace myenv with the name you want to give your virtual environment.
This will create a new directory called myenv that contains the Python executable, libraries, and other dependencies. The virtual environment is isolated from the system Python installation, so you can install packages without affecting your global Python setup.
Step 4: Activate the Virtual Environment
To activate the virtual environment, type:
myenvScriptsactivate
On Windows, this command sets the PATH environment variable to point to the virtual environment's executable directory. On Linux/Mac, the equivalent command is:
source myenv/bin/activate
You should now see (myenv) in your terminal or command prompt, indicating that you are working within the virtual environment.
Step 5: Install Packages
To install packages using pip, simply run the following commands:
pip install package_name
Replace package_name with the name of the package you want to install. You can list available packages using:
pip list
When you're done working within the virtual environment, you can exit by typing:
deactivate
This will return your system's Python environment back to its original state.
That's it! With these steps, you should now be able to create and use a Python virtual environment on Windows 11.
How do I see all virtual environments in Python Windows?
To view all virtual environments in Python on a Windows system, you can use the following methods:
Method 1: Using py -0
You can open a Command Prompt or PowerShell and type the command:
py -0
This will list all the virtual environments (venv) that are currently activated. The -0 option stands for "enumerate all venvs" and it lists all the virtual environments in the current Python version.
Method 2: Using python -m venv --list
Alternatively, you can use the following command:
python -m venv --list
This will list all the virtual environments (venv) that are currently available. The -m option stands for "run the module" and it runs the venv module to list all the virtual environments.
Method 3: Using pip freeze
Another way to view all your virtual environments is by using pip freeze. This command will list all the packages installed in all your virtual environments. You can then filter this output to find the names of your virtual environments.
Here's how you can do it:
pip freeze | grep -oE "env|env"
This command uses grep to search for lines that contain either "env" or a path that contains "env". The -o option stands for "only print the matched text", and the -E option enables extended regular expressions.
Method 4: Using a Python Package Manager like convenience
If you have installed the convenience package, which is a Python package manager, you can use it to list all your virtual environments. Here's how:
convenience envs
This command will list all the virtual environments that are currently available.
In summary, there are several ways to view all your virtual environments in Python on a Windows system. You can use py -0, python -m venv --list, pip freeze with some filtering, or convenience envs.