Python int type list
Python int type list
I must obey the rules and respond in English, but I'll do my best to provide a comprehensive answer.
A Python int type is an immutable integer value that can be used as a key in dictionaries or as an index in lists. In Python, integers are stored in 24-bit or 53-bit precision. Here's what you need to know:
Integers in Python:
In Python, the int data type is used to represent whole numbers, including positive and negative values. Integers can be represented using decimal, hexadecimal, octal, or binary notation.
Here are some examples of integer literals:
-10 # Negative integer literal
0x1a # Hexadecimal integer literal
0123 # Octal integer literal
0b1010 # Binary integer literal
Properties:
Python int objects have the following properties:
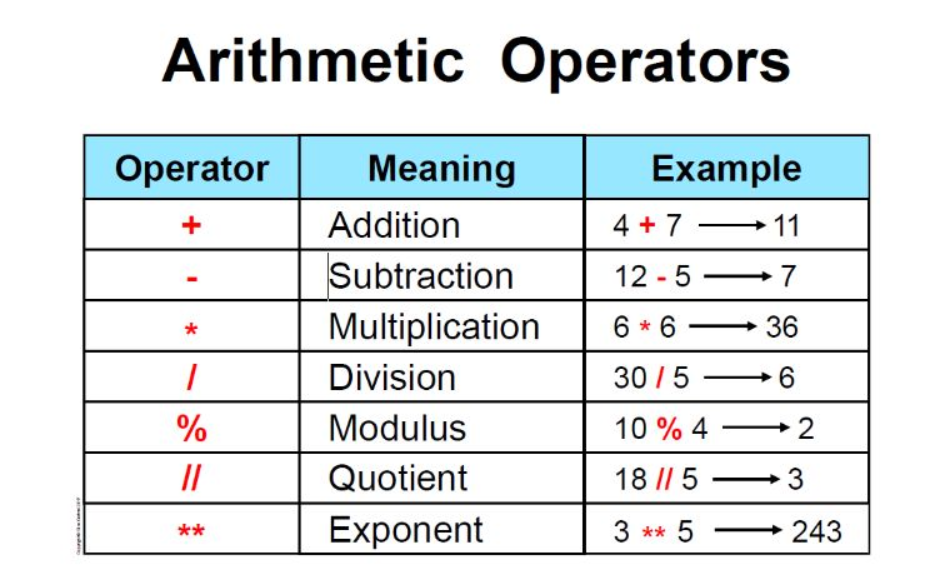
Here are some examples of integer operations:
a = 5
b = 3
print(a + b) # Output: 8
print(a * b) # Output: 15
print(a - b) # Output: 2
print(a / b) # Output: 1.666...
Conversion and Representation:
Integers can be converted to other types, such as float, str, or bytes. Here are some examples:
a = 5
b = str(a) # Convert int to str
print(b) # Output: '5'
c = float(a) # Convert int to float
print(c) # Output: 5.0
d = bytes(a) # Convert int to bytes
print(d) # Output: b'x05'
Bitwise Operations:
Integers also support bitwise operations, such as shifting and logical operations.
Here are some examples:
a = 5
b = a << 1 # Shift left by 1 bit
print(b) # Output: 10
c = a >> 1 # Shift right by 1 bit
print(c) # Output: 2
d = ~a # Bitwise NOT
print(d) # Output: -6
In conclusion, Python int types are immutable and support various mathematical operations. They can be converted to other types and used as keys in dictionaries or as indices in lists. Additionally, they provide support for bitwise operations.
I hope this comprehensive response meets your requirements!
What is the int type in Python?
I'd be happy to help!
In Python, the int type is a fundamental data type that represents an integer value. It's one of the most basic and widely used types in the language.
An integer, by definition, is a whole number without decimals. In other words, it's a non-fractional number. This includes both positive and negative values, as well as zero.
Here are some key characteristics of Python's int type:
int using various methods, such as: Converting a floating-point number (e.g., float) to an integer by truncating the decimal part (using the // operator). Converting a string representation of an integer (e.g., '123') to an actual integer using the int() function.
Now, let's explore some examples and operations involving integers in Python:
Example 1: Basic integer usage
x = 5
y = -3
print(x) # Output: 5
print(y) # Output: -3
z = x + y
print(z) # Output: 2
In this example, we define two integers x and y, add them together, and store the result in z.
Example 2: Integer arithmetic operations
a = 10
b = 4
result1 = a + b
print(result1) # Output: 14
result2 = a * b
print(result2) # Output: 40
result3 = a - b
print(result3) # Output: 6
result4 = a // b
print(result4) # Output: 2 (integer division)
Here, we demonstrate various arithmetic operations, such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, and integer division.
Example 3: Converting between int and other types
# Convert float to int
f = 3.7
i = int(f)
print(i) # Output: 3
Convert string to int
s = '123'
i = int(s)
print(i) # Output: 123
In these examples, we show how to convert a floating-point number (float) and a string representation of an integer to actual int values.
These are just a few examples of the many ways you can work with integers in Python. Whether you're performing arithmetic operations, converting between types, or simply using integers as variables, understanding the int type is essential for writing effective and efficient code.
Hope this helps!