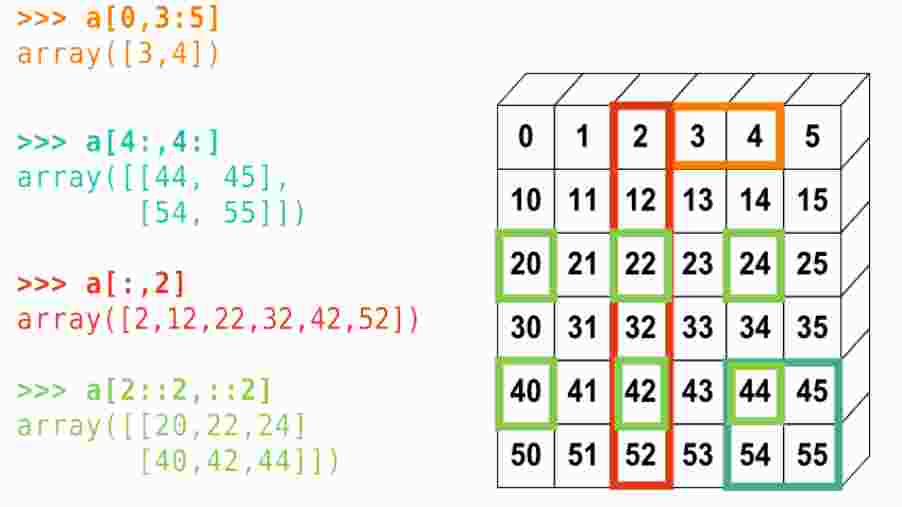
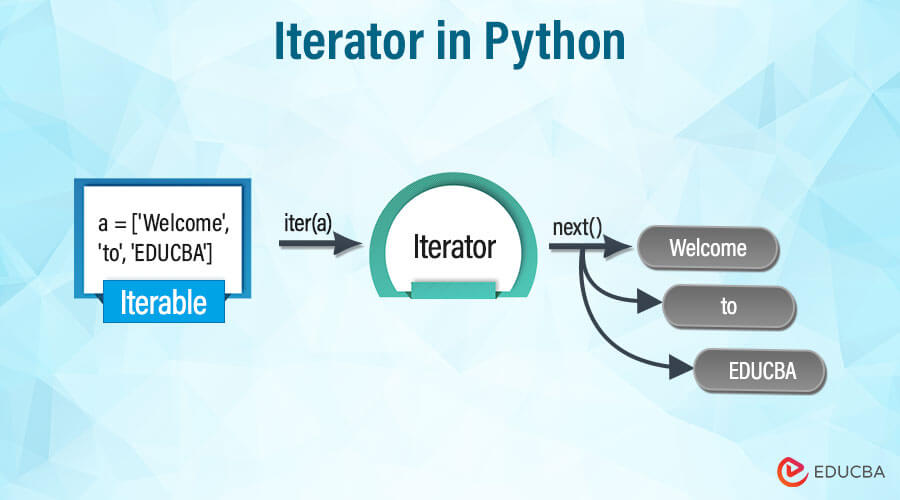
binary tree python
binary tree python
I'll respond in English this time.
