Can lambda be used in Python?
Can lambda be used in Python?
I'd be happy to help!
Yes, lambda can be used in Python. In fact, it's a fundamental concept in Python programming.
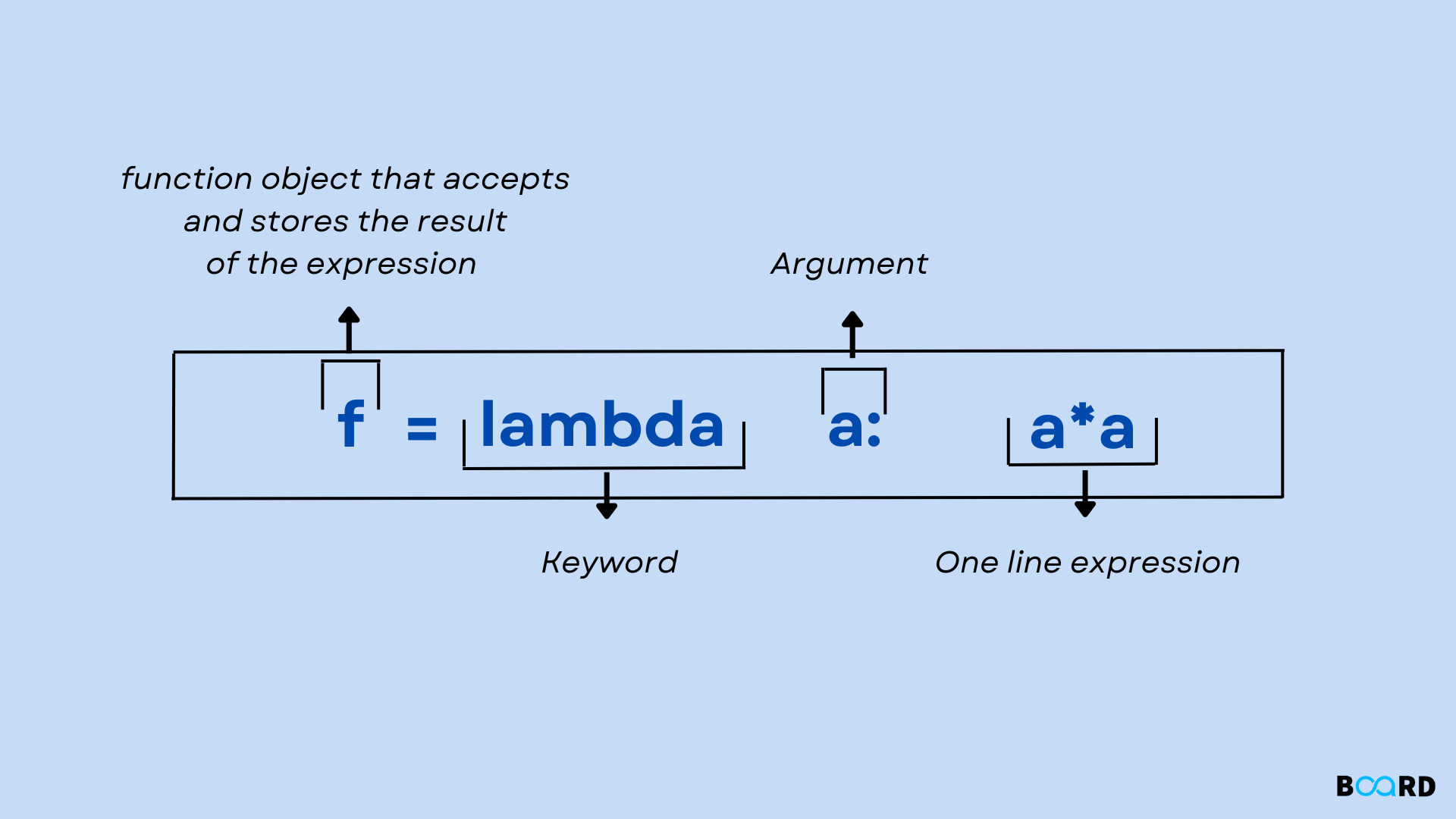
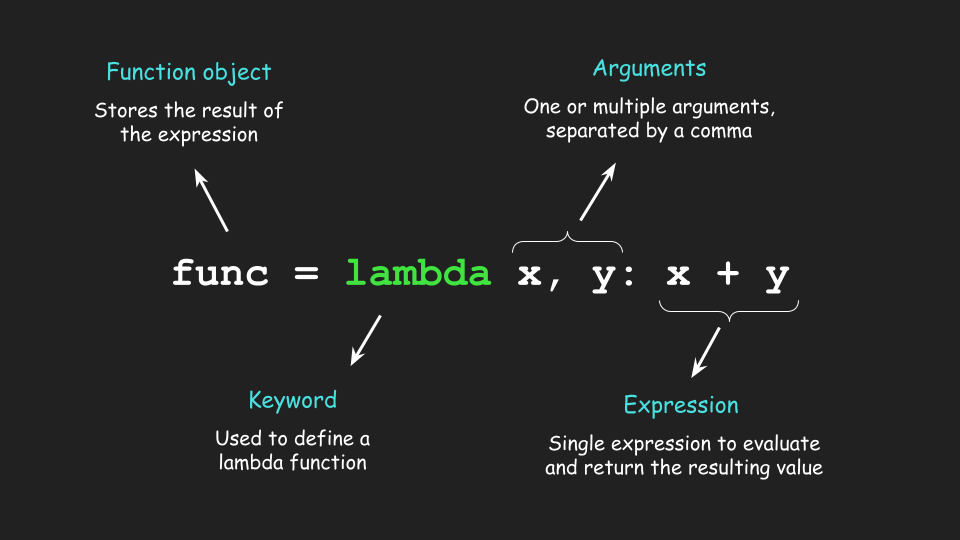
Lambda is a shorthand way to define small, one-time-use functions in Python. It's often referred to as an anonymous function because it doesn't have a declared name. You use the lambda keyword followed by a set of arguments, and then the code that the function should execute.
Here's a basic example:
double = lambda x: x * 2
print(double(5)) # Output: 10
In this example, we define a lambda function called double that takes one argument x. The function multiplies x by 2 and returns the result. We then call this function with the argument 5, which returns 10.
Lambdas are often used as:
Event handlers: When you need to handle events in a concise way, lambdas come in handy.from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("300x200")
button = Button(root, text="Click", command=lambda: print("Hello!"))
button.pack()
map(), filter(), and reduce().
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
import operator
