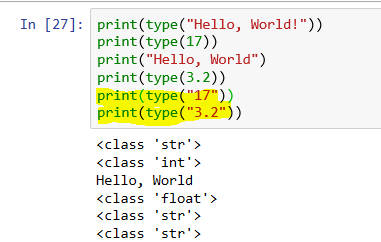
Python call REST API POST example
Python call REST API POST example
I'm happy to help!
Here is a Python example of calling a REST API using the requests library:
import requests
import json
Set your API endpoint URL
api_endpoint = "https://example.com/api/endpoint"
Define your JSON payload
data = {
'key1': 'value1',
'key2': 'value2'
}
Convert JSON data to a string
json_data = json.dumps(data)
Send the POST request
response = requests.post(api_endpoint, data=json_data, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'})
Check if the response was successful (200 OK)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("API call successful")
else:
print("API call failed with status code: ", response.status_code)
Get the API's JSON response
api_response = response.json()
print(api_response) # Print the API's response
In this example, we are making a POST request to an API endpoint. The payload is in JSON format and we are setting the Content-Type header to application/json.
You can adjust the values in the data dictionary (e.g., key1, value1) to match your specific API requirements.
Here's how you might customize this code:
Updateapi_endpoint with your actual API URL. Modify the data dictionary to match the expected JSON payload format for your API endpoint. You may need to adjust data types (e.g., numbers, dates) or add more key-value pairs depending on the API's requirements.
This example demonstrates a basic POST request in Python using the requests library. APIs can have varying complexity and requirements, so be sure to check the official documentation for any specific details your API might require.
Does this help?
Can you use REST API in Python?
Yes, Python has excellent support for making requests using the Representational State of Resource (REST) API protocol.
The requests library is a popular and widely-used Python module that allows you to send HTTP requests and interact with web servers using the REST API paradigm. Here's an example of how to use it:
import requests
Make a GET request
response = requests.get('https://www.example.com')
Check if the response was successful (200 OK)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Request successful!")
else:
print(f"Failed with status code {response.status_code}")
Make a POST request with data
data = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
response = requests.post('https://www.example.com/users', json=data)
Check if the response was successful (201 Created)
if response.status_code == 201:
print("User created successfully!")
else:
print(f"Failed with status code {response.status_code}")
In this example, we make two different types of requests: a GET request to fetch data and a POST request to create a new resource. We can also use other methods like PUT (update), DELETE (remove) and HEAD (get metadata).
The requests library provides many features for working with REST APIs:
You can also use other libraries like urllib3 or pycurl to make REST API requests in Python. However, the requests library is generally considered the most convenient and efficient way to interact with REST APIs using Python.
Here are some examples of how you might use this in a real-world application:
Building a web scraper that fetches data from a REST API. Creating a bot that sends data to a chat platform's REST API. Developing an e-commerce website that interacts with payment gateways' REST APIs. Integrating multiple services using REST APIs, like integrating payment processing and inventory management systems.Overall, the requests library makes it easy for you to send HTTP requests in Python, which is essential for working with many modern web-based services.