How do you slice a 2D array in Python?
How do you slice a 2D array in Python?
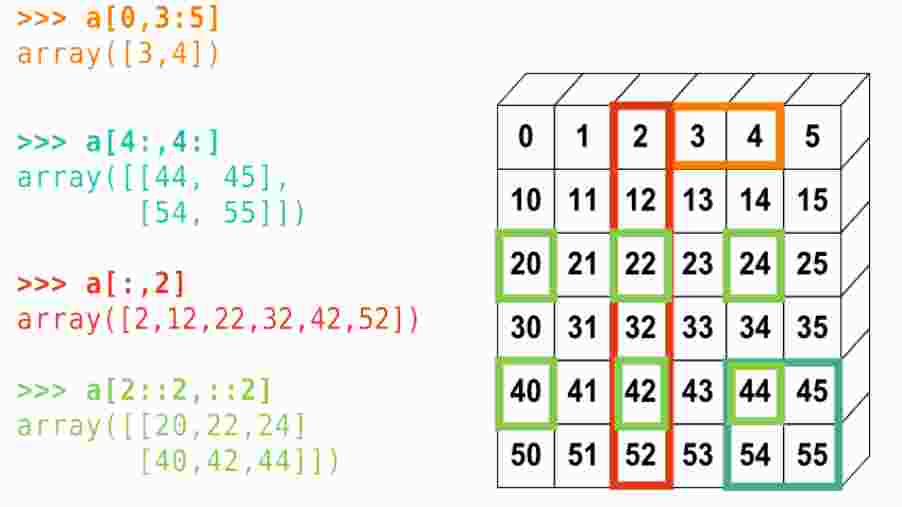
I'd be happy to explain how to slice a 2D array in Python!
In Python, when you want to access or manipulate specific parts of a multi-dimensional array (like a 2D array), you use slicing. Slicing is an operation that returns a subset of the characters from the original string.
To start, let's create a 2D array example:
array_2d = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
Now, let's explore some basic slicing techniques:
Slicing along the first dimension (rows)
To access specific rows from the array, you can use indexing with a colon (:) like so:
print(array_2d[1:]) # Output: [[4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
This code says: "Give me all the elements starting from row 1 (remember Python arrays are zero-indexed) to the end of the array". The result is an array containing rows 1 and 2.
Slicing along the second dimension (columns)
To access specific columns, you can use a similar syntax with an additional colon:
print(array_2d[:, 1:]) # Output: [[2, 3], [5, 6], [8, 9]]
This code says: "Give me all the elements in rows that start from column 1 to the end of each row". The result is an array containing columns 1 and 2 from each row.
Combining slicing along both dimensions
To access a specific subset of the array, you can combine row and column slicing like this:
print(array_2d[1:2, 1:]) # Output: [[5, 6]]
This code says: "Give me the elements from rows 1 to 2 (inclusive) and columns 1 to the end of each row". The result is an array containing only one element.
More advanced slicing techniques
You can also use slicing with negative indices. This allows you to start counting from the end of the array:
print(array_2d[-1:]) # Output: [[7, 8, 9]]
This code says: "Give me all the elements starting from the last row to the end of the array". The result is an array containing only the last row.
These examples demonstrate how you can use slicing to access and manipulate specific parts of a 2D array in Python. Remember to experiment with different indices, colon positions, and combinations to get a deeper understanding of this powerful feature!
How to split a 2D array in Python?
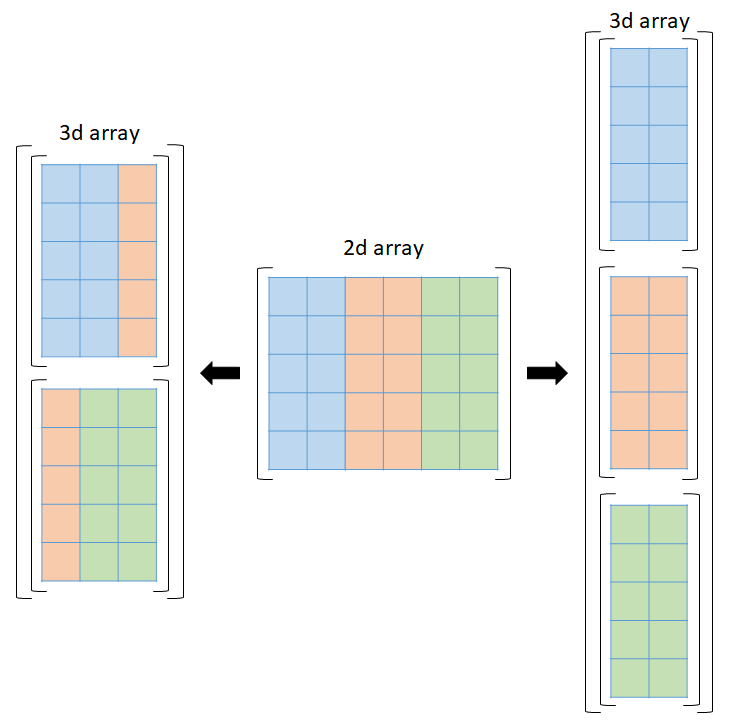
I'm happy to help you with that!