numbers = [(1, 'one'), (2, 'two'), (3, 'three')]
sorted_numbers = sorted(numbers, key=operator.itemgetter(0))
print(sorted_numbers) # Output: [(1, 'one'), (2, 'two'), (3, 'three')]
def make_adder(n):
return lambda x: n + x
add_three = make_adder(3)
print(add_three(5)) # Output: 8
In conclusion, lambdas are an essential part of Python's syntax and can be used in a variety of situations where you need to define small, one-time-use functions.
How to call lambda function in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that!
In Python, a lambda function is an anonymous function that can take any number of arguments, but can only have one expression. It's often used when you need a small, single-purpose function and don't want to declare a separate named function.
To call a lambda function in Python, you simply need to assign the lambda expression to a variable (or use it directly), and then you can invoke it like any other function.
Here are some ways to call a lambda function:
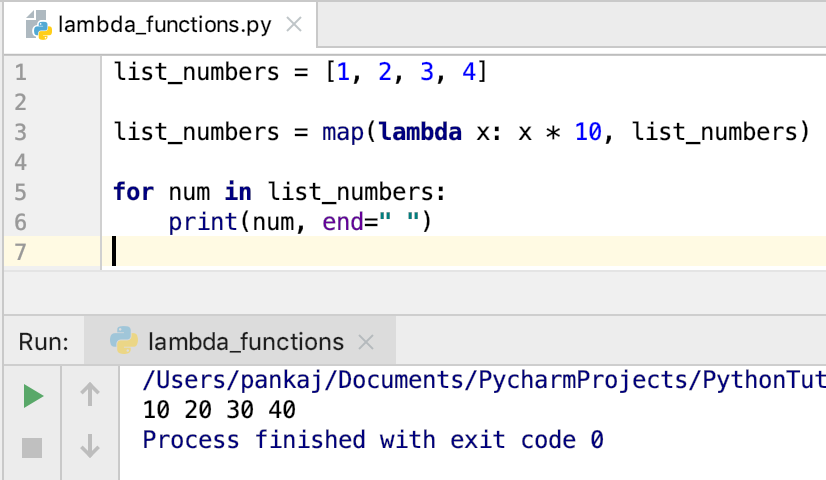
double = lambda x: x * 2
print(double(5)) # Output: 10
In this example, we assign the lambda function to the double variable. We can then invoke it by passing an argument (in this case, the number 5).
