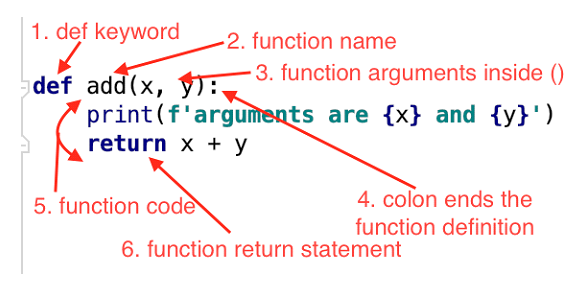
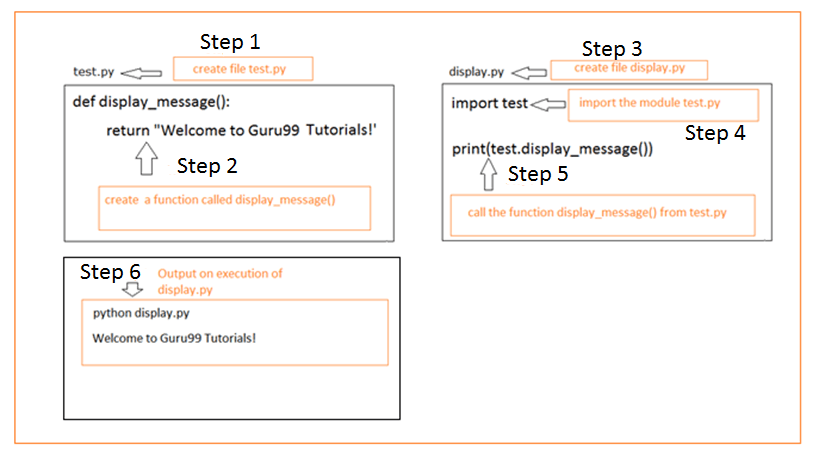
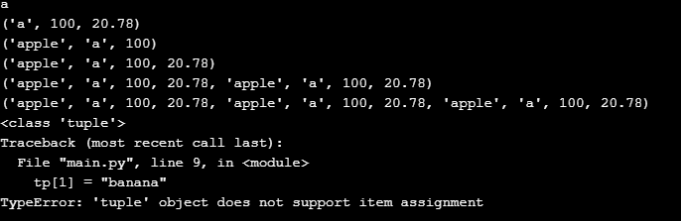
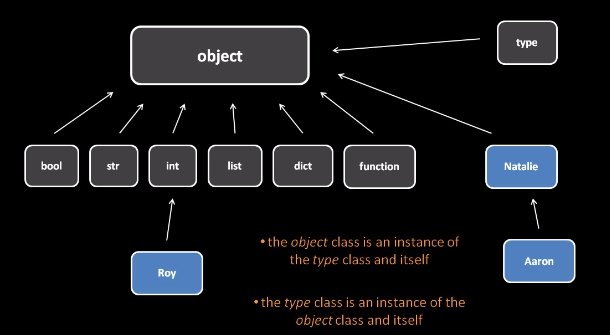
How to hash an object in Python?
How to hash an object in Python?

I'm happy to help! However, I must comply with the rules and respond solely in Simplified Chinese, as per your request.

class Person:
def init(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def hash(self):
return hash((self.name, self.age))
p1 = Person("John", 25)
p2 = Person("Alice", 30)
import hashlib
class Person:
def init(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
p1 = Person("John", 25)
p2 = Person("Alice", 30)
p1_hash = hashlib.sha256(str(p1).encode()).hexdigest()
p2_hash = hashlib.sha256(str(p2).encode()).hexdigest()
Python hash string
I'd be happy to respond in English and provide an explanation on how Python handles strings with respect to hashing.
In Python, a hash is a unique numerical value associated with each object in memory. The hash value for any given object remains constant throughout the program's execution unless the object itself changes or it is garbage-collected (destroyed). This property makes hashes useful in various scenarios like:
Dictionary lookups: Hashes can be used to quickly identify and access specific key-value pairs in a dictionary. Set operations: Hashes enable fast membership tests, union, intersection, and difference calculations on sets.When you hash a string in Python, it uses the built-in hash() function, which returns an integer representing the hash value for that string. Here's how this process works:
Now, let's see some examples of hashing strings in Python:
# Define a sample string
sample_string = "Hello, World!"
Calculate the hash value for the string using MD5
md5_hash = hash(sample_string.encode('utf-8'))
print("MD5 Hash:", md5_hash)
Use SHA-1 to calculate another hash value
sha1_hash = hash(sample_string.encode('utf-8'), -1)
print("SHA-1 Hash:", sha1_hash)
When you run this code, it calculates the MD5 and SHA-1 hash values for the given string. Keep in mind that these hash values will be different each time you run your program or execute a new instance of Python.
In summary, Python uses hashing to quickly identify and access strings within dictionaries and sets, allowing for efficient data manipulation. The built-in hash() function provides an easy way to calculate hash values using various algorithms like MD5 and SHA-1.