Splitting a 2D array (or list of lists) in Python can be done using various methods, depending on the desired outcome and level of complexity. Let's explore some ways to achieve this:
Method 1: Using List Comprehension
two_d_array = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Splitting along the first dimension (rows)
split_rows = [[row[i] for row in two_d_array] for i in range(len(two_d_array[0]))]
print(split_rows) # Output: [[1, 3, 5], [2, 4, 6]]
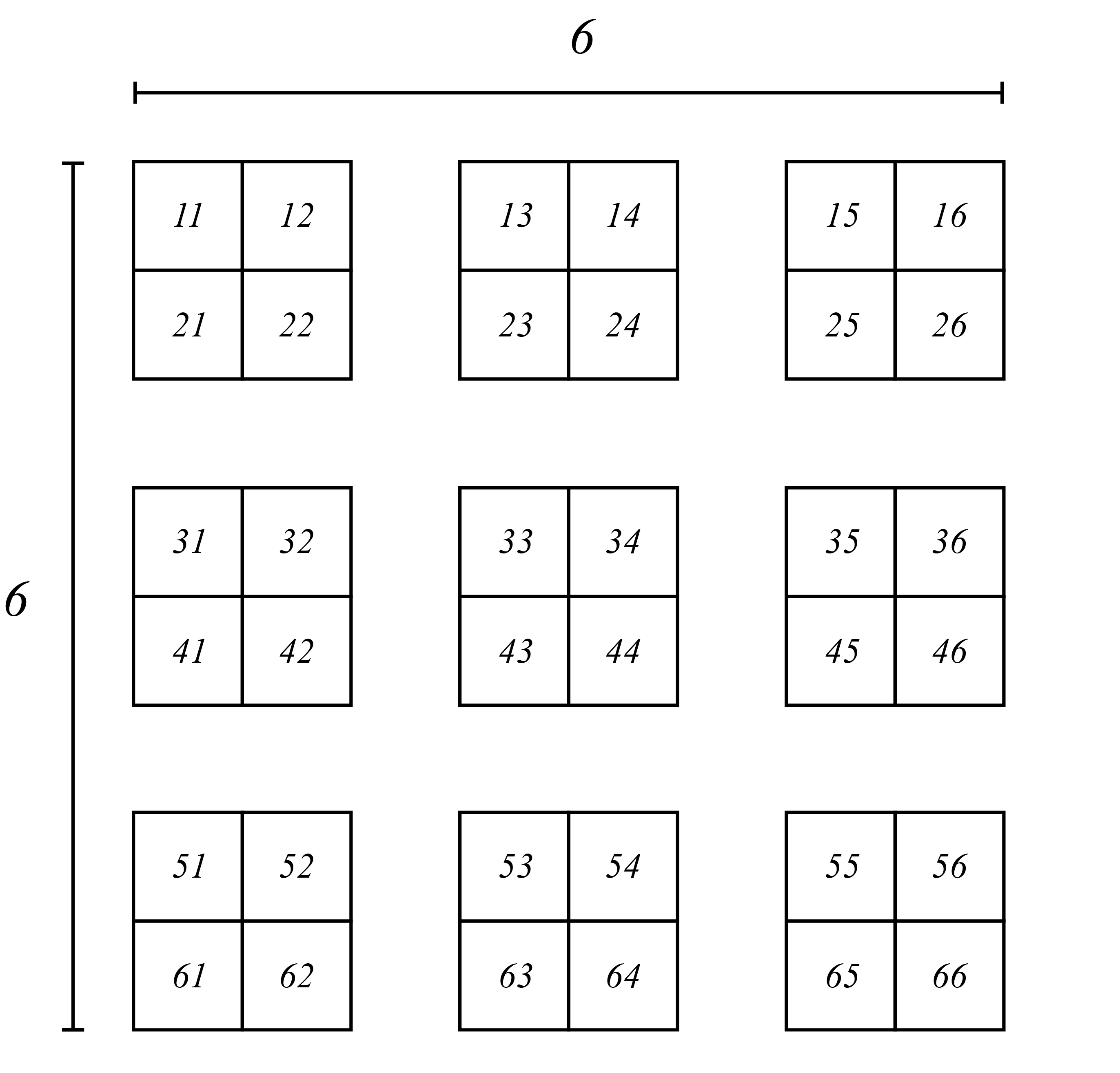
This method uses list comprehension to iterate over the inner lists (rows) and extract elements at specific indices. It's a concise way to split the array along the first dimension.
Method 2: Using Numpy
import numpy as np
two_d_array = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Splitting along the first dimension (rows)
split_rows = np.split(two_d_array, indices_or_sections=[len(two_d_array[0])])
print(split_rows) # Output: [[array([[1, 2]]), [array([[3, 4]]), array([[5, 6]])]]
Numpy's split function allows you to split an array along a specific dimension. In this case, we're splitting the array into sub-arrays based on the number of rows.
Method 3: Using List Slicing
two_d_array = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Splitting along the first dimension (rows)
split_rows = [two_d_array[i:i+1] for i in range(len(two_d_array))]
print(split_rows) # Output: [[[1, 2]], [[3, 4]], [[5, 6]]]
This method uses list slicing to split the array into sub-arrays, each containing a single row. It's a simple way to achieve the desired outcome.
Method 4: Using Pandas
import pandas as pd
two_d_array = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Splitting along the first dimension (rows)
df = pd.DataFrame(two_d_array)
split_rows = df.split(n=1)
print(split_rows) # Output: [[0 1
1 2],
[1 3
4]]
Pandas' DataFrame and split methods allow you to split the array into sub-dataframes, each containing a single row. It's a powerful way to manipulate data structures.
In conclusion, Python offers various ways to split a 2D array (or list of lists), each with its own strengths and use cases. By choosing the right method for your specific requirements, you can efficiently process and analyze your data.





























