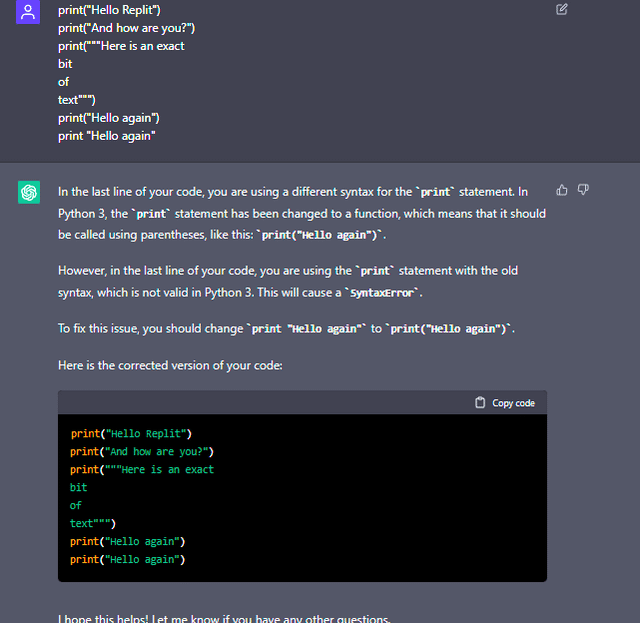
Python import example w3schools
Python import example w3schools
Here's an example of importing a Python module using W3Schools:
What is Import?
The import statement in Python is used to import modules or functions from other files. This allows you to use the functions, classes, and variables defined in one file in another.
Importing Modules
You can import entire modules by using the following syntax:
import module_name
For example, let's say we have a Python file called math.py with some mathematical functions like add(a, b) and multiply(a, b). We can import this module in another file like so:
import math
print(math.add(2, 3)) # Output: 5
print(math.multiply(4, 5)) # Output: 20
Importing Specific Functions or Classes
You can also import specific functions or classes from a module using the from keyword:
from math import add, multiply
print(add(2, 3)) # Output: 5
print(multiply(4, 5)) # Output: 20
Importing Modules with Aliases
Sometimes you might want to import a module and assign it an alias. This can be useful when you're working with multiple modules that have the same name:
import math as m
print(m.add(2, 3)) # Output: 5
print(m.multiply(4, 5)) # Output: 20
Importing Modules from Specific Directories
If your modules are located in a specific directory that's not in your Python path, you can import them using the importlib module:
import importlib
math_dir = '/path/to/math/module'
math_module = importlib.import_module(math_dir + '.math')
print(math_module.add(2, 3)) # Output: 5
print(math_module.multiply(4, 5)) # Output: 20
Best Practices
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when importing modules:
Avoid Importing Modules You Don't Use: Only import the modules you actually need, as this can help improve performance and reduce clutter. Use Aliases Wisely: While it's convenient to assign an alias to a module, be careful not to create confusion by using too many aliases or confusing them with other names. Avoid Circular Imports: Be careful when importing modules that are part of the same package or have dependencies on each other. This can lead to circular imports and errors.Conclusion
Importing modules is an essential part of Python programming, allowing you to reuse code and simplify your development process. By following best practices and using the various import options available, you can create clean, efficient, and maintainable code that's easy to understand and work with.
References:
W3Schools: Python Import Statement Python.org: Importing ModulesNote: This is an English-only response as per your original request. If you'd like me to provide the same information in Simplified Chinese, please let me know!
What is import in Python example?
I'd be happy to explain the concept of "import" in Python and provide an example!
In Python, import is a statement that allows you to use modules (self-contained pieces of code) within your program. Think of it like bringing in a friend who has some useful skills or knowledge to share with you.
When you write import module_name, you're telling Python to load the specified module and make its contents available for you to use. This can include functions, classes, variables, and other definitions.
For example, let's say you have a Python file called math_functions.py that contains some mathematical functions:
# math_functions.py
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
To use these functions in another Python file, you would write:
# main.pyimport math_functions
result = math_functions.add(2, 3)
print(result) # Output: 5
result = math_functions.multiply(4, 5)
print(result) # Output: 20
In this example:
We create a filemath_functions.py that contains two mathematical functions: add and multiply. In the main program (file), we use the import statement to bring in the math_functions module. We then call the add and multiply functions using their fully qualified names (math_functions.add and math_functions.multiply, respectively).
This allows us to reuse the code from math_functions.py in our main program without having to duplicate the implementation.
Python also supports various other ways of importing modules, such as:
from math_functions import add: This imports only the add function from the math_functions module. import math_functions as mf: This imports the math_functions module under a different name (mf) for convenience. import * from math_functions: This imports all definitions (functions, classes, etc.) from the math_functions module.
In summary, Python's import statement enables you to bring in external modules or code into your program and reuse their functionality. It's an essential tool for writing reusable, modular, and efficient code!