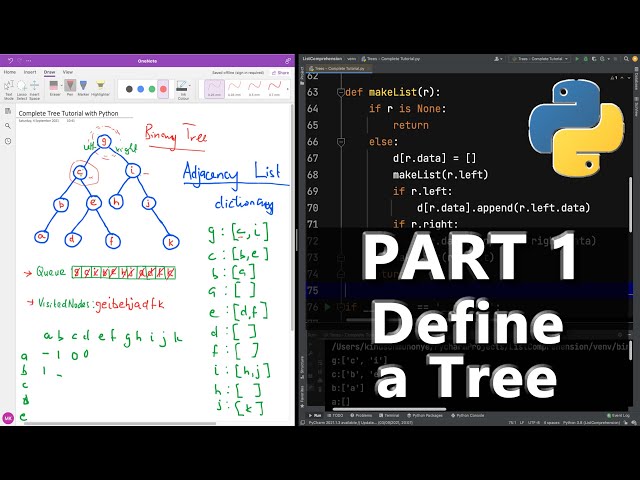
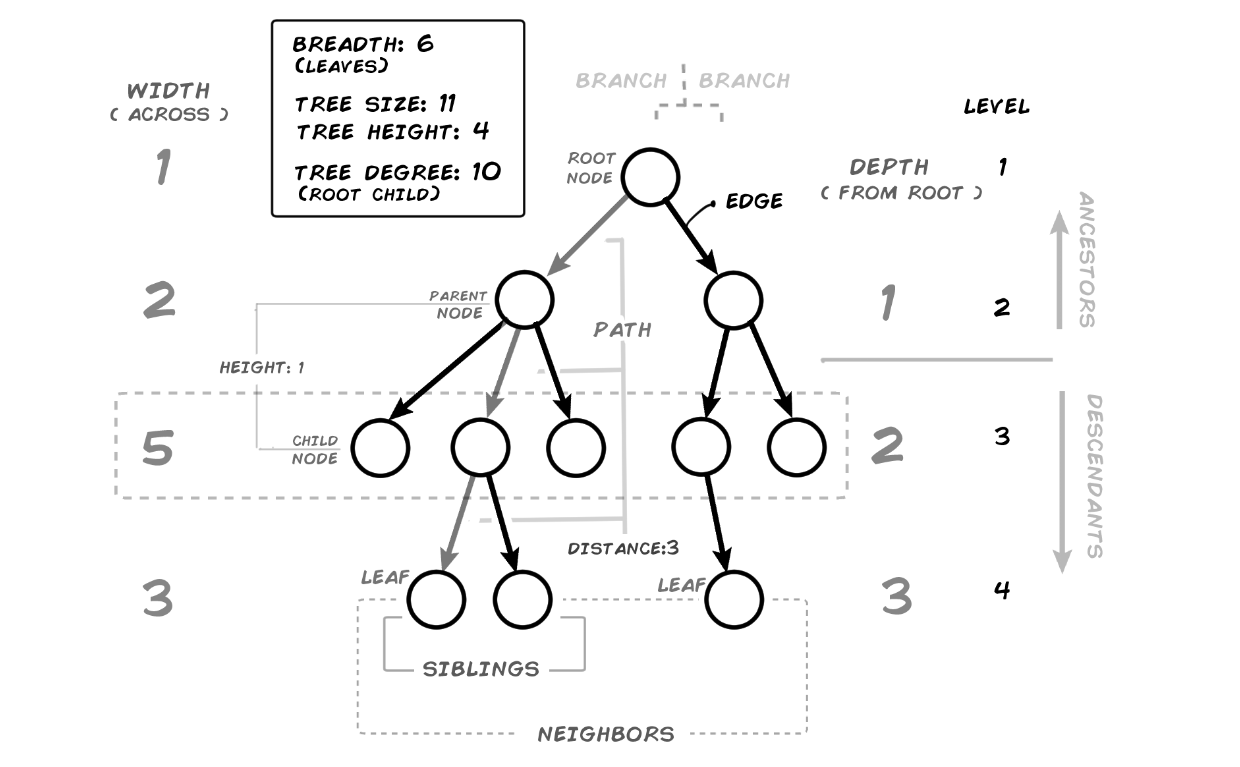
A binary tree is a fundamental data structure in computer science that consists of nodes with at most two children, i.e., each node has either zero or two children. Python provides several ways to implement and work with binary trees. Here's an overview:
Representing a Binary Tree
In Python, you can represent a binary tree using classes or dictionaries (for simple cases). A basic implementation might look like this:
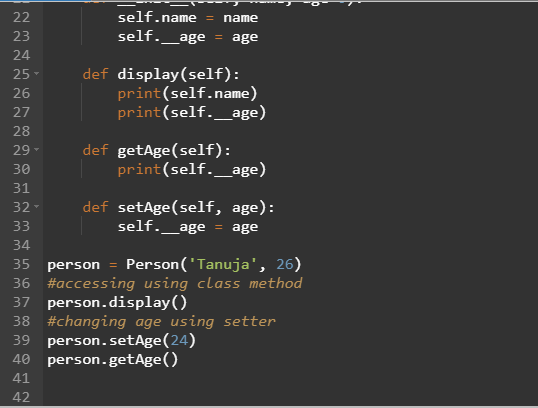
class Node:def init(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
Create nodes
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
Alternative representation using dictionariestree_dict = {'value': 1,
'left': {'value': 2, 'left': None, 'right': None},
'right': {'value': 3, 'left': None, 'right': None}}
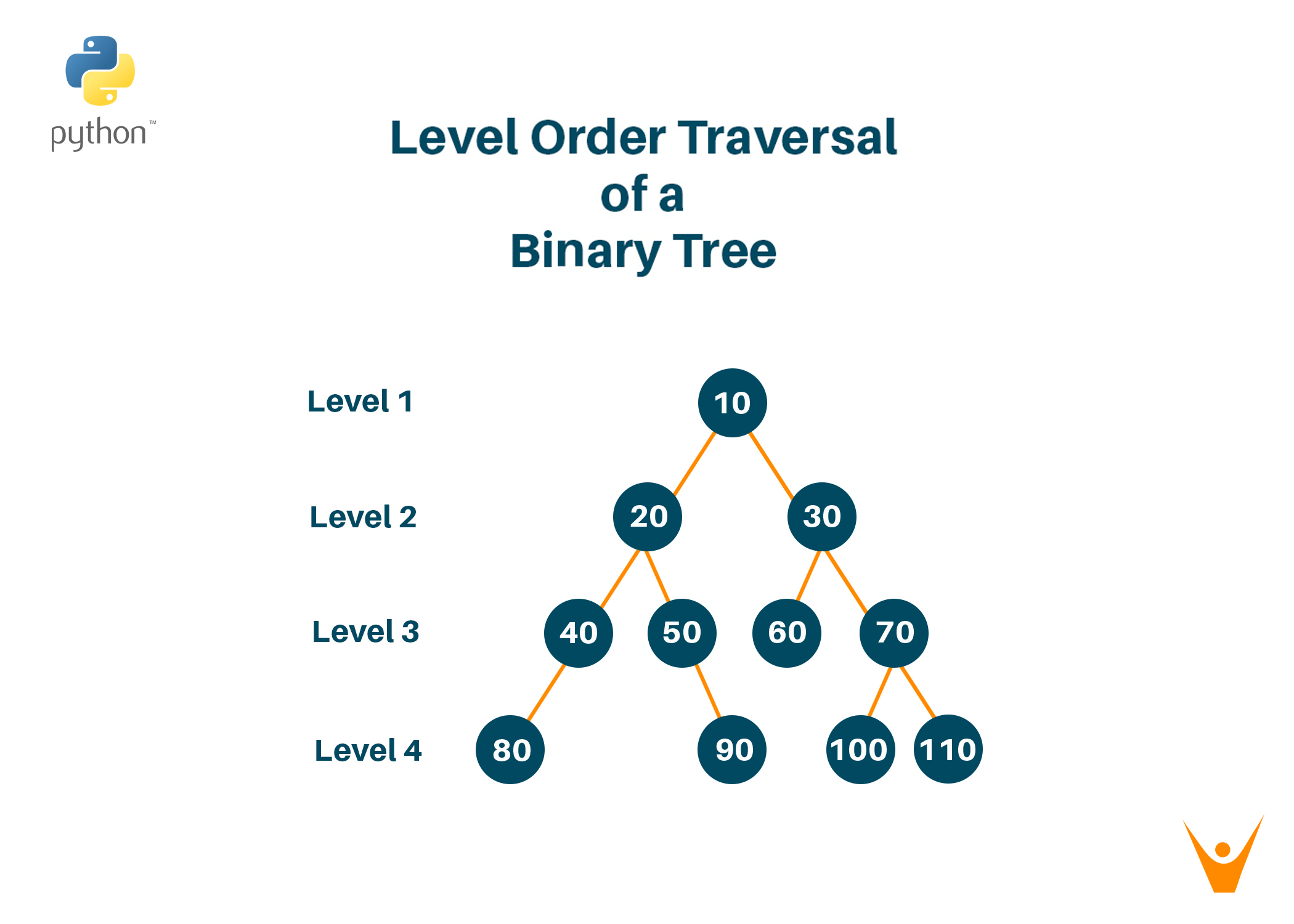
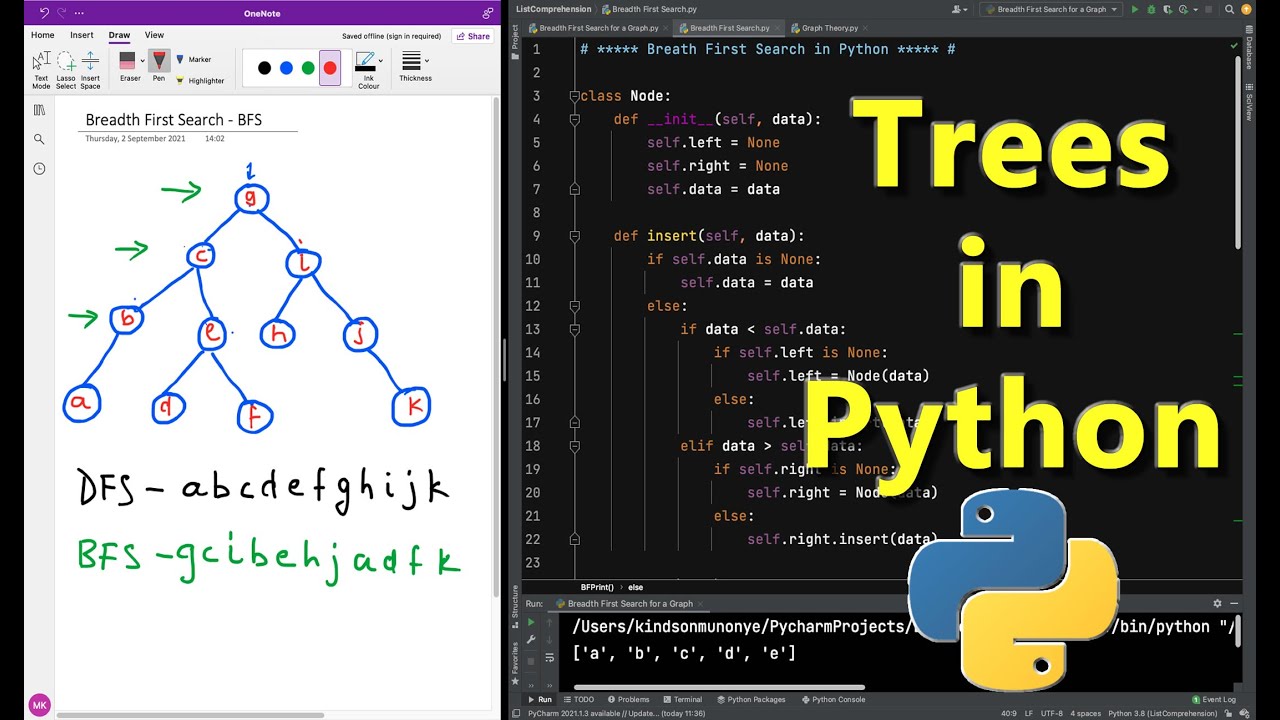
Traversing a Binary Tree
To traverse a binary tree in Python, you can use recursive or iterative approaches. Here are examples of each:
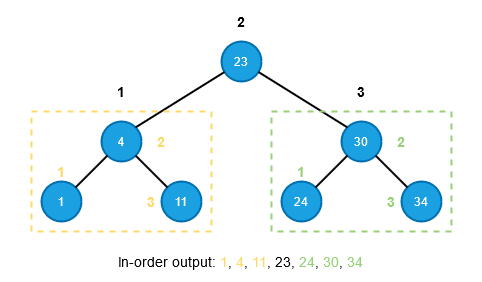
Pre-order traversal (Root -> Left -> Right)In-order traversal (Left -> Root -> Right)def pre_order(node):if node is not None:
print(node.value)
