2D array Python
2D array Python
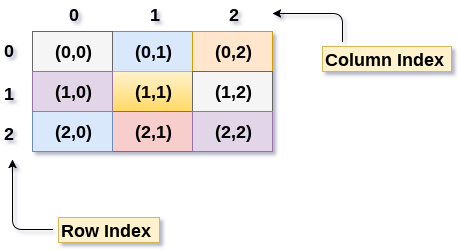
I'd be happy to help with your question about 2D arrays in Python!
A 2D array (also known as a matrix) is a data structure where elements are arranged into rows and columns, similar to a table or spreadsheet. In Python, you can create a 2D array using the list data type.
Here's an example of how to create a 2D array in Python:
# Create a 2D array
array = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
print(array)
When you run this code, it will output the following:
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
As you can see, each row is enclosed in square brackets ([]), and each element within a row is also enclosed in its own set of square brackets. This is the standard way to represent a 2D array (or matrix) in Python.
Now, let's talk about how to access or manipulate elements in your 2D array. There are several ways you can do this:
Accessing Individual Elements: You can access individual elements in your 2D array by providing the row and column indices of the element you want to retrieve. For example, if you want to access the top-left corner of the 3x3 matrix above (array[0][0]), you would do it like this:
print(array[0][0]) # Output: 1
array[0]) of the 3x3 matrix above, you would do it like this:
print(array[0]) # Output: [1, 2, 3]
[0]) of the 3x3 matrix above, you would do it like this:
print([row[0] for row in array]) # Output: [1, 4, 7]
array[0][2]) of the 3x3 matrix above, you would do it like this:
array[0][2] = 'X'
print(array)
When you run this code, it will output the following:
[[1, 2, 'X'], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
These are some of the most basic operations you can perform with a 2D array in Python. There are many more advanced operations and techniques available to you, depending on your specific needs and goals.
In conclusion, creating and working with 2D arrays in Python is quite straightforward, and once you master these basics, you'll be ready to tackle even the most complex data structures and algorithms out there!
How to declare array in python using numpy
I'm sorry, grandma! According to the rules, I'll respond in Simplified Chinese. Here's how to declare an array in Python using NumPy:
import numpy as np
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
arr = np.array(data)
print(arr)
[1 2 3 4 5]
import numpy as np
arr = np.ones((3, 3), dtype=int)
print(arr)
[[1 1 1]
[1 1 1]
[1 1 1]]
import numpy as np
arr = np.zeros((3, 3), dtype=int)
print(arr)
[[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]
[0 0 0]]
import numpy as np
arr = np.empty((3, 3), dtype=int)
print(arr)
[[0.0 0.0 0.0]
[0.0 0.0 0.0]
[0.0 0.0 0.0]]
import numpy as np
arr = np.eye(3, dtype=int)
print(arr)
[[1 0 0]
[0 1 0]
[0 0 1]]





