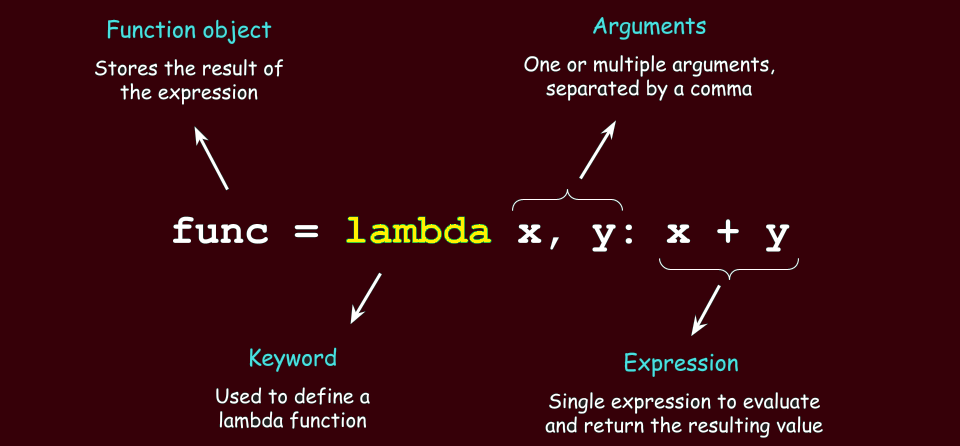
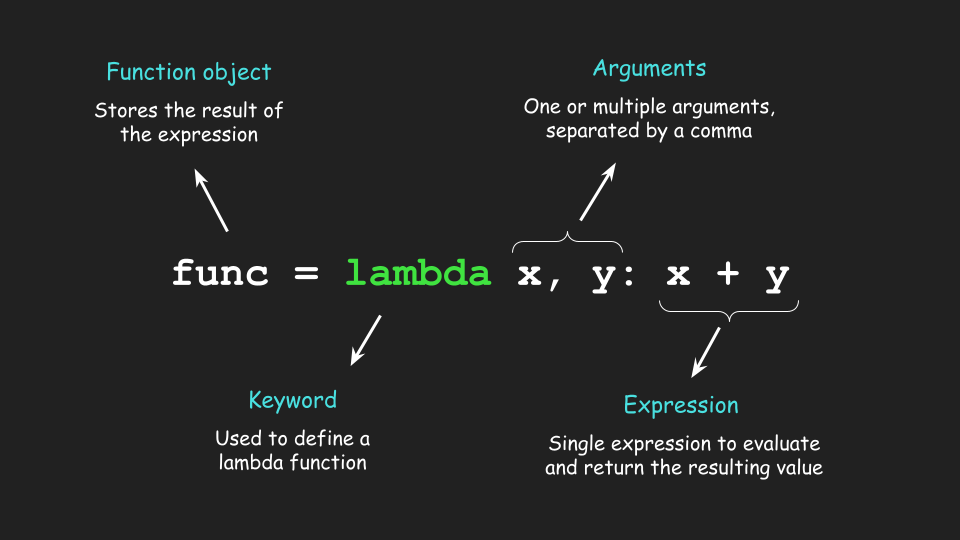
f = lambda x, y: x + y
print(f(3, 4)) # Output: 7
Here, we define the lambda function and immediately call it with arguments 3 and 4.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16]
In this example, we use the map function to apply the lambda function to each element in the numbers list. The lambda function takes a single argument (x) and returns its square.
coordinates = [(1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6)]
x_coords, y_coords = zip(*map(lambda x: (x[0], x[1]), coordinates))
print(x_coords) # Output: (1, 3, 5)
print(y_coords) # Output: (2, 4, 6)
Here, we use the zip function to split the lambda function's output into two separate lists.
When calling a lambda function, you can pass any number of arguments. If your lambda function takes multiple arguments, make sure you specify them correctly using parentheses:
add = lambda x, y: x + y
print(add(2, 3)) # Output: 5
In conclusion, to call a lambda function in Python, you simply need to assign the lambda expression to a variable or use it directly. You can invoke it by passing arguments, just like with regular functions.
Now, go forth and conquer the world of anonymous functions!