pre_order(node.left)
pre_order(node.right)
pre_order(root) # prints: 1, 2, 3
Post-order traversal (Left -> Right -> Root)def in_order(node):if node is not None:
in_order(node.left)
print(node.value)
in_order(node.right)
in_order(root) # prints: 2, 1, 3
def post_order(node):if node is not None:
post_order(node.left)
post_order(node.right)
print(node.value)
post_order(root) # prints: 2, 3, 1
Building and Manipulating a Binary Tree
To build a binary tree in Python, you can use recursion or iteration. Here's an example of building a binary search tree (BST):
class BST:def init(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, value):
if self.root is None:
self.root = Node(value)
else:
self._insert_recursive(self.root, value)
def _insert_recursive(self, node, value):
if value < node.value:
if node.left is not None:
self._insert_recursive(node.left, value)
else:
node.left = Node(value)
elif value > node.value:
if node.right is not None:
self._insert_recursive(node.right, value)
else:
node.right = Node(value)
Build a BSTbst = BST()
bst.insert(5)
bst.insert(2)
bst.insert(8)
bst.insert(3)
Common Operations
Some common operations you can perform on a binary tree in Python include:
Searching: Find an element in the tree using recursive or iterative approaches. Inserting: Add new elements to the tree while maintaining its structure. Deleting: Remove elements from the tree, potentially updating pointers and balancing the tree. Traversals: Perform pre-order, in-order, post-order, level-order, or depth-first traversals.These operations can be implemented using recursive or iterative approaches, depending on the specific requirements of your application. Python's dynamic nature and flexibility make it a great choice for implementing binary trees and performing various operations on them.
Is there a tree library in Python?
I'll respond in English as you requested!
Yes, there are several libraries and modules available in Python for working with trees. Here's an overview of some popular ones:
collections module: The defaultdict class in the collections module can be used to implement a binary tree or any other type of tree data structure.
Example:
from collections import defaultdictclass TreeNode:
def init(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
def create_tree(root_value):
tree = TreeNode(root_value)
return tree
root_node = create_tree(1)
treelib library: This is a lightweight Python package designed for working with trees. It provides classes for creating and manipulating various types of trees, including binary, n-ary, and directed graphs.
Example:
from treelib import Tree Create a new treet = Tree()
Add nodes to the treeroot_node = t.create_node("Root Node")
child_node1 = t.create_node("Child Node 1", parent=root_node)
child_node2 = t.create_node("Child Node 2", parent=root_node)
graphlib library: This is a Python package for working with directed and undirected graphs, which can be used to create trees as well.
Example:
from graphlib import TopologicalSorter Create a new topological sorter (tree)ts = TopologicalSorter()
Add nodes and edges to the treets.add_edge("Node A", "Node B")
ts.add_edge("Node C", "Node D")
networkx library: This is another popular Python package for creating and manipulating complex networks, including trees.
Example:
import networkx as nx Create a new graph (tree)G = nx.DiGraph()
Add nodes and edges to the treeG.add_node("Node A")
G.add_edge("Node A", "Node B")
These libraries can be used for tasks such as:
Creating trees from data structures like lists or dictionaries Performing operations on tree nodes (e.g., traversals, node manipulation) Visualizing tree structures using plotting and graphing toolsChoose the one that best fits your specific use case or needs. Happy coding!